 Ethereum uses the Keccak-256 algorithm to produce all hash values. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Secure Hashing Algorithm 3 (SHA-3) is a subset of the Keccak algorithm. Ethereum was introduced before the SHA-3 standard was finalized, and Keccak-256 does not follow the SHA-3 official standard.
Ethereum uses the Keccak-256 algorithm to produce all hash values. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Secure Hashing Algorithm 3 (SHA-3) is a subset of the Keccak algorithm. Ethereum was introduced before the SHA-3 standard was finalized, and Keccak-256 does not follow the SHA-3 official standard.
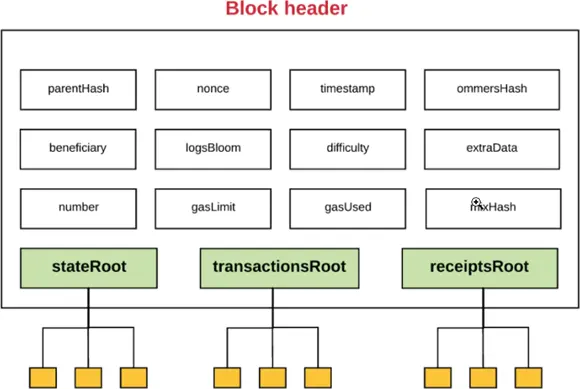
FIGURE 3-5:Ethereum block header.
Each Ethereum block header contains information that defines and describes the block, and records its place in the blockchain. The block header contains the following fields:
Previous hash: The hash value of the previous block’s header, where the previous block is the last block on the blockchain when the current block gets added.
Nonce: A number that causes the hash value of the current block’s header to adhere to a specific pattern. If you change this value (or any header value), the hash of the header changes.
Timestamp: The date and time the current block was created.
Uncles hash: The hash value of the current block’s list of uncle blocks, which are stale blocks that were successfully mined but arrived just after the accepted block was added to the blockchain.
Beneficiary: The miner’s account that receives the reward for mining this block.
Logs bloom: Logging information, stored in a Bloom filter (a data structure useful for quickly finding out if some element is a member of a set).
Difficulty: The difficulty level for mining this block.
Extra data: Any extra data used to describe this block. Miners can put any data here they want, or they can leave it blank. For example, some miners write data that they can use to identify blocks they mined.
Block number: The unique number for this block (assigned sequentially).
Gas limit: The limit of gas for this block. (You learn about gas later in this chapter.)
Gas used: The amount of gas used by transactions in this block.
Mix hash: A hash value combined with the nonce value to show that the mined nonce meets the difficulty requirements. This hash makes it more difficult for attackers to modify the block.
State root: The hash value of the root node of the block’s state trie. A trie is a data structure that efficiently stores data for quick retrieval. The state trie expresses information about the state of transactions in the block without having to look at the transactions.
Transaction root: The hash value of the root node of the trie, which stores all transactions for this block.
Receipt root: The hash value of the root node of the trie, which stores all transaction receipts for this block.
The body of an Ethereum block is just a list of transactions. Unlike other blockchain implementations, the number of transactions, and as a result the size of the blocks, isn’t fixed. Every transaction has a processing cost associated with it, and each block has a limited budget. Ethereum blocks can contain lots of transactions that don’t cost much or just a few expensive ones or anything in between. Ethereum designed a lot of flexibility into what blocks can contain. Figure 3-6 shows the contents of an Ethereum transaction.

FIGURE 3-6:Contents of an Ethereum transaction.
Ethereum transactions contain the following fields:
Nonce: Each Ethereum account keeps track of the number of transactions it executes. This field is the latest transaction, based on the account’s counter. The transaction nonce is used by the network to ensure that transactions are executed in the proper order.
Signature: The digital signature of the account owner, proving the identity of the account requesting this transaction.
Gas price: The unit price you're willing to pay to execute this transaction.
Gas limit: The maximum total amount you're willing to pay to execute this transaction.
To: The address of the recipient of this transaction. For transfers, the To address is the account that will receive the transfer. For calling functions, the To address is the address of the smart contract.
Value: The total amount of ether you want to send to the recipient.
Data: The actual data submitted as the transaction body. Each type of transaction may have different data, based on its functionality. For calling functions, the data might contain parameters.
As users submit transaction requests to nodes, the nodes create transactions and submit them to the transaction pool. Miners then pick transactions from the pool and build new blocks. After an Ethereum mining node constructs a block, it starts the mining process. The first miner to complete the mining process adds the block to the blockchain and broadcasts the new block to the rest of the network.
 You can look at the public Ethereum blockchain at any time by going to Etherscan at
You can look at the public Ethereum blockchain at any time by going to Etherscan at https://etherscan.io/ . Etherscan lets you see blockchain statistics as well as block and transaction details.
Etherscan presents blockchain data in a readable format. But in doing so, it hides some important details. Blockchain data isn’t always stored in a format that is easily readable, at least to most people. For many reasons beyond the scope of this book, blockchain implementations store some data as a hash, not in a raw format. Storing data as hash values makes common querying and analytics operations more difficult than interacting with databases.
Each type of blockchain data has nuances in the way its data is formatted and stored. For example, a transaction’s input data value in its raw format, shown in Figure 3-7, isn't very helpful. You can see this by clicking or tapping View Input As ⇒ Original.
FIGURE 3-7:Original format of input data.
Etherscan can decode the input data for you. Click or tap the Decode Input Data button and Etherscan will try to translate the input data into easy-to-read input parameters for the called function. Figure 3-8 shows successfully decoded data for the cancelOrder()function. (In Figure 3-4, you saw that this transaction calls the cancelOrder()smart contract function.)

FIGURE 3-8:Decoded data for the cancelOrder()function.
You don't get this level of detail in every transaction. This transaction called a function in a registered smart contract. Registering a smart contract means that the developer submitted the application binary interface (ABI) for the contract, along with the compiled bytecode. An ABI is a definition of a smart contract’s state data, events, and functions, including each function’s input and return parameters. Etherscan uses the ABI, if it is available, to provide more descriptive information. If the ABI is not available, Etherscan can display only the raw input data.
Читать дальше

 Ethereum uses the Keccak-256 algorithm to produce all hash values. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Secure Hashing Algorithm 3 (SHA-3) is a subset of the Keccak algorithm. Ethereum was introduced before the SHA-3 standard was finalized, and Keccak-256 does not follow the SHA-3 official standard.
Ethereum uses the Keccak-256 algorithm to produce all hash values. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Secure Hashing Algorithm 3 (SHA-3) is a subset of the Keccak algorithm. Ethereum was introduced before the SHA-3 standard was finalized, and Keccak-256 does not follow the SHA-3 official standard.

 You can look at the public Ethereum blockchain at any time by going to Etherscan at
You can look at the public Ethereum blockchain at any time by going to Etherscan at 












