5 Chapter 7Table 7.1 Critical path vectors for component 1.
6 Chapter 10Table 10.1 Failure times (operating days) in chronological order.Table 10.2 Data set for Problem 13.
7 Chapter 11Table 11.1 Possible states of a structure of two components.Table 11.2 Possible states of a series structure of two components where fail...Table 11.3 The possible states of a two‐item parallel system with cold standb...
8 Chapter 13Table 13.1 PFD of some 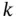 oo
oo 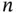 structures of identical and independent components...Table 13.2 PFD and spurious trip rate for three simple structures.Table 13.3 Safety integrity levels for safety functions.Table 13.4 Failure rates for the “fail to function” mode.
structures of identical and independent components...Table 13.2 PFD and spurious trip rate for three simple structures.Table 13.3 Safety integrity levels for safety functions.Table 13.4 Failure rates for the “fail to function” mode.
9 Chapter 14Table 14.1 A complete and ordered dataset of survival times.Table 14.2 Computation of the Kaplan–Meier Estimate (censored times are marke...Table 14.3 The Kaplan–Meier estimate as a function of time.Table 14.4 Nelson–Aalen estimate for the censored dataset in Example 14.12, c...Table 14.5 TTT Estimates for the dataset in Example 14.15.Table 14.6 Dataset for Problem 14.2.Table 14.7 Dataset for Problem 14.3.Table 14.8 Dataset for Problem 14.11.Table 14.9 Dataset for Problem 14.12.Table 14.10 Dataset for Problem 14.13.Table 14.11 Dataset for Problem 14.16.Table 14.12 Dataset for Problem 14.17.Table 14.13 Dataset for Problem 14.18.
10 Chapter 16Table 16.1 Pumps, subdivision in maintainable items in OREDA.
11 2Table B.1 Some main properties of Laplace transforms.Table B.2 Some Laplace transforms.
1 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 The reliability concept. Figure 1.2 Main drivers for high reliability. Figure 1.3 Main steps of risk analysis, with main methods. The methods cover... Figure 1.4 Reliability as basis of other applications. Figure 1.5 Load and the strength distributions at a specified time 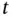 . Figure 1.6 Possible realization of the load and the strength of an item. Figure 1.7 The system reliability analysis process. Figure 1.8 The phases of a system development project (example). Figure 1.9 Factors that influence item requirements.
. Figure 1.6 Possible realization of the load and the strength of an item. Figure 1.7 The system reliability analysis process. Figure 1.8 The phases of a system development project (example). Figure 1.9 Factors that influence item requirements.
2 Chapter 2 Figure 2.1 System breakdown structure (simplified). Figure 2.2 A study object (system) and its boundary. Figure 2.3 A function illustrated as a functional block. Figure 2.4 Function tree (generic). Figure 2.5 SADT diagram for subsea oil and gas stimulation. Figure 2.6 Top‐down approach to establish an SADT model. Figure 2.7 System analysis and synthesis. Figure 2.8 Component function 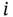 shown as a block. Figure 2.9 Alternative representation of the block in Figure 2.8 Figure 2.10 A simple reliability block diagram with three blocks. Figure 2.11 An alternative, and identical, version of the RBD in Figure 2.10... Figure 2.12 RBD for a series structure. Figure 2.13 Parallel structure. Figure 2.14 Voted structure 2oo3, (left) a physical diagram and (right) an R... Figure 2.15 Standby structure. Figure 2.16 RBD for a series–parallel structure. Figure 2.17 Two safety valves in a pipeline: (a) physical layout, (b) RBD fo... Figure 2.18 Construction of the RBD in levels.
shown as a block. Figure 2.9 Alternative representation of the block in Figure 2.8 Figure 2.10 A simple reliability block diagram with three blocks. Figure 2.11 An alternative, and identical, version of the RBD in Figure 2.10... Figure 2.12 RBD for a series structure. Figure 2.13 Parallel structure. Figure 2.14 Voted structure 2oo3, (left) a physical diagram and (right) an R... Figure 2.15 Standby structure. Figure 2.16 RBD for a series–parallel structure. Figure 2.17 Two safety valves in a pipeline: (a) physical layout, (b) RBD fo... Figure 2.18 Construction of the RBD in levels.
3 Chapter 3 Figure 3.1 States and transitions for a safety valve. Figure 3.2 Failure as a transition from a functioning state to a failed stat... Figure 3.3 Illustration of the difference between failure and fault for a de... Figure 3.4 Doorbell and associated circuitry. Figure 3.5 Relation between failure causes, failure modes, and failure effec... Figure 3.6 Relationship between failure cause, failure mode, and failure eff... Figure 3.7 Failure classification.. Figure 3.8 A primary failure leading to an item fault. Figure 3.9 A secondary failure, caused by an overstress event, leading to an... Figure 3.10 A systematic fault leading to a systematic failure. Figure 3.11 The structure of a security failure. Figure 3.12 Failure causes and mechanisms. A failure mechanism is a specific... Figure 3.13 Cause and effect diagram for the event “car will not start.” Figure 3.14 Repeatedly asking why?
4 Chapter 4 Figure 4.1 Deductive versus inductive analysis of a fault or deviation in th... Figure 4.2 Timeline of the development of FMECA variants (not in scale). Figure 4.3 The mains steps of FMECA. Figure 4.4 Example of an FMECA worksheet. Figure 4.5 Risk matrix of the different failure modes. Figure 4.6 A simple fault tree. Figure 4.7 System overview of fire detector system. Figure 4.8 Schematic layout of the fire detector system. Figure 4.9 Fault tree for the fire detector system in Example 4.1. Figure 4.10 Example of a fault tree. Figure 4.11 Sketch of a first stage gas separator. Figure 4.12 Fault tree for the first stage separator in Example 4.2. Figure 4.13 A simple event tree for a dust explosion. Figure 4.14 Presentation of results from ETA. Figure 4.15 Activation pressures for the three protection layers of the proc... Figure 4.16 An event tree for the initiating event “blockage of the gas outl... Figure 4.17 Relationship between some simple RBDs and fault trees. Figure 4.18 RBD for the fire detector system. Figure 4.19 Component 2 is irrelevant. Figure 4.20 Example structure. Figure 4.21 Redundancy at system level. Figure 4.22 Redundancy at component level. Figure 4.23 Bridge structure. Figure 4.24 2oo3 structure represented as a series structure of the minimal ... Figure 4.25 The bridge structure represented as a parallel structure of the ... Figure 4.26 The bridge structure represented as a series structure of the mi... Figure 4.27 The structure 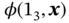 of the bridge structure. Figure 4.28 The structure
of the bridge structure. Figure 4.28 The structure 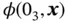 of the bridge structure. Figure 4.29 RBD. Figure 4.30 Structure of modules. Figure 4.31 The three substructures. Figure 4.32 Module II. Figure 4.33 Two prime modules. Figure 4.34 The main BN symbols.Figure 4.35 (a) Linear, (b) converging, and (c) diverging BN with three node...Figure 4.36 BN for a system
of the bridge structure. Figure 4.29 RBD. Figure 4.30 Structure of modules. Figure 4.31 The three substructures. Figure 4.32 Module II. Figure 4.33 Two prime modules. Figure 4.34 The main BN symbols.Figure 4.35 (a) Linear, (b) converging, and (c) diverging BN with three node...Figure 4.36 BN for a system 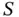 of two independent components
of two independent components  and
and 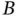 .Figure 4.37 BN for a 2oo3 structure
.Figure 4.37 BN for a 2oo3 structure 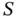 of three components
of three components 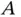 ,
, 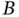 , and
, and 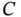 .Figure 4.38 A simple fault tree and the corresponding BN.Figure 4.39 Hydraulically operated gate valve (Problem 4.2).Figure 4.40 RBD for Problem 4.4.Figure 4.41 RBD for Problem 4.6.Figure 4.42 Lubrication system on a ship engine (Problem 4.7).Figure 4.43 RBD for Problem 4.11.Figure 4.44 Fault tree for Problem 4.12.Figure 4.45 RBD for Problem 12.Figure 4.46 RBD for Problem 4.13.Figure 4.47 RBD for Problem 4.14.
.Figure 4.38 A simple fault tree and the corresponding BN.Figure 4.39 Hydraulically operated gate valve (Problem 4.2).Figure 4.40 RBD for Problem 4.4.Figure 4.41 RBD for Problem 4.6.Figure 4.42 Lubrication system on a ship engine (Problem 4.7).Figure 4.43 RBD for Problem 4.11.Figure 4.44 Fault tree for Problem 4.12.Figure 4.45 RBD for Problem 12.Figure 4.46 RBD for Problem 4.13.Figure 4.47 RBD for Problem 4.14.
Читать дальше

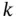 oo
oo 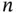 structures of identical and independent components...Table 13.2 PFD and spurious trip rate for three simple structures.Table 13.3 Safety integrity levels for safety functions.Table 13.4 Failure rates for the “fail to function” mode.
structures of identical and independent components...Table 13.2 PFD and spurious trip rate for three simple structures.Table 13.3 Safety integrity levels for safety functions.Table 13.4 Failure rates for the “fail to function” mode.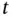 . Figure 1.6 Possible realization of the load and the strength of an item. Figure 1.7 The system reliability analysis process. Figure 1.8 The phases of a system development project (example). Figure 1.9 Factors that influence item requirements.
. Figure 1.6 Possible realization of the load and the strength of an item. Figure 1.7 The system reliability analysis process. Figure 1.8 The phases of a system development project (example). Figure 1.9 Factors that influence item requirements.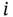 shown as a block. Figure 2.9 Alternative representation of the block in Figure 2.8 Figure 2.10 A simple reliability block diagram with three blocks. Figure 2.11 An alternative, and identical, version of the RBD in Figure 2.10... Figure 2.12 RBD for a series structure. Figure 2.13 Parallel structure. Figure 2.14 Voted structure 2oo3, (left) a physical diagram and (right) an R... Figure 2.15 Standby structure. Figure 2.16 RBD for a series–parallel structure. Figure 2.17 Two safety valves in a pipeline: (a) physical layout, (b) RBD fo... Figure 2.18 Construction of the RBD in levels.
shown as a block. Figure 2.9 Alternative representation of the block in Figure 2.8 Figure 2.10 A simple reliability block diagram with three blocks. Figure 2.11 An alternative, and identical, version of the RBD in Figure 2.10... Figure 2.12 RBD for a series structure. Figure 2.13 Parallel structure. Figure 2.14 Voted structure 2oo3, (left) a physical diagram and (right) an R... Figure 2.15 Standby structure. Figure 2.16 RBD for a series–parallel structure. Figure 2.17 Two safety valves in a pipeline: (a) physical layout, (b) RBD fo... Figure 2.18 Construction of the RBD in levels.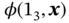 of the bridge structure. Figure 4.28 The structure
of the bridge structure. Figure 4.28 The structure 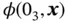 of the bridge structure. Figure 4.29 RBD. Figure 4.30 Structure of modules. Figure 4.31 The three substructures. Figure 4.32 Module II. Figure 4.33 Two prime modules. Figure 4.34 The main BN symbols.Figure 4.35 (a) Linear, (b) converging, and (c) diverging BN with three node...Figure 4.36 BN for a system
of the bridge structure. Figure 4.29 RBD. Figure 4.30 Structure of modules. Figure 4.31 The three substructures. Figure 4.32 Module II. Figure 4.33 Two prime modules. Figure 4.34 The main BN symbols.Figure 4.35 (a) Linear, (b) converging, and (c) diverging BN with three node...Figure 4.36 BN for a system  of two independent components
of two independent components 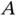 and
and 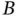 .Figure 4.37 BN for a 2oo3 structure
.Figure 4.37 BN for a 2oo3 structure 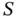 of three components
of three components 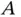 ,
, 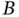 , and
, and 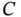 .Figure 4.38 A simple fault tree and the corresponding BN.Figure 4.39 Hydraulically operated gate valve (Problem 4.2).Figure 4.40 RBD for Problem 4.4.Figure 4.41 RBD for Problem 4.6.Figure 4.42 Lubrication system on a ship engine (Problem 4.7).Figure 4.43 RBD for Problem 4.11.Figure 4.44 Fault tree for Problem 4.12.Figure 4.45 RBD for Problem 12.Figure 4.46 RBD for Problem 4.13.Figure 4.47 RBD for Problem 4.14.
.Figure 4.38 A simple fault tree and the corresponding BN.Figure 4.39 Hydraulically operated gate valve (Problem 4.2).Figure 4.40 RBD for Problem 4.4.Figure 4.41 RBD for Problem 4.6.Figure 4.42 Lubrication system on a ship engine (Problem 4.7).Figure 4.43 RBD for Problem 4.11.Figure 4.44 Fault tree for Problem 4.12.Figure 4.45 RBD for Problem 12.Figure 4.46 RBD for Problem 4.13.Figure 4.47 RBD for Problem 4.14.










