Remark 1.3 (Broad interpretation of reliability)
In this book, the term “reliability” is used quite broadly, rather similar to RAM as defined above. The same interpretation is used by Birolini (2014).
Throughout this book, it is assumed that the time‐to‐failure and the repair time of an item are random variables with probability distributions that describe the future behavior of the item. The future behavior may be evaluated based on one or more reliability metrics . A reliability metric is a “quantity” that is derived from the reliability model and is, as such, not directly measurable. When performance data become available, we may estimate or predict quantitative values for each reliability metric.
A single reliability metric is not able to tell the whole truth. Sometimes, we need to use several reliability metrics to get a sufficiently clear picture of how reliable an item is.
1.4.1 Reliability Metrics for a Technical Item
Common reliability metrics for an item include
1 The mean time‐to‐failure (MTTF)
2 The number of failures per time unit (failure frequency)
3 The probability that the item does not fail in a time interval (survivor probability)
4 The probability that the item is able to function at time (availability at time )
These and several other reliability metrics are given a mathematical precise definition in Chapter 5, and are discussed and exemplified in all the subsequent chapters.
Example 1.1 (Average availability and downtime)
Consider the electricity supply, which is supposed to be available at any time. The achieved average availability  of the supply is quantified as
of the supply is quantified as

If we consider a period of one year, the total time is approximately 8760 hours. The downtime is the time, during the specified time period, the service is not available. The relationship between the average availability and the length of the downtime is illustrated in Table 1.1.
Table 1.1Availability and downtime.
| 90 |
36.5 d |
| 99 |
3.65 d |
| 99.9 |
8.76 h |
| 99.99 |
52 min |
| 99.999 |
5 min |
1.4.2 Reliability Metrics for a Service
A wide range of service reliability metrics have been defined, but these vary significantly between the application areas. The most detailed metrics are available for electric power supply (e.g. see IEEE Std. 1366 2012).
Example 1.2 (Airline reliability and availability)
Airline passengers are mainly concerned about whether the journey will be safe and whether the aircraft will take off and land on the scheduled times. The second concern is, by airlines, expressed by the dispatch reliability , which is defined as the probability that a scheduled departure takes place within a specified time after the scheduled departure time. Many airlines use a 15‐minutes margin between actual and scheduled departure time for a flight to be considered as having departed on time. The achieved dispatch reliability indicator for a (past) period is reported as the percentage of all departures that departed on time.

For technical items, the airlines are mainly using the reliability metrics listed in Section 1.4.1
1.5 Approaches to Reliability Analysis
Three main branches of reliability can be distinguished:
Hardware reliability
Software reliability
Human reliability
The present book is concerned with hardware items (existing or in design) that may or may not have embedded software. Within hardware reliability, two different approaches may be used: the physical approach and/or the systems approach .
1.5.1 The Physical Approach to Reliability
In the physical approach, the strength of a technical item is modeled as a random variable  . The item is exposed to a load
. The item is exposed to a load  that is also modeled as a random variable. The distributions of the strength and the load at a specific time
that is also modeled as a random variable. The distributions of the strength and the load at a specific time  are shown in Figure 1.5. A failure will occur as soon as the load is higher than the strength. The survival probability
are shown in Figure 1.5. A failure will occur as soon as the load is higher than the strength. The survival probability  of the item is defined as the probability that the strength is greater than the load,
of the item is defined as the probability that the strength is greater than the load,

where  is the probability of event
is the probability of event  .
.

Figure 1.5Load and the strength distributions at a specified time 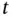 .
.
The load may vary with time and be modeled as a time‐dependent variable  . The item may deteriorate with time, due to failure mechanisms, such as, corrosion, erosion, and fatigue. The strength of the item will therefore also be a function of time,
. The item may deteriorate with time, due to failure mechanisms, such as, corrosion, erosion, and fatigue. The strength of the item will therefore also be a function of time,  . A possible realization of
. A possible realization of 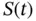 and
and  is shown in Figure 1.6. The time‐to‐failure
is shown in Figure 1.6. The time‐to‐failure  of the item is the (shortest) time until
of the item is the (shortest) time until 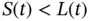 ,
,

and the survivor probability  of the item may be defined as
of the item may be defined as
Читать дальше

 of the supply is quantified as
of the supply is quantified as

 . The item is exposed to a load
. The item is exposed to a load  that is also modeled as a random variable. The distributions of the strength and the load at a specific time
that is also modeled as a random variable. The distributions of the strength and the load at a specific time  are shown in Figure 1.5. A failure will occur as soon as the load is higher than the strength. The survival probability
are shown in Figure 1.5. A failure will occur as soon as the load is higher than the strength. The survival probability  of the item is defined as the probability that the strength is greater than the load,
of the item is defined as the probability that the strength is greater than the load,
 is the probability of event
is the probability of event  .
.
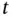 .
. . The item may deteriorate with time, due to failure mechanisms, such as, corrosion, erosion, and fatigue. The strength of the item will therefore also be a function of time,
. The item may deteriorate with time, due to failure mechanisms, such as, corrosion, erosion, and fatigue. The strength of the item will therefore also be a function of time,  . A possible realization of
. A possible realization of 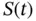 and
and  is shown in Figure 1.6. The time‐to‐failure
is shown in Figure 1.6. The time‐to‐failure  of the item is the (shortest) time until
of the item is the (shortest) time until 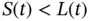 ,
,
 of the item may be defined as
of the item may be defined as










