However, in repairable system, one generally has times of successive failures of a single system, often violating the i.i.d assumption. Hence, it is not surprising that statistical methods required for repairable system differ from those needed in reliability analysis of non-repairable items. In order to address the reliability characteristics of complex repairable systems, a process rather than a distribution is often used. For a repairable system, time to next failure depends on both the life distribution (the probability distribution of the time to first failure) and the impact of maintenance actions performed after the first occurrence of a failure. The most popular process model is the Power Law Process (PLP). This model is popular for several reasons. For instance, it has a very practical foundation in terms of minimal repair —a situation when the repair of a failed system is just enough to get the system operational again by repair or replacement of its constituent item(s). Second, if the time to first failure follows the Weibull distribution, then the Power Law model repair governs each succeeding failure and adequately models the minimal repair phenomenon. In other words, the Weibull distribution addresses the very first failure and the PLP addresses each succeeding failure for a repairable system. From this viewpoint, the PLP can be regarded as an extension of the Weibull distribution and a generalization of Poisson process. Besides, the PLP is generally computationally easy in providing useful and practical solutions, which have been usually comprehended and accepted by the management for many real-world applications.
The usual notion and assumption of overhauling of a system is to bringing it back to “as-good-as-new” (AGAN) condition. This notion may not be true in practice and an overhaul may not achieve the system reliability back to where it was when the system was new. However, there is concurrence among all the stakeholders that an overhaul indeed makes the system more reliable than just before its overhaul. For systems that are not overhauled, there is only one cycle and we are interested in the reliability characteristics of such systems as the system ages during its operational life. For systems that are overhauled several times during their lifetime, our interest would be in the reliability characteristics of the system as it ages during its cycles, i.e., the age of the system starts from the beginning of the cycle and each cycle starts with a new zero time.
1.2 Perfect, Minimal, and Imperfect Repairs
As discussed earlier, a repairable system is a system that is restored to its functionable state after the loss of functionability by the actions other than replacement of the entire system. The quantum of repair depends upon various factors like criticality of the component failed, operational status of the system, risk index, etc. Accordingly, the management takes a decision on how much repair a system has to undergo. The two extremes of the repair are perfect and minimal repairs. A system is said to be perfectly repaired, if the system is restored to AGAN condition (as it is replaced with a new one). Normally, a perfect repair in terms of the replacement is carried out for very critical components, which may compromise operation ability, safety of the system, and/or personnel working with the system. On the other hand, a system is said to be minimally repaired, if its working state is restored to “as-bad-as-old” (ABAO). This type of repair is undertaken when there is heavy demand for the system to work for a finite time or the system will be undergoing preventive maintenance shortly or will be scrapped soon.
Any repair other than perfect and minimal repair comes under imperfect repair. Most of the repairs observed in day-to-day systems are imperfect repairs, i.e., a system is neither restored to AGAN conditions nor to ABAO conditions. The three types of repairs are pictorially represented in Figure 1.1.
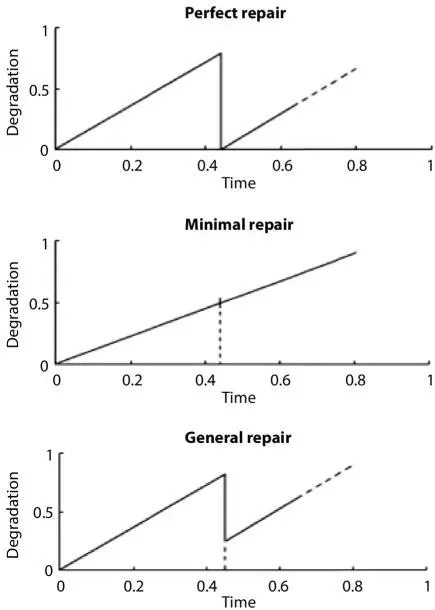
Figure 1.1Types of repair.
It can be seen from Figure 1.1 that in case of perfect repair, the system is rendered “AGAN” and the life starts at zero in the time scale signifying that the performance degradation is completely restored. In case of minimal repair, after the system is subjected to a repair action, its age remains same as before the repair action and there is no restoration of life below the previous age. So far the general repair is concerned, some of its life is renewed and the system starts functioning after being restored to somewhere between “ABAO” and “AGAN” state.
Figure 1.2 summarizes the techniques in vogue for reliability analysis for both repairable and non-repairable items, respectively.
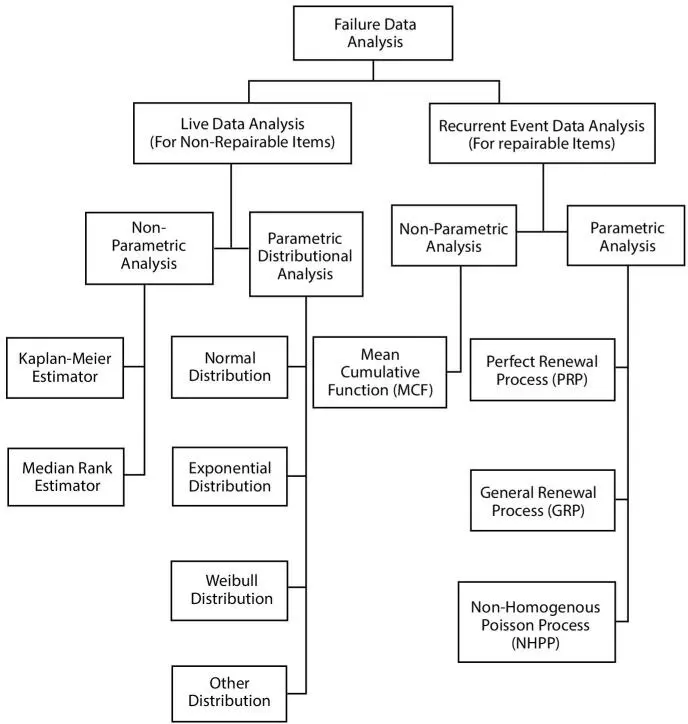
Figure 1.2Various techniques for reliability analysis.
A renewal process (RP) is a counting process where the inter-occurrence times are stochastically i.i.d. with an arbitrary life distribution. Under the RP, a single distribution can characterize the time between failures (TBF), and the frequency of repair appears constant. The non-renewal behavior occurs if this frequency of repairs increases (deteriorating systems) or decreases (system improving) influencing the corresponding maintenance costs. The homogeneous Poisson process (HPP) describes a sequence of statistically i.i.d. exponential random variables. Conversely, a non-homogeneous Poisson process (NHPP) [3, 4] describes a sequence of random variables that are neither statistically independent nor identically distributed. The NHPP is often used to model repairable systems that are subject to minimal repair. The generalized renewal process (GRP) allows the goodness of repairs within two extremities, viz. , AGAN repair (RP) to the same-as-old repair (NHPP). The GRP is particularly useful in modeling the failure behavior of a specific unit and understanding the effects of repair actions on the age of that system. An example of a system to which the GRP is especially applicable is a system, which is repaired after a failure and whose repair neither brings the system to an AGAN or an ABAO condition, but instead partially rejuvenates the system. Therefore, one should be cautious on the fact that without looking at the actual behavior of the data may lead to underestimation or overestimation of engineering metrics.
The analysis by employing the parametric methods on scenarios of failure-repair requires a certain degree of statistical knowledge, the ability to solve complex equations and verification of distributional assumptions. Further, these equations cannot be solved analytically and require an iterative procedure or special software. Besides, parametric approaches are computationally intensive and not intuitive to a novice or an average person. The analysis of events, irrespective of the nature of the system-reparable or not reparable, should take an analysis path from non-parametric to versatile parametric model with graphical analysis being a common denominator. Undoubtedly, the choice of method depends on the data available and the questions we wish to answer.
A repairable system is a system that is restored to its functionable state after the loss of functionability by the actions other than replacement of the entire system. The two extremes of the repair are perfect and minimal repairs. A system is said to be perfectly repaired, if the system is restored to AGAN condition (as it is replaced with a new one). On the other hand, a system is said to be minimally repaired, if its working state is restored to ABAO. Any repair other than perfect and minimal repair comes under imperfect repair. Most of the repairs observed in day-to-day systems are imperfect repairs, i.e., a system is neither restored to AGAN conditions nor to ABAO conditions. The RP is used to model AGAN condition. The NHPP is often used to model repairable systems that are subject to minimal repair. The GRP allows the goodness of repairs within two extremities, viz. , AGAN repair (RP) to the same-as-old repair (NHPP).
Читать дальше














