1 Cover
2 Title page Waves and Scattering Set coordinated by Jean-Michel L. Bernard Volume 2
3 Copyright
4 Preface
5 Introduction
6 4 Exact Solutions for Electromagnetic Impedance Wedges4.1. Introduction 4.2. A list of the impedance wedge problems amenable to exact WH solutions 4.3. Cases involving classical WH equations 4.4. Exact solutions for impedance wedge problems with the GWHE form of section 3.5 – form #1 4.5. Exact solutions for the impedance wedge problems with the GWHEs written in an alternative form – form #2 4.6. A general form of the GWHEs to study the arbitrary face impedance wedges – form #3 Appendix 4.A. Some important formulas of decomposition for wedge problems
7 5 Fredholm Factorization Solutions of GWHEs for the Electromagnetic Impedance Wedges Surrounded by an Isotropic Medium5.1. Introduction 5.2. Generalized Wiener-Hopf equations for the impenetrable wedge scattering problem of an electromagnetic plane wave at skew incidence 5.3. Fredholm factorization solution in the η plane of GWHEs 5.4. Fredholm factorization solution in the w plane of GWHEs 5.5. Approximate solution of FIEs derived from GWHEs 5.6. Analytic continuation of approximate solutions of GWHEs 5.7. Far-field computation 5.8. Criteria for the examples 5.9. Example 1: Symmetric isotropic impedance wedge at normal incidence with Ez polarization 5.10. Example 2: Non-symmetric isotropic impedance wedge at normal incidence with Hz polarization and surface wave contribution 5.11. Example 3: PEC wedge at skew incidence 5.12. Example 4: Arbitrary impedance half-plane at skew incidence 5.13. Example 5: Arbitrary impedance wedge at skew incidence 5.14. Example 6: Arbitrary impedance concave wedge at skew incidence 5.15. Discussion Appendix 5.A. Fredholm properties of the integral equation (5.3.1)
8 6 Diffraction by Penetrable Wedges6.1. Introduction 6.2. GWHEs for the dielectric wedge at normal incidence (Ez-polarization) 6.3. Reduction of the GWHEs for the dielectric wedge at Ez-polarization to Fredholm integral equations 6.4. Analytic continuation for the solution of the dielectric wedge at Ez-polarization 6.5. Some remarks on the Fredholm integral equations (6.3.24), (6.3.26) and numerical solutions 6.6. Field evaluation in any point of the space 6.7. The dielectric wedge at skew incidence 6.8. Criteria for examples of the scattering by a dielectric wedge at normal incidence (Ez-polarization) 6.9. Example: the scattering by a dielectric wedge at normal incidence (Ez-polarization) 6.10. Discussion Appendix 6.A. Fredholm factorization applied to (6.3.2)–(6.3.5) Appendix 6.B. Source term η
9 References
10 Index
11 Summary of Volume 1
12 End User License Agreement
1 Chapter 4 Figure 4.1.1. Scattering by an impendence wedge Figure 4.1.2. Particular cases of impedance wedges. Left: half-plane (γa = γb = ... Figure 4.3.1. Particular cases of impedance wedges. Left: half-plane (γa = γb =π...Figure 4.3.3.1. Full-plane junction with different face impendencesFigure 4.3.5.1. An example of a right-angled wedge that can be solved exactly at...Figure 4.4.1. Impenetrable wedge with arbitrary aperture and face impendences at...
2 Chapter 5Figure 5.2.1. Scattering of an impenetrable wedge by a plane wave at skew incide...Figure 5.4.1. Left: contour deformation of integration line from the real axis o...Figure 5.7.1. Horizontal (Im[η] = cost) Bromwich contours Br and SDP contour in ...Figure 5.9.1. Top-left (bottom-left): absolute value of ĝ1+ (w) (ĝ2+ (w)) for –Φ...Figure 5.9.2. Top-left (bottom-left): absolute value of 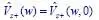
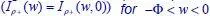 obtained with strate...Figure 5.9.3. Plot of the relative error in log10 scale of the results in terms ...Figure 5.9.4. Top (bottom): imaginary part of the initial spectrum
obtained with strate...Figure 5.9.3. Plot of the relative error in log10 scale of the results in terms ...Figure 5.9.4. Top (bottom): imaginary part of the initial spectrum 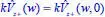
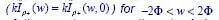 obtained w...Figure 5.9.5. Top: total field (solid line), GO field component (circles) and UT...Figure 5.10.1. Top: total field (solid line), GO field component (circles), UTD ...Figure 5.11.1. Top: the exact GTD diffraction coefficient dB. Bottom: relative e...Figure 5.12.1. GTD co-polar diffraction coefficient in dB versus the azimuthal o...Figure 5.12.2.The relative error on the evaluation of GTD diffraction coefficien...Figure 5.13.1. Co-polar component Ez of total far field at kρ = 10 for the test ...Figure 5.13.2. Cross-polar component ΖoHz of total far field at kρ = 10 for the ...Figure 5.14.1. Impendence concave wedge with multiple reflections. For a color v...Figure 5.14.2. Co-polar Hz (left) and cross-polar Ez/Zo (right) far-field compon...Figure 5.14.3. Co-polar (Ez) and cross-polar (Zo Hz) GTD diffraction coefficient...
obtained w...Figure 5.9.5. Top: total field (solid line), GO field component (circles) and UT...Figure 5.10.1. Top: total field (solid line), GO field component (circles), UTD ...Figure 5.11.1. Top: the exact GTD diffraction coefficient dB. Bottom: relative e...Figure 5.12.1. GTD co-polar diffraction coefficient in dB versus the azimuthal o...Figure 5.12.2.The relative error on the evaluation of GTD diffraction coefficien...Figure 5.13.1. Co-polar component Ez of total far field at kρ = 10 for the test ...Figure 5.13.2. Cross-polar component ΖoHz of total far field at kρ = 10 for the ...Figure 5.14.1. Impendence concave wedge with multiple reflections. For a color v...Figure 5.14.2. Co-polar Hz (left) and cross-polar Ez/Zo (right) far-field compon...Figure 5.14.3. Co-polar (Ez) and cross-polar (Zo Hz) GTD diffraction coefficient...
3 Chapter 6Figure 6.1.1. Dielectric wedge problem: 2π – 2Φ is the aperture angle of the wed...Figure 6.9.1. GO field, UTD component and the total far-field pattern at kρ = 10...Figure 6.9.2. a, b) Imaginary parts  in the regularity segment –Φ ≤ w ≤ 0 that ...Figure 6.9.3. a, b) Imaginary parts
in the regularity segment –Φ ≤ w ≤ 0 that ...Figure 6.9.3. a, b) Imaginary parts  in the regularity segment –Φ1 ≤ w1 ≤ 0 tha...Figure 6.9.4. a, d) Absolute value of the spectral unknowns
in the regularity segment –Φ1 ≤ w1 ≤ 0 tha...Figure 6.9.4. a, d) Absolute value of the spectral unknowns 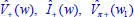 and
and 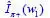 in (–2π,0) a...Figure 6.9.5. a) Absolute value of the total GTD diffraction coefficient (dB), b...Figure 6.9.6. Left: total field (solid line), GO field component (squares), UTD ...Figure 6.9.7. w = Φ + g1(w1 + Φ1) mapping used for the analytical continuation o...
in (–2π,0) a...Figure 6.9.5. a) Absolute value of the total GTD diffraction coefficient (dB), b...Figure 6.9.6. Left: total field (solid line), GO field component (squares), UTD ...Figure 6.9.7. w = Φ + g1(w1 + Φ1) mapping used for the analytical continuation o...
1 Cover
2 Table of Contents
3 Title Page
4 Copyright
5 Preface
6 Introduction
7 Begin Reading
8 References
9 Index
10 Summary of Volume 1
11 End User License Agreement
1 v
2 ii
3 iii
4 iv
5 ix
6 x
7 xi
8 xiii
9 xiv
10 xv
11 1
12 2
13 3
14 4
15 5
16 6
17 7
18 8
19 9
20 10
21 11
22 12
23 13
24 14
25 15
26 16
27 17
28 18
29 19
30 20
31 21
32 22
33 23
34 24
35 25
36 26
37 27
38 28
39 29
40 30
41 31
42 32
43 33
44 34
45 35
46 36
47 37
48 38
49 39
50 40
51 41
52 42
53 43
54 44
55 45
56 46
57 47
58 48
59 49
60 50
61 51
62 52
63 53
64 54
65 55
66 56
67 57
68 58
Читать дальше

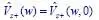
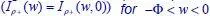 obtained with strate...Figure 5.9.3. Plot of the relative error in log10 scale of the results in terms ...Figure 5.9.4. Top (bottom): imaginary part of the initial spectrum
obtained with strate...Figure 5.9.3. Plot of the relative error in log10 scale of the results in terms ...Figure 5.9.4. Top (bottom): imaginary part of the initial spectrum 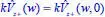
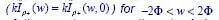 obtained w...Figure 5.9.5. Top: total field (solid line), GO field component (circles) and UT...Figure 5.10.1. Top: total field (solid line), GO field component (circles), UTD ...Figure 5.11.1. Top: the exact GTD diffraction coefficient dB. Bottom: relative e...Figure 5.12.1. GTD co-polar diffraction coefficient in dB versus the azimuthal o...Figure 5.12.2.The relative error on the evaluation of GTD diffraction coefficien...Figure 5.13.1. Co-polar component Ez of total far field at kρ = 10 for the test ...Figure 5.13.2. Cross-polar component ΖoHz of total far field at kρ = 10 for the ...Figure 5.14.1. Impendence concave wedge with multiple reflections. For a color v...Figure 5.14.2. Co-polar Hz (left) and cross-polar Ez/Zo (right) far-field compon...Figure 5.14.3. Co-polar (Ez) and cross-polar (Zo Hz) GTD diffraction coefficient...
obtained w...Figure 5.9.5. Top: total field (solid line), GO field component (circles) and UT...Figure 5.10.1. Top: total field (solid line), GO field component (circles), UTD ...Figure 5.11.1. Top: the exact GTD diffraction coefficient dB. Bottom: relative e...Figure 5.12.1. GTD co-polar diffraction coefficient in dB versus the azimuthal o...Figure 5.12.2.The relative error on the evaluation of GTD diffraction coefficien...Figure 5.13.1. Co-polar component Ez of total far field at kρ = 10 for the test ...Figure 5.13.2. Cross-polar component ΖoHz of total far field at kρ = 10 for the ...Figure 5.14.1. Impendence concave wedge with multiple reflections. For a color v...Figure 5.14.2. Co-polar Hz (left) and cross-polar Ez/Zo (right) far-field compon...Figure 5.14.3. Co-polar (Ez) and cross-polar (Zo Hz) GTD diffraction coefficient... in the regularity segment –Φ ≤ w ≤ 0 that ...Figure 6.9.3. a, b) Imaginary parts
in the regularity segment –Φ ≤ w ≤ 0 that ...Figure 6.9.3. a, b) Imaginary parts  in the regularity segment –Φ1 ≤ w1 ≤ 0 tha...Figure 6.9.4. a, d) Absolute value of the spectral unknowns
in the regularity segment –Φ1 ≤ w1 ≤ 0 tha...Figure 6.9.4. a, d) Absolute value of the spectral unknowns 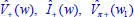 and
and 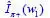 in (–2π,0) a...Figure 6.9.5. a) Absolute value of the total GTD diffraction coefficient (dB), b...Figure 6.9.6. Left: total field (solid line), GO field component (squares), UTD ...Figure 6.9.7. w = Φ + g1(w1 + Φ1) mapping used for the analytical continuation o...
in (–2π,0) a...Figure 6.9.5. a) Absolute value of the total GTD diffraction coefficient (dB), b...Figure 6.9.6. Left: total field (solid line), GO field component (squares), UTD ...Figure 6.9.7. w = Φ + g1(w1 + Φ1) mapping used for the analytical continuation o...










