Empirical Data
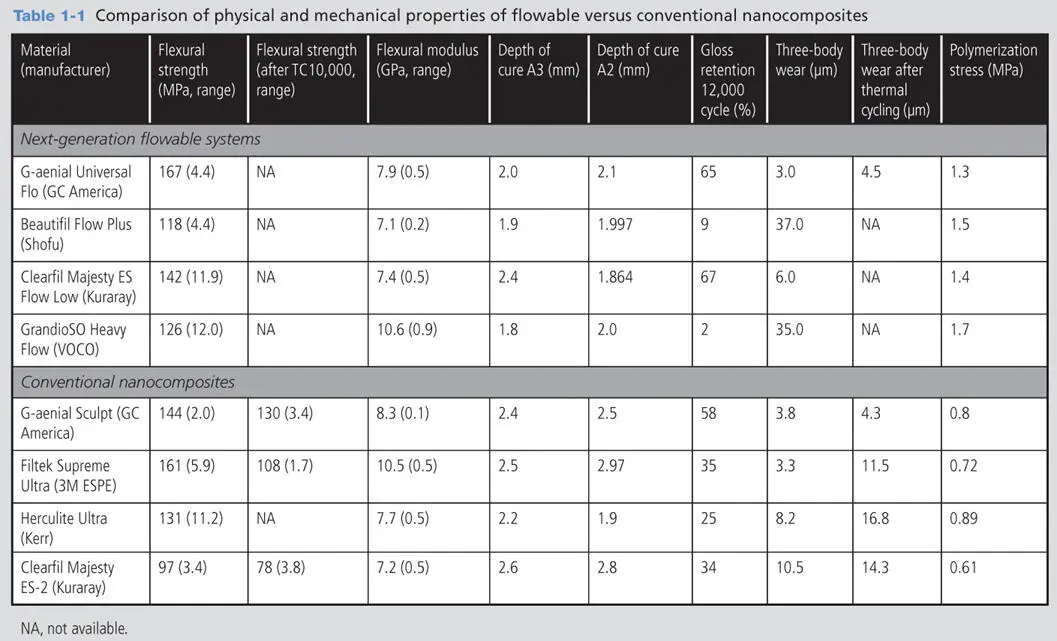
Flowable composite materials have been evaluated in numerous studies 1 – 5 , 7 , 27 – 45 since their inception. Some of the more recent studies 39 , 42 , 43 indicate that the clinical performance of specifically tested flowable resin composites is similar to or better than that of specifically tested universal resin composites. Attar et al 28 showed that different flowable composites possessed a wide range of mechanical and physical properties. Earlier studies by Gallo et al 29 on specific flowable resin composites suggested that these materials should be limited to small- and moderate-sized restorations with isthmus widths of one-fourth or less of the intercuspal distance. 36 However, Torres et al 43 reported that, after 2 years of clinical service, no significant differences were found between Class II restorations restored with GrandioSO (VOCO) conventional nanocomposites and those restored with GrandioSO Heavy Flow (VOCO) flowable hybrid nanocomposites. A study by Karaman et al 39 showed similar clinical performances over 24 months in restorations of noncarious cervical lesions restored with conventional nanocomposites (Grandio, VOCO) and those restored with flowable material (Grandio Flow, VOCO). A more recent study by Sumino et al 42 indicated that the flowable materials G-aenial Universal Flo, G-aenial Flo, and Clearfil Majesty Flow (Kuraray) had significantly greater flexural strength and a higher elastic modulus than the corresponding conventional nanocomposite materials, Kalore (GC America) and Clearfil Majesty Esthetic (Kuraray). The wear and mechanical properties of these specific flowable materials suggested an improved clinical performance compared with that of the universal composites. Several in vitro studies conducted at GC Research and Development comparing specific flowable material properties of several conventional composites found results similar to those of Sumino et al. Of the next-generation flowable systems studied, G-aenial Universal Flo and Clearfil Majesty ES Flow (Kuraray) showed superior gloss retention and similar wear resistance to the conventional nanocomposites tested, which included Filtek Supreme Ultra (3M ESPE), Herculite Ultra (Kerr), Clearfil Majesty ES-2, and G-aenial Sculpt (Table 1-1).
According to these studies, the recently developed specific nanohybrid flowable resin (or universal injectable) composite systems (ie, Clearfil Majesty ES Flow and G-aenial Universal Flo) may possess properties that meet the aforementioned mechanical, physical, and optical requisites. These properties and the clinical behavior of the biomaterial formulations are contingent on their structure. New resin filler technology allows higher filler loading because of the surface treatment of the particles and the increase in the distribution of particle sizes. The unique resin filler matrix allows the particles to be situated very closely to each other, and this reduced interparticle spacing and homogenous dispersion of the particles in the resin matrix increases the reinforcement and protects the matrix. 46 – 48 In addition, the proprietary chemical treatment of the filler particles allows proper wettability of the filler surface by the monomer and thus an improved dispersion and a stable and stronger bond between the filler and resin. Research studies 48 – 52 clearly indicate the importance that filler content and coupling agents represent in determining characteristics such as strength and wear resistance. Recent studies 4 , 36 , 53 report that flowable composites have comparable shrinkage stress to conventional composites. According to the manufacturers, these next-generation flowable composite formulations are purported to offer mechanical, physical, and esthetic properties similar to or better than those of many universal composites. 54 The clinical attributes of universal flowable composites include easier insertion and manipulation, improved adaptation to the internal cavity wall 55 ( Fig 1-2), increased wear resistance, greater elasticity, color stability, enhanced polishability and retention of polish, and radiopacity similar to enamel. Furthermore, the clinical indications for these next-generation flowable resin composites are increasing as the properties of the materials and the bond strength of adhesives to dental tissues improve. With improved mechanical properties reported, 42 these highly filled formulations are indicated for use in anterior and posterior restorative applications. 56 The clinical applications of these specific next-generation composites include sealants and preventive resin restorations; emergency repair of fractured teeth and restorations; fabrication, modification, and repair of composite prototypes and provisional restorations 57 ; anterior and posterior composite restorations; composite tooth splinting 58 ; and intraoral repair of fractured ceramic and composite restorations. 58 In addition, these composites can be used to repair denture teeth, 58 establish vertical dimension, alter occlusal schemes before definitive restoration, 56 manage spatial parameters during orthodontic treatment, eliminate cervical sensitivity, 58 resurface occlusal wear on posterior composite restorations, 58 establish incisal edge length before esthetic crown lengthening, 56 develop composite prototypes for copy milling, 56 and place pediatric composite crowns. 59
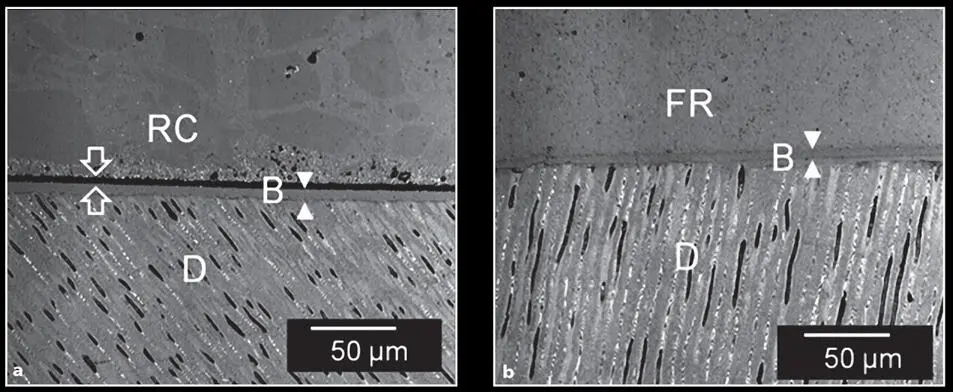
Fig 1-2 (a) Hybrid resin composite (Estelite Sigma Quick, Tokuyama) placed without a flowable resin composite liner. Note the gap at the interface between the resin composite (RC) and the all-in-one bonding agent (B). (b) Same hybrid resin composite placed with a flowable resin (FR) composite liner. There is no gap between the flowable resin composite and the bonding agent. D, dentin. (Confocal laser scanning microscope images courtesy of Alireza Sadr, DDS, PhD.)
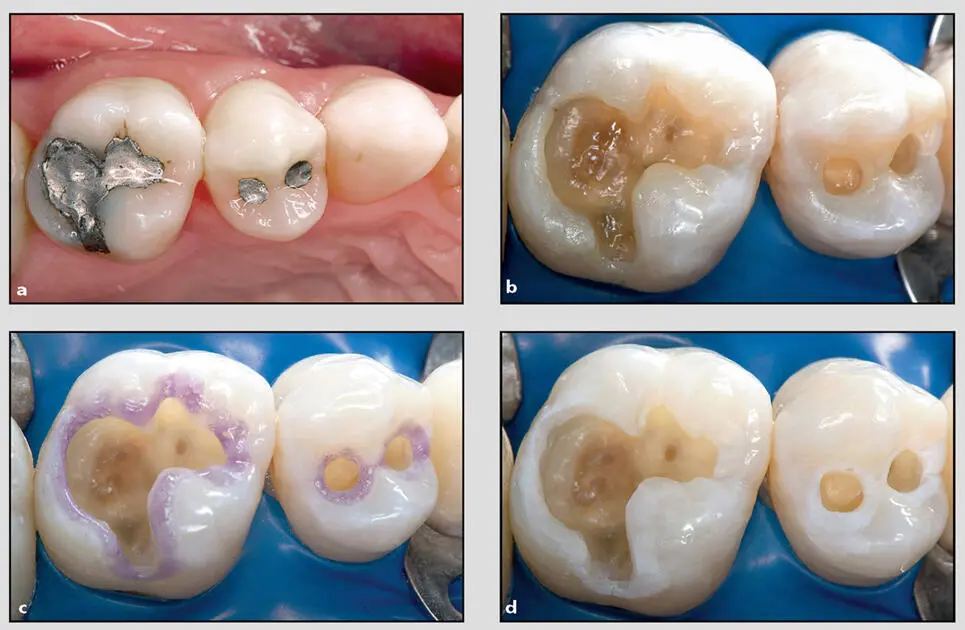
Fig 1-3 (a) Preoperative occlusal view of defective amalgam restorations with recurrent decay on the maxillary right second premolar and first molar. (b) After the preexisting amalgam restorations were removed, the occlusal outline was extended to include carious enamel, provide access to the carious dentin, and remove any residual amalgam staining. (c and d) A selective enamel etch procedure was performed on the prepared and unprepared enamel. A 37.5% phosphoric acid gel (Gel Etchant, Kerr) was applied for 15 seconds, and then the surfaces were rinsed for 5 seconds.
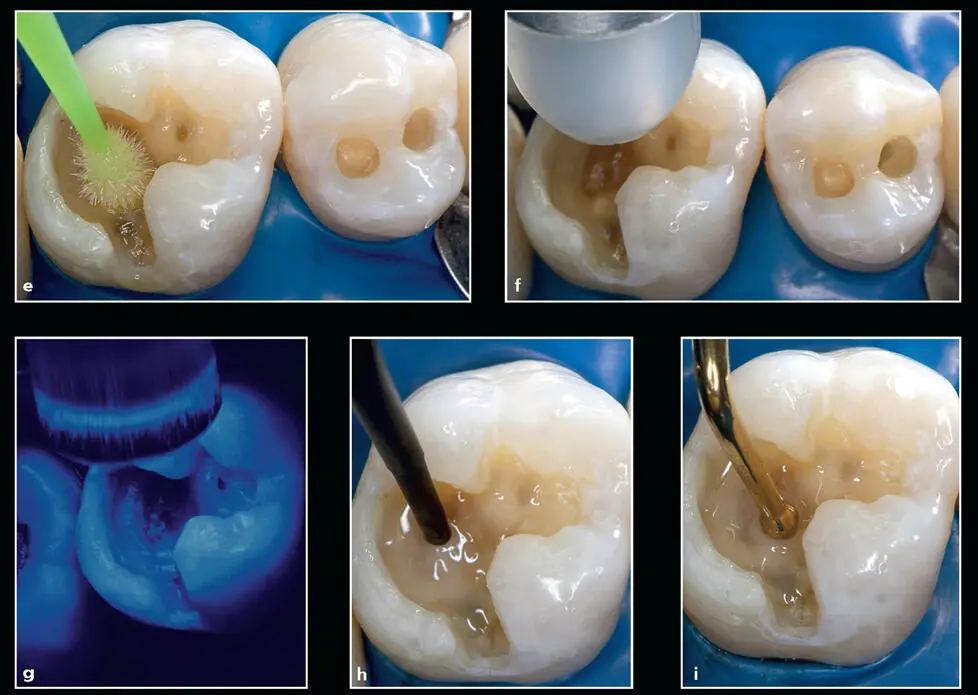
Fig 1-3 (cont) (e to g) A self-etch adhesive (G-aenial Bond, GC America) was placed on the enamel and dentin surfaces with an applicator tip for 10 seconds, air dried for 5 seconds using an Adec warm air tooth dryer, and light cured for 10 seconds. (h and i) An opacious A2-shaded flowable resin composite (G-aenial Universal Flo) was applied to the first molar as a cavity liner with a syringe applicator, uniformly distributed with a ball-tipped instrument (M-1 Ball Burnisher XP, American Eagle), and light cured for 20 seconds.
The lack of evidence-based research and clinical trial data on flowable biomaterials requires clinicians to evaluate the individual mechanical properties of these materials to determine whether their properties are equal or superior to those of existing materials. As the clinical performance of these next-generation flowable materials has improved over time, the research data have concurred. Although no direct correlation has been found between a material’s mechanical and physical properties and its clinical performance, such a correlation might suggest the potential success of a restorative biomaterial for a specific clinical situation. 1 However, clinical longevity for restorations developed with these biomaterials remain to be determined through clinical studies for each specific clinical application ( Figs 1-3and 1-4).
Читать дальше















