| Year |
Prizewinner(s) |
For work on … |
| 1909 |
Emil Theodor Kocher |
Physiology, pathology and surgery of the thyroid gland |
| 1923 |
Frederick Grant Banting and John James Richard Macleod |
Discovery of insulin |
| 1928 |
Adolf Otto Reinhold Windaus |
Constitution of the sterols and their connection with the vitamins |
| 1939 |
Adolf Friedrich and Johann Butenandt |
Sex hormones |
| 1943 |
George de Hevesy |
Use of isotopes as tracers in the study of chemical processes |
| 1946 |
James Batcheller Sumner, John Howard Northrop and Wendell Meredith Stanley |
Discovery that enzymes can be crystallized and prepared in a pure form |
| 1947 |
Carl Ferdinand Cori, Getty Theresa Cori (neé Radnitz) and Bernardo Alberto Houssay |
Discovery of the course of the catalytic conversion of glycogen |
| 1950 |
Edwin Calvin Kendall, Tadeus Reichstein and Philip Showalter Hench |
Discoveries relating to the hormones of the adrenal cortex, their structure and biological effects |
| 1955 |
Vincent du Vigneaud |
Biochemically important sulphur compounds, especially for the first synthesis of a polypeptide hormone |
| 1958 |
Frederick Sanger |
Structures of proteins, especially that of insulin |
| 1964 |
Konrad Bloch and Feodor Lynen |
Discoveries concerning the mechanism and regulation of cholesterol and fatty acid metabolism |
| 1964 |
Dorothy Hodgkin |
X‐ray crystallography, a method used to determine the three‐dimensional structures of molecules, including insulin |
| 1966 |
Charles Brenton Huggins |
Discoveries concerning hormonal treatment of prostatic cancer |
| 1969 |
Derek HR Barton and Odd Hassel |
Development of the concept of conformation and its application in chemistry |
| 1970 |
Bernard Katz, Ulf von Euler and Julius Axelrod |
Discoveries concerning the humoral transmitters in the nerve terminals and the mechanism for their storage, release and inactivation |
| 1971 |
Earl W Sutherland Jr |
Discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones |
| 1977 |
Roger Guillemin, Andrew V Schally and Rosalyn Yalow |
Discoveries concerning peptide hormones in the production in the brain and the development of radioimmunoassay from peptide hormones |
| 1979 |
Allan M Cormack and Godfrey N Hounsfield |
Development of computer‐assisted tomography |
| 1982 |
Sune K Bergström, Bengt I Samuelson and John R Vane |
Discoveries concerning prostaglandins and related biologically active substances |
| 1985 |
Michael S Brown and Joseph L Goldstein |
Discoveries concerning the regulation of cholesterol metabolism |
| 1986 |
Stanley Cohen and Rita Levi‐Montalcini |
Discoveries of growth factors |
| 1992 |
Edmond H Fischer and Edwin G Krebs |
Discoveries concerning reversible protein phosphorylation as a biological regulatory mechanism |
| 1994 |
Alfred G Gilman and Martin Rodbell |
Discovery of G‐proteins and the role of these proteins in signal transduction in cells |
| 2003 |
Peter Agre and Roderick MacKinnon |
Discovery of water channels, and the structural and mechanistic studies of ion channels |
| 2003 |
Paul Lauterbur and Sir Peter Mansfield |
Discoveries concerning magnetic resonance imaging |
| 2010 |
Robert G Edwards |
Development of in vitro fertilisation |
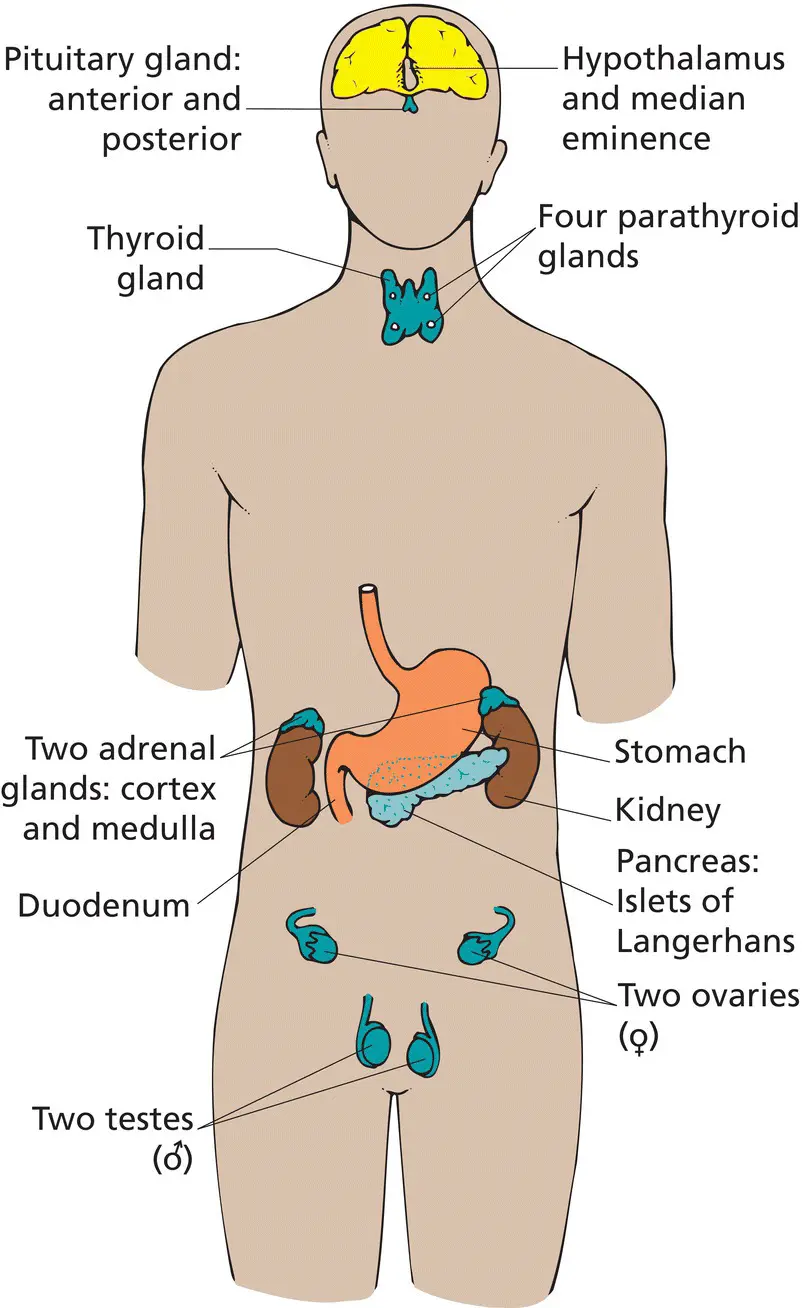
Traditionally, endocrinology has centred on specialized hormone‐secreting organs ( Figure 1.2), largely founded on the ‘endocrine postulates’ of Edward Doisy ( Box 1.3). While the focus of this textbook remains on these organs, virtually all tissues make hormones of some description or, equally relevant, modulate the action of hormones from other sites. All of these different aspects are important for a complete appreciation of endocrinology and its significance.
The hormone must be capable of isolation for its structure to be determined and for synthesis
The hormone must act on specific target cells via a receptor such that excess or deficiency causes a specific phenotype
Endocrine (i.e. hormone‐secreting) cells may exist as distinct glands or be located as single cells within other organs, such as the gastrointestinal tract ( Table 1.2). The chapters in Part 2 are largely organized on this anatomical basis.
Hormones act by binding to specific receptors, either on the surface of or inside the target cell, to initiate a cascade of intracellular reactions, which frequently amplifies the original stimulus and generates a final response. These responses are altered in hormone deficiency or excess: for instance, GH deficiency leads to short stature in children, while excess causes over‐growth (either gigantism or acromegaly; Chapter 5).
| Gland |
Hormone |
Molecular characteristics |
| Hypothalamus/median eminence |
Releasing and inhibiting hormones: |
|
| Thyrotrophin‐releasing hormone (TRH) |
Peptide |
| Somatostatin (SS; inhibits GH) |
Peptide |
| Gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone (GnRH) |
Peptide |
| Corticotrophin‐releasing hormone (CRH) |
Peptide |
| Growth hormone‐releasing hormone (GHRH) |
Peptide |
| Dopamine (inhibits prolactin) |
Tyrosine derivative |
| Anterior pituitary |
Thyrotrophin or thyroid‐stimulating hormone (TSH) |
Glycoprotein |
| Luteinizing hormone (LH) |
Glycoprotein |
| Follicle‐stimulating hormone (FSH) |
Glycoprotein |
| Growth hormone (GH) (also called somatotrophin) |
Protein |
| Prolactin (PRL) |
Protein |
| Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) |
Peptide |
| Posterior pituitary |
Vasopressin [also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH)] |
Peptide |
| Oxytocin |
Peptide |
| Thyroid |
Thyroxine (T4) and tri‐iodothyronine (T3) |
Tyrosine derivatives |
| Calcitonin |
Peptide |
| Parathyroid |
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) |
Peptide |
| Adrenal cortex |
Aldosterone |
Steroid |
| Cortisol |
Steroid |
| Androstenedione |
Steroid |
| Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) |
Steroid |
| Adrenal medulla |
Epinephrine (also called adrenaline) |
Tyrosine derivative |
| Norepinephrine (also called noradrenaline) |
Tyrosine derivative |
| Stomach † |
Gastrin |
Peptide |
| Pancreas (islets of Langerhans) |
Insulin |
Protein |
| Glucagon |
Protein |
| Somatostatin (SS) |
Protein |
| Pancreatic polypeptide |
Protein |
| Ghrelin |
Protein |
| Small and large intestine † |
Secretin |
Protein |
| Glucagon‐like peptide 1 (GLP‐1) |
Protein |
| Liver |
Insulin‐like growth factor I (IGF‐I) |
Protein |
| Ovary |
Oestrogens |
Steroid |
| Progesterone |
Steroid |
| Testis |
Testosterone |
Steroid |
*The distinction between peptide and protein is somewhat arbitrary. Shorter than 50 amino acids is termed a peptide in this table.