Big data is distinguished by its exceptional characteristics with various dimensions. Figure 1.2illustrates various dimensions of big data. The first of its dimensions is the size of the data. Data size grows partially because the cluster storage with commodity hardware has made it cost effective. Commodity hardware is a low cost, low performance, and low specification functional hardware with no distinctive features. This is referred by the term “volume” in big data technology. The second dimension is the variety, which describes its heterogeneity to accept all the data types, be it structured, unstructured, or a mix of both. The third dimension is velocity, which relates to the rate at which the data is generated and being processed to derive the desired value out of the raw unprocessed data. The complexities of the data captured pose a new opportunity as well as a challenge for today’s information technology era.
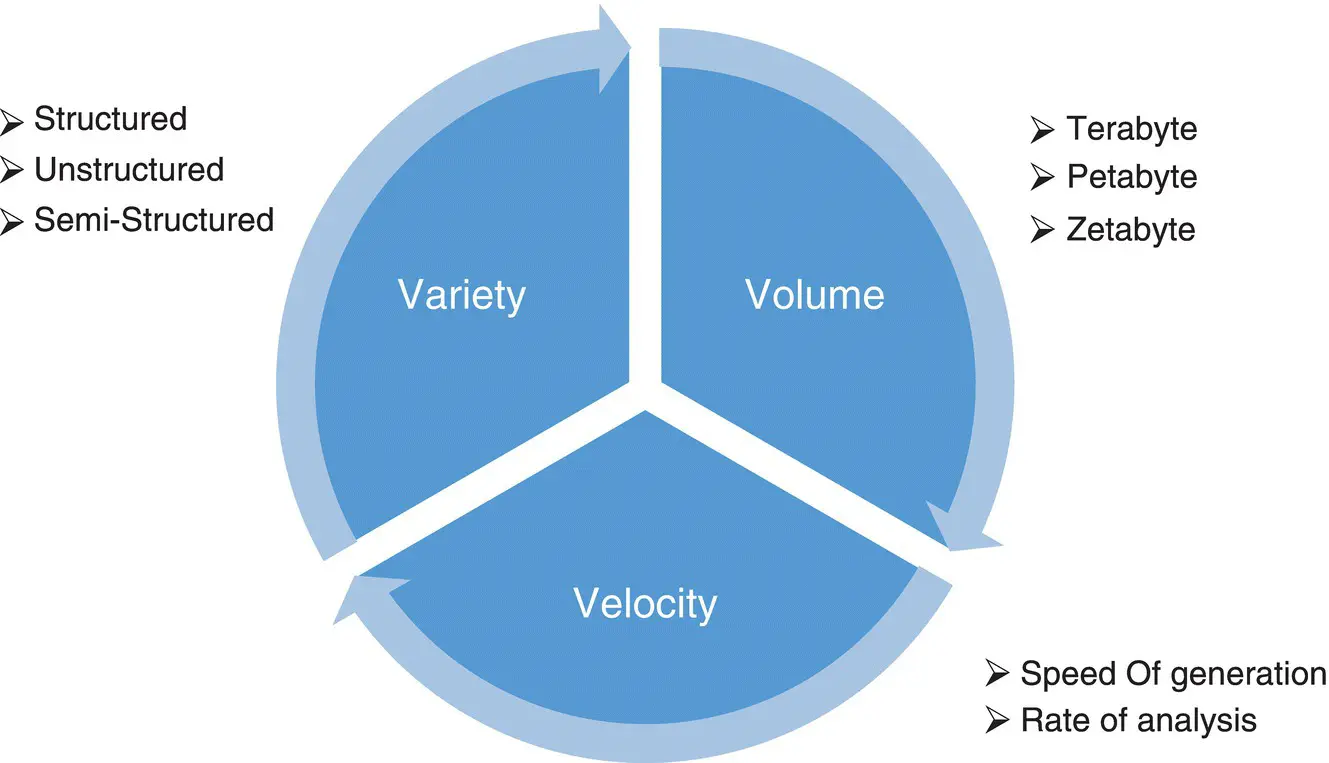
Figure 1.2 3 Vs of big data.
Data generated and processed by big data are continuously growing at an ever increasing pace. Volume grows exponentially owing to the fact that business enterprises are continuously capturing the data to make better and bigger business solutions. Big data volume measures from terabytes to zettabytes (1024 GB = 1 terabyte; 1024 TB = 1 petabyte; 1024 PB = 1 exabyte; 1024 EB = 1 zettabyte; 1024 ZB = 1 yottabyte). Capturing this massive data is cited as an extraordinary opportunity to achieve finer customer service and better business advantage. This ever increasing data volume demands highly scalable and reliable storage. The major sources contributing to this tremendous growth in the volume are social media, point of sale (POS) transactions, online banking, GPS sensors, and sensors in vehicles. Facebook generates approximately 500 terabytes of data per day. Every time a link on a website is clicked, an item is purchased online, a video is uploaded in YouTube, data are generated.
With the dramatic increase in the volume of data, the speed at which the data is generated also surged up. The term “velocity” not only refers to the speed at which data are generated, it also refers to the rate at which data is processed and analyzed. In the big data era, a massive amount of data is generated at high velocity, and sometimes these data arrive so fast that it becomes difficult to capture them, and yet the data needs to be analyzed. Figure 1.3illustrates the data generated with high velocity in 60 seconds: 3.3 million Facebook posts, 450 thousand tweets, 400 hours of video upload, and 3.1 million Google searches.
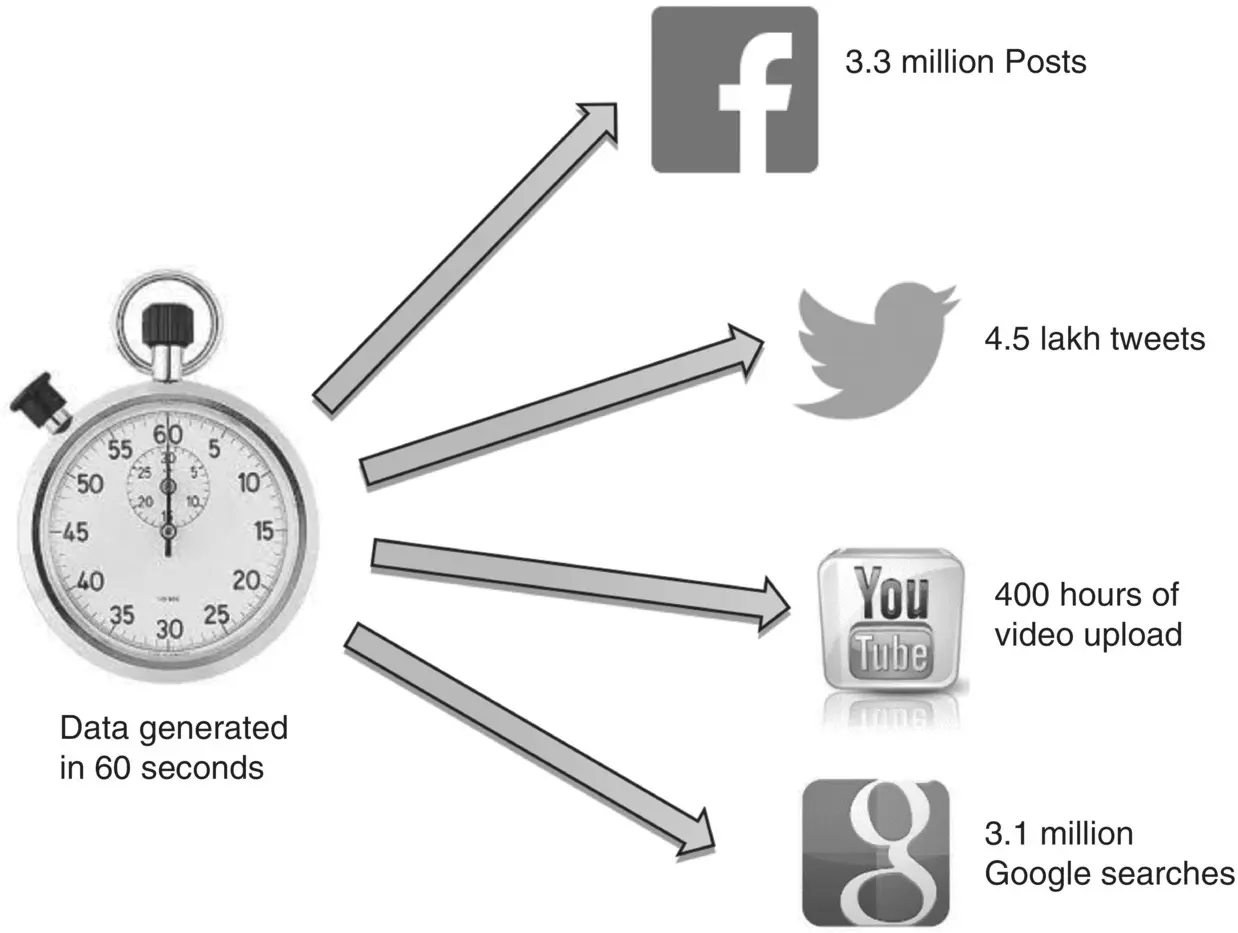
Figure 1.3 High‐velocity data sets generated online in 60 seconds.
Variety refers to the format of data supported by big data. Data arrives in structured, semi‐structured, and unstructured format. Structured data refers to the data processed by traditional database management systems where the data are organized in tables, such as employee details, bank customer details. Semi‐structured data is a combination of structured and unstructured data, such as XML. XML data is semi‐structured since it does not fit the formal data model (table) associated with traditional database; rather, it contains tags to organize fields within the data. Unstructured data refers to data with no definite structure, such as e‐mail messages, photos, and web pages. The data that arrive from Facebook, Twitter feeds, sensors of vehicles, and black boxes of airplanes are all unstructured, which the traditional database cannot process, and here is when big data comes into the picture. Figure 1.4represents the different data types.

Figure 1.4 Big data—data variety.
Multiple disparate data sources are responsible for the tremendous increase in the volume of big data. Much of the growth in data can be attributed to the digitization of almost anything and everything in the globe. Paying E‐bills, online shopping, communication through social media, e‐mail transactions in various organizations, a digital representation of the organizational data, and so forth, are some of the examples of this digitization around the globe.
Sensors: Sensors that contribute to the large volume of big data are listed below.Accelerometer sensors installed in mobile devices to sense the vibrations and other movements.Proximity Sensors used in public places to detect the presence of objects without physical contact with the objects.Sensors in vehicles and medical devices.
Health care: The major sources of big data in health care are:Electronic Health Records (EHRs) collect and display patient information such as past medical history, prescriptions by the medical practitioners, and laboratory test results.Patient portals permit patients to access their personal medical records saved in EHRs.Clinical data repository aggregates individual patient records from various clinical sources and consolidates them to give a unified view of patient history.
Black box: Data are generated by the black box in airplanes, helicopters, and jets. The black box captures the activities of flight, flight crew announcements, and aircraft performance information. Figure 1.5 Sources of big data.
Web data: Data generated on clicking a link on a website is captured by the online retailers. This is perform click stream analysis to analyze customer interest and buying patterns to generate recommendations based on the customer interests and to post relevant advertisements to the consumers.
Organizational data: E‐mail transactions and documents that are generated within the organizations together contribute to the organizational data. Figure 1.5illustrates the data generated by various sources that were discussed above.
1.6 Different Types of Data
Data may be machine generated or human generated. Human‐generated data refers to the data generated as an outcome of interactions of humans with the machines. E‐mails, documents, Facebook posts are some of the human‐generated data. Machine‐generated data refers to the data generated by computer applications or hardware devices without active human intervention. Data from sensors, disaster warning systems, weather forecasting systems, and satellite data are some of the machine‐generated data. Figure 1.6represents the data generated by a human in various social media, e‐mails sent, and pictures that were taken by them and machine data generated by the satellite.
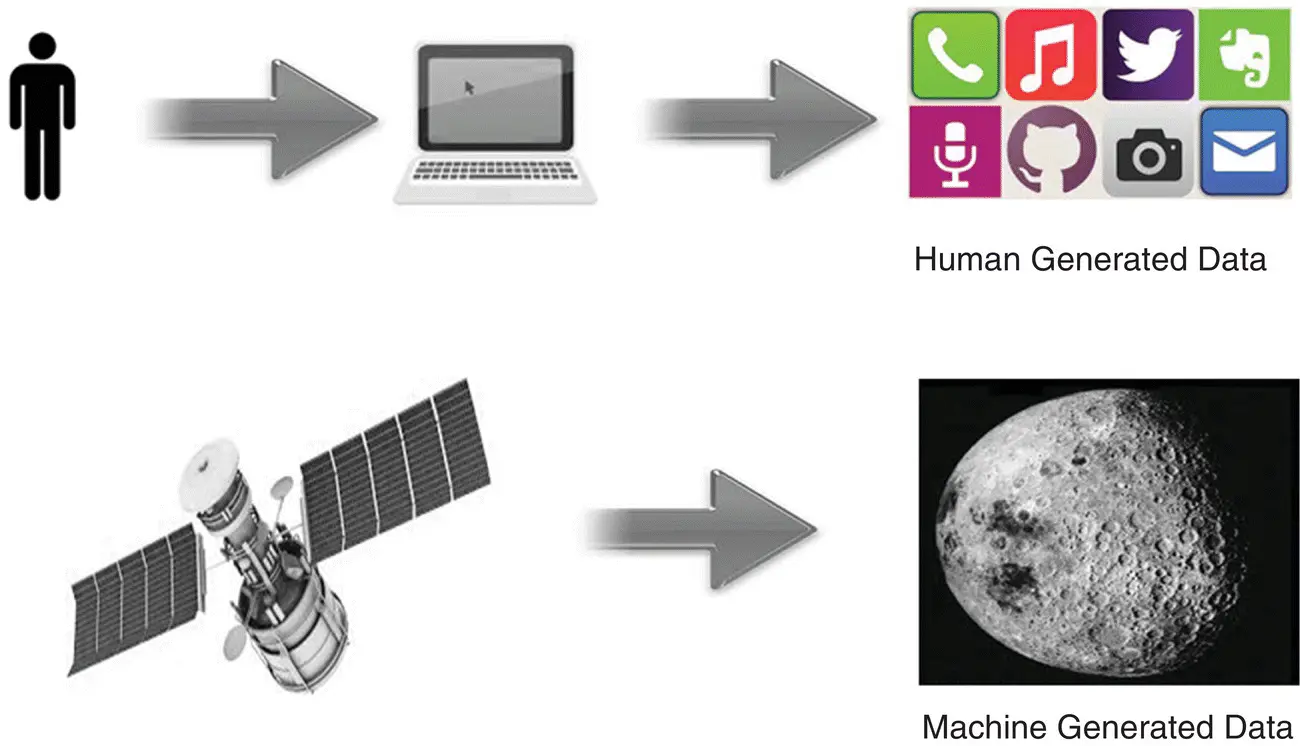
Figure 1.6 Human‐ and machine‐generated data.
The machine‐generated and human‐generated data can be represented by the following primitive types of big data:
Structured data
Unstructured data
Semi‐structured data
Data that can be stored in a relational database in table format with rows and columns is called structured data. Structured data often generated by business enterprises exhibits a high degree of organization and can easily be processed using data mining tools and can be queried and retrieved using the primary key field. Examples of structured data include employee details and financial transactions. Figure 1.7shows an example of structured data, employee details table with EmployeeID as the key.
Читать дальше








![Алексей Благирев - Big data простым языком [litres]](/books/416853/aleksej-blagirev-big-data-prostym-yazykom-litres-thumb.webp)







