Remember, improving a process and achieving patient or customer satisfaction are the underlying targets of the QI project. Developing CTQ requirements allows us to define the expectations of the customer (i.e. quality from the customer’s perspective), and set the goal and aims of the project. Once we understand what is critical for the customer, we can
Define our current performance.
Define the gap in performance and understand the magnitude of the problem.
Set the scope for the project.
Define the goals of the improvement initiative.
Set the targets we need to achieve.
Because patients, providers, and staff are the customers of our healthcare processes, CTQs are the critical patients’ requirements, critical physicians’ requirements, or the critical staff’s requirementswhose performance standards or specifications must be met in order to meet their expectations.
THE CRITICAL‐TO‐QUALITY TREE
From the Voice of the Customer, the CTQs can be developed using a tree diagram. The CTQ treeis a diagram‐based tool used to organize identified specifications of an outcome’s attributes and requirements that the customer expects.
A tree diagram provides the clarity and structure needed to develop CTQs and focus our improvement efforts. To create a CTQ tree, follow these six steps:
1 Define the customer. First, find the customer of your process.
2 Get the Voice of the Customer. Use interviews, surveys, or any other means to get the customer’s needs and expectations. Record the VOC statements. Make sure you write down the attributes and requirements of each outcome they expect.
3 Aggregate the VOC statements into families with similar meaning. Combine the statements from the VOC according to categories or topics. Group ideas or statements with similar meaning. Topic categories could be: “expectations of the clinic environment”; “quality of clinical care”; “staff and physician interaction”; “the registration process” and so on. You may want to repeat these steps for each customer segment.
4 For each family, create the drivers. For each family or group of statements, create the “drivers” or single word or short sentence that defines the group. Ask yourself, “What do all these statements have in common? What attributes or requirements of the outcome are customers referring to?” Use the word or sentence that best describes the idea.
5 Develop the specifications or CTQs. For each driver or group of statements, drill down to the specifics. What does the driver mean to the customer (patient, staff, provider)? What are the technical characteristics? How can it be measured? What are the specifics? How can you operationalize it in the clinical setting? Identify one or more specific and measurable characteristics for each driver, that the process must satisfy to provide the high‐quality care or level of service the customer expects. You may need to go back to the patients or customer groups and clarify the exact meaning and specifics for each driver.
6 Validate the CTQ tree. Validate the CTQs (attributes and requirements) with the customer. Ask the customers if this is what they mean and ask them if they agree with your characterization of their needs and expectations.
Once you and your team create the CTQ requirements, you will have a better chance to define metrics and focus the QI project on specifics. Project metrics are key to evaluating the success of the project in meeting the patient or customer’s expectations.
Example: Patient Satisfaction with UI Health Outpatient Care Center
If our QI project aimed to improve patient satisfaction with UI Health Outpatient Care Center, we would first need to define what are the attributes and requirements of a visit to the Center that deliver the experience the patient expects. The first step would be to get the Voice of the Customer. Remember, these statements are usually too broad and lack specificity to be used as guidance in our improvement efforts. Once we got the VOC, we would develop the CTQs, or specifications that are going to make our patients’ statements meaningful, specific, and more importantly, measurable. To do this, we would group the VOC statements with similar meaning into families and then ask ourselves, “What do these statements have in common?” We would then summarize each group or family of statements into single‐word descriptors or “drivers” of patient satisfaction. We may need to dig deeper within the VOC statements to find specifics, or go back to patients to ask questions about the drivers. This would allow us to create one or more CTQ for each driver. The CTQs are the specifications for the attributes and requirements of the outcome the patient expects. In the UIH clinic example, CTQs would be: “greeted with a smile”; “registered within 5 minutes”; “accurate information”; “seen by provider within 30 minutes of my arrival”; and “availability of guest features.” The great thing about a CTQ is that it can be measured to establish our current performance, and audited to assess the degree to which we are continuing to achieve patient satisfaction (see Figure 8‐4).
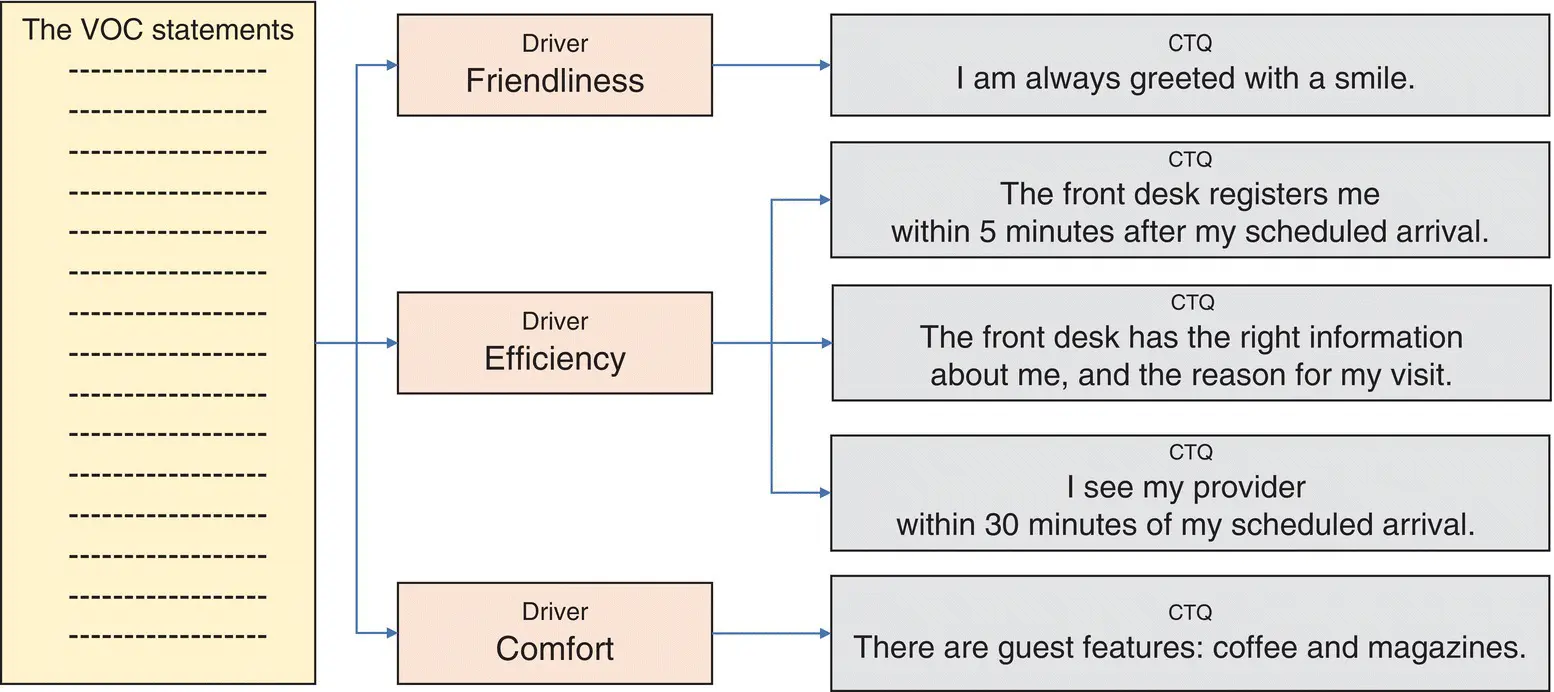
FIGURE 8‐4The attributes and requirements for patient satisfaction (CTQs) at UI Health Outpatient Care Center.
Example: Improving the Organization of Medical Supplies in the EDRR
Assume you wanted to improve the organization of medical supplies in the emergency department’s resuscitation room (EDRR). First, you would need to define what attributes and requirements characterize a well‐organized EDRR. What does “well‐organized” really mean for providers and staff (the customer!)? How do they define it? What are the specific characteristics of the layout, organization of cabinets, and shelving that make it so? Following the steps outlined before, we would collect the Voice of the Customer, find the “drivers,” and, with a bit more work, develop one or more CTQs for each driver. It is always a good idea to validate the CTQs with front line providers and staff (see Figure 8‐5).
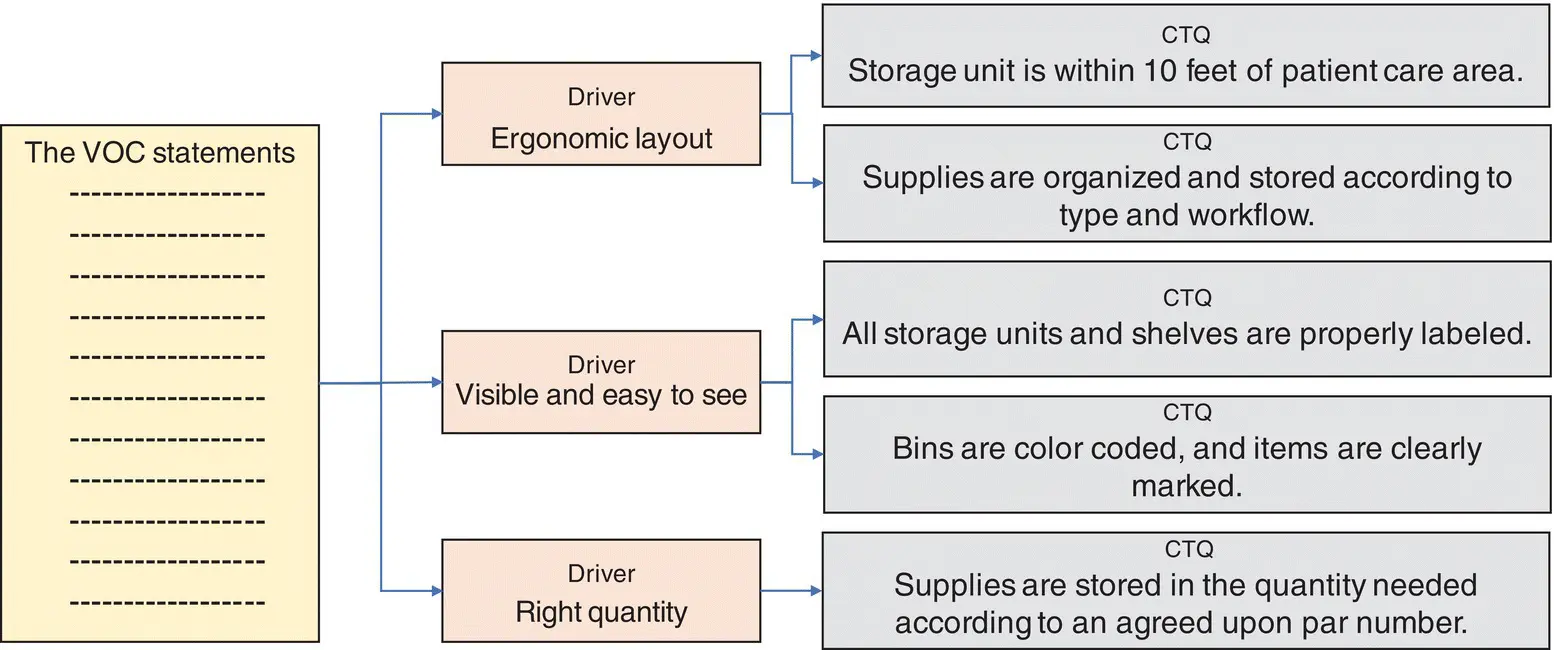
FIGURE 8‐5The attributes and requirements for staff and provider satisfaction (CTQs) with the organization of clinical supplies in the ED’s resuscitation room.
EXERCISE: CTQS FOR THE NEW WOMEN’S CENTER
The new Women’s Center at Lake Hospital had been up and running for the last three months. Dr. Sonia Watson decided it was time to launch a couple of improvement projects to improve patient care. She was eager to provide the community with the kind of service they had long waited for and deserved. For her first QI project, she decided to focus her efforts on mammographies, specifically to improve the appointment, registration, and follow‐up processes. Dr. Watson and her staff held several focus groups within the community to better understand their patients’ needs and expectations, get feedback from previous experiences, and identify critical requirements of patient satisfaction. The team recorded the following statements from their interviews:
“When I go to a clinic, it’s really important for me to have staff that is kind and understanding.”
“Mammograms are no fun! A smile at the other end is always welcomed.”
“I really appreciate it when I receive a timely phone call from the doctor with my test results; ideally I should get it within a day or two after my scheduled appointment.”
Читать дальше














