Wetland restoration focuses on the construction of water conservation and protection of riverine wetlands, as they provide shelter to aquatic animals and plants. Water quality improvement, biodiversity maintenance, flood abatement, and socioeconomic uplift are among the additions to the ecosystem [6]. Another important future aspect of wetland restoration is its contribution to controlling global climate change. About 6% of the world's land is covered by wetlands, while approximately 12% of the global carbon pool is known to exist in these wetlands; thus they play a vital role in the global carbon cycle [15]. Climate change must also be addressed during the implementation and practice of restoration projects, with future ecosystem management policies as an inevitable domain of climate change and mitigation processes.

Figure 3.3 A 2.6 km section of Nippersink Creek (Illinois, US) is filled in to make farming more efficient.
Source: Reproduced with permission from Zedler, Joy B. (2000). “Progress in wetland restoration ecology.” Trends in Ecology & Evolution 15: 402–407. ©2000, Elsevier.
On the other hand, there has been a decline in several ecosystem services resulting in severe alteration or complete disappearance of wetlands in recent years. For instance, alteration of habitat by a multistage dam constructed on the Min River in China led to a rapid decrease in the population of S. Prenanti 8 [46]. A very common example is floodplains, which can include one or more types of wetlands, primarily including submerged grasslands, wet meadows, forests, woodlands, and shrublands. Degradation of these ecosystems can be correlated with the deterioration of freshwater biodiversity due to habitat alteration, species migration, pollution, and flood‐control mechanisms. The disappearance of natural floodplains and rapid extinction of aquatic and riparian species pose a worldwide threat to the biodiversity of these systems. Perseverance of existing floodplains and restoration of hydrological ecosystems, riparian vegetation, and sediment transportation require urgent attention to retain ecological integrity and sustainability.
3.4.4 Ecological Engineering in Soil Restoration and Agriculture
Agriculture is influenced by an array of biotic and abiotic stresses; a strategic technique is required to address plant health and issues that affect productivity. The integrity and conservation of the agro‐atmosphere is critical for sustainable agriculture. Extensive exploitation of ecosystems to enhance productivity can affect agro‐ecosystems via erosion of soil, contamination of water, loss of biodiversity, pest issues, and disruption in the usual flow of the surrounding ecology in order to allow safe food manufacturing. The role of ecological engineering is to assimilate soil and pest management schemes with conventional agricultural practices that benefit both the ecosystem and productivity. It is a combination of agricultural knowledge, crop economics, and ecology applied to development and restoration to retain an overall sustainable agricultural ecosystem that has been disturbed by human activities.
The prime focus of management schemes is to reduce the use of chemical pesticides and overuse of fertilizers and agricultural chemicals that cause environmental pollution that further can enter the food chain; and also to minimize drug resistance and resurgence in pests and bugs over time. Replacing these detrimental chemicals with biofertilizers such as mycorrhiza improves the soil health, helps plants to uptake micro/macro nutrients from the soil, and supplies these nutrients at an optimum level that inhibits the growth of pests. Thus ecological engineering uses traditional vegetation management practices to control the pests without damaging soil health. A collective eco‐friendly approach adopted by the farming community can successfully implement this technology to manage the pest population and build up the biota by enriching the organic matter content in the soil.
To support a good agricultural system, the soil ecosystem must support the growth and sustainability of the land. However, soil erosion interrupts agriculture in many parts of the world. Although soil erosion is a naturally occurring process, it is accelerated by anthropogenic interventions into Nature and landscapes. Improper management of agricultural land also contributes to soil erosion.
Land consolidation is a tool for creating sustainable rural agriculture and improving the efficiency of cultivation, which ultimately helps develop the rural cultivation culture in countries like the Czech Republic (CR) [43]. Land consolidation is a process of systematically reallocating or redistributing fragmented agricultural land and properly arranging the shape and size of these lands in rural areas [23]. At the same time, land consolidation contributes to the improvement of environmental status, protects soil, provides ecological stability, helps with water management, and controls flooding and erosion. Soil degradation and the urgent need to conserve soil have been the most‐discussed topics in the last few decades. Land consolidation can improve soil stability when proper management policies are implemented. However, soil management practices (in terms of agricultural soil) such as till age 9 may have negative consequences on the soil biota since they can lead to soil decomposition and the mineralization of organically bound nutrients. Therefore, these practices must be devised wisely to minimize the adverse impact on soil quality while providing agricultural benefits. In this context, tillage is often combined with other practices like mulches and cover crops, whereas enrichment with organic wastes, compost, and biochar favors soil fertility and biota. In addition, conservation of soil's natural and biological efficiency improves and maintains the soil's organic matter content, thus facilitating soil preservation.
At this point, ecological engineering can play a pivotal role that combines management practices with soil biota enhancement designs to achieve maximum crop yield, improve overall service, and maintain sustainable biodiversity with maximum yield ( Figure 3.4). A compromise between agricultural yield and sustainability can be achieved by appropriate manipulation of ecosystem processes. Figure 3.4depicts a direct correlation between land‐use intensity and yield. It suggests that yield is directly proportional to the magnitude of land‐use intensity. The yield is maximum under intensive management when the external source inputs are highest. Soil ecological engineering in harmony with naturally occurring biological processes is known to replace external inputs by either maintaining yields with fewer external inputs or increasing yields without simultaneous increment in external inputs.
Several other fields have developed ecological engineering practices, such as desert forest restoration, ocean and aquatic life restoration, forest restoration, urban reconciliation of living roofs and walls, all kinds of riparian ecosystem restoration, arctic megafaunal restoration, etc. With the aim of mitigating past adverse impacts and creating novel projects to benefit sustainable ecological growth in the near future, improved environmental policies using ecological engineering approaches can create awareness at the local, regional, and international level regardless of the field where these policies have been adopted.
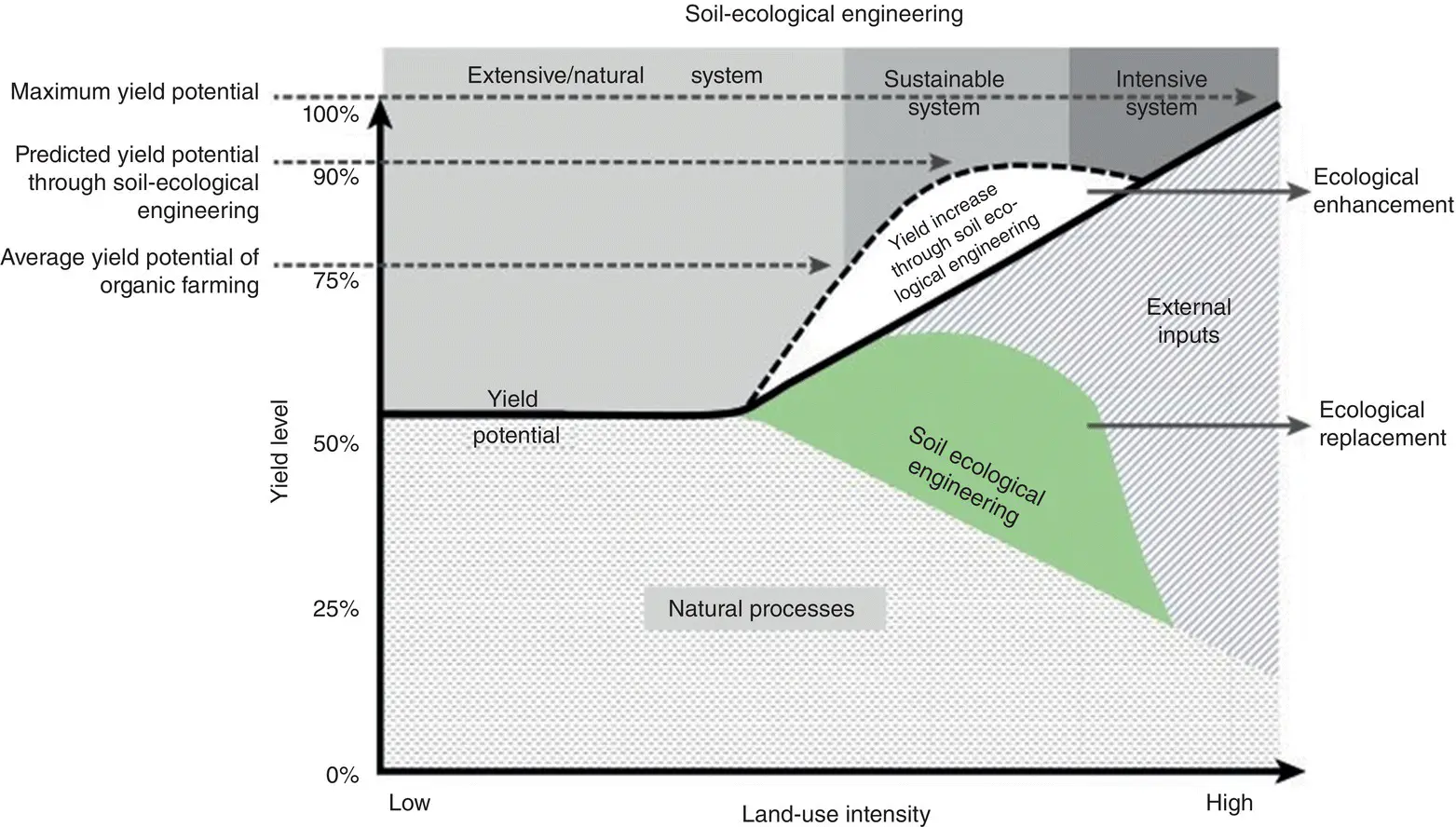
Figure 3.4 Conceptual model showing the contribution of external resource inputs and natural biological processes to an ecosystem function (yield), depending on land‐use intensity.
Читать дальше














