8 Chapter 21Table 21.1 Computed and exp. f p.Table 21.2 Extracted RLC Lparameters.Table 21.3 Frequency response of the composite permittivity–permeability func...
1 Chapter 2 Figure 2.1 Delayed oscillation as a wave motion‐initial oscillation v(t) at ... Figure 2.2 Double periodic variations of wave motion. Figure 2.3 Wave motion as a motion of constant phase surface. It is shown as... Figure 2.4 The ω‐β dispersion diagram of nondispersive wave. Figure 2.5 Cross‐section of a few two‐conductor transmission lines. Figure 2.6 RLCG lumped circuit model of a transmission line. Figure 2.7 Equivalent lumped circuit of a transmission line with a shunt cur... Figure 2.8 Transmission line circuit. The distance x is measured from the so... Figure 2.9 Load connections to a source. Figure 2.10 The multisection transmission line. Figure 2.11 A shunt current source at the junction of two‐line sections. Figure 2.12 A series voltage source at the junction of two‐line sections. Figure 2.13 Nonuniform transmission line.
2 Chapter 3 Figure 3.1 Two‐port network to determine [Z] and [Y] parameters. Figure 3.2 Lumped T‐network. Figure 3.3 A transmission line section. Figure 3.4 Two‐port network for transmission parameter. Figure 3.5 Cascading of two networks to get one equivalent network. Figure 3.6 Series impedance. Figure 3.7 Shunt admittance. Figure 3.8 Basic networks. Figure 3.9 Two‐port network for evaluation of S‐parameter. Figure 3.10 A section of the multiport network. Port is shown extended with ... Figure 3.11 N‐port network showing power variables (a i, b i) in terms of volt... Figure 3.12 At the i thport, the load is terminated in port characteristic i... Figure 3.13 N‐port network showing phase‐shifting property. Figure 3.14 A two‐port network with arbitrary termination. Figure 3.15 Network of series impedance. Figure 3.16 Network of shunt admittance. Figure 3.17 A transmission line circuit with an arbitrary characteristic imp... Figure 3.18 Network for Z‐parameter. Figure 3.19 Network for [ABCD] parameter. Figure 3.20 Calibration process in the measurement of S‐parameters of a devi... Figure 3.21 Nature of normal (positive) dispersion. Figure 3.22 Nature of anomalous (negative) dispersion. Figure 3.23 Description of phase and group velocities of a forward‐moving mo... Figure 3.24 Formation of a wave‐packet. Figure 3.25 ω − β diagram to get phase and group velocities. Figure 3.26 Nature of dispersion on (ω − β) the diagram. Figure 3.27 Shunt inductor loaded line and its characteristics. Figure 3.28 Lumped elements models of short transmission line sections and d... Figure 3.29 Inductor loaded CL‐line. Figure 3.30 Series capacitor loaded LC‐line.
3 Chapter 4 Figure 4.1 The unit vector 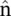 is in the direction normal to the surface. Figure 4.2 Response of nonlinear medium showing generation of harmonics. Figure 4.3 Inhomogeneous medium showing a step variation of relative permitt... Figure 4.4 The crystal axes (ξ, η, ς) and the physical axes (x, y, z) of a p... Figure 4.5 Classification of bianisotropic and bi‐isotropic materials. Figure 4.6 Circuit model, parameters of a dielectric medium. Figure 4.7 Circuit model and frequency response of lossy magnetic material.... Figure 4.8 Surfaces and volume used in the integral form of Maxwell equation... Figure 4.9 TEM mode wave in an unbounded medium. Figure 4.10 Type of polarizations. Figure 4.11 Polarizing device described by Jones matrix. Figure 4.12 The (y–z) and rotated (e 1–e 2) Coordinate systems. Figure 4.13 Wave propagation uniaxial media. Figure 4.14 Dispersion diagrams of the wave propagating in the z‐direction i... Figure 4.15 Dispersion diagrams in the uniaxial anisotropic medium.
is in the direction normal to the surface. Figure 4.2 Response of nonlinear medium showing generation of harmonics. Figure 4.3 Inhomogeneous medium showing a step variation of relative permitt... Figure 4.4 The crystal axes (ξ, η, ς) and the physical axes (x, y, z) of a p... Figure 4.5 Classification of bianisotropic and bi‐isotropic materials. Figure 4.6 Circuit model, parameters of a dielectric medium. Figure 4.7 Circuit model and frequency response of lossy magnetic material.... Figure 4.8 Surfaces and volume used in the integral form of Maxwell equation... Figure 4.9 TEM mode wave in an unbounded medium. Figure 4.10 Type of polarizations. Figure 4.11 Polarizing device described by Jones matrix. Figure 4.12 The (y–z) and rotated (e 1–e 2) Coordinate systems. Figure 4.13 Wave propagation uniaxial media. Figure 4.14 Dispersion diagrams of the wave propagating in the z‐direction i... Figure 4.15 Dispersion diagrams in the uniaxial anisotropic medium.
4 Chapter 5 Figure 5.1 Normal incidence of TM‐polarized plane wave at the interface of t... Figure 5.2 Oblique incidence of a plane wave with TE‐polarization at the int... Figure 5.3 Oblique incidence of a plane wave with TM‐polarization at the int... Figure 5.4 Dispersion diagrams of refracted waves. Figure 5.5 Oblique incidence of plane wave at three different angles of inci... Figure 5.6 Plane‐wave incident on a dielectric slab. Figure 5.7 Electrical grouping of the materials media in the (μ r, ε r)‐plane.... Figure 5.8 RH and LH‐coordinate systems for the DPS and DNG media. Figure 5.9 Refraction of the obliquely incident EM‐wave at the interface of ... Figure 5.10 Circuit models of four kinds of the medium on the (μ, ε)‐plane.... Figure 5.11 EM‐wave propagation through the DNG and composite DPS‐DNG slabs.... Figure 5.12 Creation of image using wave optics. Figure 5.13 Ray diagram of a DNG flat lens. Figure 5.14 Doppler effect in the DPS and DNG media. The source receding the... Figure 5.15 Cerenkov radiation in DPS and DNG media. Figure 5.16 Composite surface absorber. Figure 5.17 Free space matched lossy DNG absorber.
5 Chapter 6 Figure 6.1 Several kinds of electric polarization and magnetization in the m...Figure 6.2 1D and 2D artificial media created by spherical inclusions in low...Figure 6.3 Metallic spherical and disk inclusions in low permittivity dielec...Figure 6.4 Metallic strips, conducting rods and parallel‐plate waveguide inc...Figure 6.5 A heterogeneous mixture and equivalent circuit models of the limi...Figure 6.6 Comparisons of several mixture formulae against the FDTD and expe...Figure 6.7 Polarization and depolarization process in a dielectric material....Figure 6.8 Relaxation type Debye dispersion behaviors of a dielectric materi...Figure 6.9 Harmonic oscillator model of resonance type Lorentz polarization ...Figure 6.10 Dispersion behavior of a hypothetical material showing two relax...Figure 6.11 Interfacial polarization at the interface of two‐layered lossy d...Figure 6.12 Series and parallel equivalent circuits of the relaxation and no...Figure 6.13 Circuit model and relaxation response of Debye material.Figure 6.14 Circuit model of the two‐layered inhomogeneous medium under the ...Figure 6.15 Series resonant circuit for modeling of Lorentz type material.Figure 6.16 Response of Debye model for FR‐4 substrate [J.59].Figure 6.17 8 terms Debye models for relative permittivity and loss‐tangent....Figure 6.18 Wire loaded and loop loaded magneto‐dielectric substrates.
6 Chapter 7Figure 7.1 Generation of TM zand TE zmodes by the longitudinal field or curr...Figure 7.2 Hybrid mode fields in the layered medium.Figure 7.3 The EM‐field at (a) PEC surface (b) PMC surface (c) interface of ...Figure 7.4 A parallel‐plate waveguide.Figure 7.5 Rectangular waveguide constructed using EW and MWs. “m” is the mo...Figure 7.6 Wave impedance behavior and inductive surface.Figure 7.7 Field and current distribution of 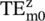 modes (m = 1,2,3).Figure 7.8 Field lines of
modes (m = 1,2,3).Figure 7.8 Field lines of 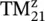 mode.Figure 7.9 Conductor loss for the
mode.Figure 7.9 Conductor loss for the 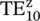 and higher‐order modes.Figure 7.10 Current distributions for the TE 10mode.Figure 7.11 Longitudinal current distributions for the TM z 01,
and higher‐order modes.Figure 7.10 Current distributions for the TE 10mode.Figure 7.11 Longitudinal current distributions for the TM z 01, 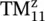 , and
, and 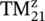 modes...Figure 7.12 Conductor‐backed dielectric surface wave waveguide.Figure 7.13 Lumped element circuit model of the waveguide modes.Figure 7.14 TRM applied to the rectangular waveguide.Figure 7.15 Dielectric loaded rectangular waveguide.Figure 7.16 Slab waveguide supporting even and odd surface wave modes.Figure 7.17 TE zEven and odd modes for slab waveguide.Figure 7.18 Double‐layer slow‐wave structure.Figure 7.19 Synthetic SIW created through two rows of metalized via holes.Figure 7.20 Dispersion and loss characteristic of the SIW.Figure 7.21 Modeling of HM‐SIW.Figure 7.22 Dispersion and attenuation characteristics of ‐TE 0.5, 0‐mode HM‐...
modes...Figure 7.12 Conductor‐backed dielectric surface wave waveguide.Figure 7.13 Lumped element circuit model of the waveguide modes.Figure 7.14 TRM applied to the rectangular waveguide.Figure 7.15 Dielectric loaded rectangular waveguide.Figure 7.16 Slab waveguide supporting even and odd surface wave modes.Figure 7.17 TE zEven and odd modes for slab waveguide.Figure 7.18 Double‐layer slow‐wave structure.Figure 7.19 Synthetic SIW created through two rows of metalized via holes.Figure 7.20 Dispersion and loss characteristic of the SIW.Figure 7.21 Modeling of HM‐SIW.Figure 7.22 Dispersion and attenuation characteristics of ‐TE 0.5, 0‐mode HM‐...
Читать дальше

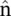 is in the direction normal to the surface. Figure 4.2 Response of nonlinear medium showing generation of harmonics. Figure 4.3 Inhomogeneous medium showing a step variation of relative permitt... Figure 4.4 The crystal axes (ξ, η, ς) and the physical axes (x, y, z) of a p... Figure 4.5 Classification of bianisotropic and bi‐isotropic materials. Figure 4.6 Circuit model, parameters of a dielectric medium. Figure 4.7 Circuit model and frequency response of lossy magnetic material.... Figure 4.8 Surfaces and volume used in the integral form of Maxwell equation... Figure 4.9 TEM mode wave in an unbounded medium. Figure 4.10 Type of polarizations. Figure 4.11 Polarizing device described by Jones matrix. Figure 4.12 The (y–z) and rotated (e 1–e 2) Coordinate systems. Figure 4.13 Wave propagation uniaxial media. Figure 4.14 Dispersion diagrams of the wave propagating in the z‐direction i... Figure 4.15 Dispersion diagrams in the uniaxial anisotropic medium.
is in the direction normal to the surface. Figure 4.2 Response of nonlinear medium showing generation of harmonics. Figure 4.3 Inhomogeneous medium showing a step variation of relative permitt... Figure 4.4 The crystal axes (ξ, η, ς) and the physical axes (x, y, z) of a p... Figure 4.5 Classification of bianisotropic and bi‐isotropic materials. Figure 4.6 Circuit model, parameters of a dielectric medium. Figure 4.7 Circuit model and frequency response of lossy magnetic material.... Figure 4.8 Surfaces and volume used in the integral form of Maxwell equation... Figure 4.9 TEM mode wave in an unbounded medium. Figure 4.10 Type of polarizations. Figure 4.11 Polarizing device described by Jones matrix. Figure 4.12 The (y–z) and rotated (e 1–e 2) Coordinate systems. Figure 4.13 Wave propagation uniaxial media. Figure 4.14 Dispersion diagrams of the wave propagating in the z‐direction i... Figure 4.15 Dispersion diagrams in the uniaxial anisotropic medium.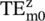 modes (m = 1,2,3).Figure 7.8 Field lines of
modes (m = 1,2,3).Figure 7.8 Field lines of 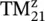 mode.Figure 7.9 Conductor loss for the
mode.Figure 7.9 Conductor loss for the 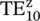 and higher‐order modes.Figure 7.10 Current distributions for the TE 10mode.Figure 7.11 Longitudinal current distributions for the TM z 01,
and higher‐order modes.Figure 7.10 Current distributions for the TE 10mode.Figure 7.11 Longitudinal current distributions for the TM z 01, 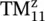 , and
, and 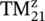 modes...Figure 7.12 Conductor‐backed dielectric surface wave waveguide.Figure 7.13 Lumped element circuit model of the waveguide modes.Figure 7.14 TRM applied to the rectangular waveguide.Figure 7.15 Dielectric loaded rectangular waveguide.Figure 7.16 Slab waveguide supporting even and odd surface wave modes.Figure 7.17 TE zEven and odd modes for slab waveguide.Figure 7.18 Double‐layer slow‐wave structure.Figure 7.19 Synthetic SIW created through two rows of metalized via holes.Figure 7.20 Dispersion and loss characteristic of the SIW.Figure 7.21 Modeling of HM‐SIW.Figure 7.22 Dispersion and attenuation characteristics of ‐TE 0.5, 0‐mode HM‐...
modes...Figure 7.12 Conductor‐backed dielectric surface wave waveguide.Figure 7.13 Lumped element circuit model of the waveguide modes.Figure 7.14 TRM applied to the rectangular waveguide.Figure 7.15 Dielectric loaded rectangular waveguide.Figure 7.16 Slab waveguide supporting even and odd surface wave modes.Figure 7.17 TE zEven and odd modes for slab waveguide.Figure 7.18 Double‐layer slow‐wave structure.Figure 7.19 Synthetic SIW created through two rows of metalized via holes.Figure 7.20 Dispersion and loss characteristic of the SIW.Figure 7.21 Modeling of HM‐SIW.Figure 7.22 Dispersion and attenuation characteristics of ‐TE 0.5, 0‐mode HM‐...










