John Ruskin - The Stones of Venice (Vol. 1-3)
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «John Ruskin - The Stones of Venice (Vol. 1-3)» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:The Stones of Venice (Vol. 1-3)
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
The Stones of Venice (Vol. 1-3): краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «The Stones of Venice (Vol. 1-3)»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
The Stones of Venice (Vol. 1-3) — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «The Stones of Venice (Vol. 1-3)», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
§ X. One other form of the dogtooth is of great importance in northern architecture, that produced by oblique cuts slightly curved, as in the margin, Fig. LVI.It is susceptible of the most fantastic and endless decoration; each of the resulting leaves being, in the early porches of Rouen and Lisieux, hollowed out and worked into branching tracery: and at Bourges, for distant effect, worked into plain leaves, or bold bony processes with knobs at the points, and near the spectator, into crouching demons and broad winged owls, and other fancies and intricacies, innumerable and inexpressible.
Fig. LVI.
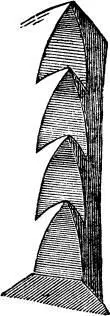
§ XI. Thus much is enough to be noted respecting edge decoration. We were next to consider the fillet. Professor Willis has noticed an ornament, which he has called the Venetian dentil, “as the most universal ornament in its own district that ever I met with;” but has not noticed the reason for its frequency. It is nevertheless highly interesting.
The whole early architecture of Venice is architecture of incrustation: this has not been enough noticed in its peculiar relation to that of the rest of Italy. There is, indeed, much incrusted architecture throughout Italy, in elaborate ecclesiastical work, but there is more which is frankly of brick, or thoroughly of stone. But the Venetian habitually incrusted his work with nacre; he built his houses, even the meanest, as if he had been a shell-fish—roughly inside, mother-of-pearl on the surface: he was content, perforce, to gather the clay of the Brenta banks, and bake it into brick for his substance of wall; but he overlaid it with the wealth of ocean, with the most precious foreign marbles. You might fancy early Venice one wilderness of brick, which a petrifying sea had beaten upon till it coated it with marble: at first a dark city—washed white by the sea foam. And I told you before that it was also a city of shafts and arches, and that its dwellings were raised upon continuous arcades, among which the sea waves wandered. Hence the thoughts of its builders were early and constantly directed to the incrustation of arches.
Fig. LVII.
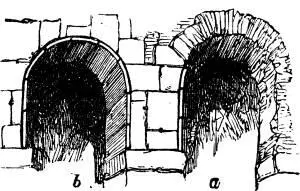
§ XII. In Fig. LVII.I have given two of these Byzantine stilted arches: the one on the right, a , as they now too often appear, in its bare brickwork; that on the left, with its alabaster covering, literally marble defensive armor, riveted together in pieces, which follow the contours of the building. Now, on the wall, these pieces are mere flat slabs cut to the arch outline; but under the soffit of the arch the marble mail is curved, often cut singularly thin, like bent tiles, and fitted together so that the pieces would sustain each other even without rivets. It is of course desirable that this thin sub-arch of marble should project enough to sustain the facing of the wall; and the reader will see, in Fig. LVII., that its edge forms a kind of narrow band round the arch ( b ), a band which the least enrichment would render a valuable decorative feature. Now this band is, of course, if the soffit-pieces project a little beyond the face of the wall-pieces, a mere fillet, like the wooden gunwale in Plate IX.; and the question is, how to enrich it most wisely. It might easily have been dogtoothed, but the Byzantine architects had not invented the dogtooth, and would not have used it here, if they had; for the dogtooth cannot be employed alone, especially on so principal an angle as this of the main arches, without giving to the whole building a peculiar look, which I can not otherwise describe than as being to the eye, exactly what untempered acid is to the tongue. The mere dogtooth is an acid moulding, and can only be used in certain mingling with others, to give them piquancy; never alone. What, then, will be the next easiest method of giving interest to the fillet?
Fig. LVIII.
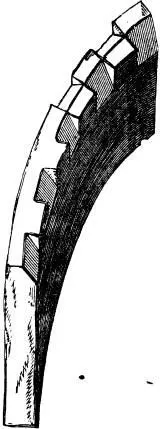
§ XIII. Simply to make the incisions square instead of sharp, and to leave equal intervals of the square edge between them. Fig. LVIII.is one of the curved pieces of arch armor, with its edge thus treated; one side only being done at the bottom, to show the simplicity and ease of the work. This ornament gives force and interest to the edge of the arch, without in the least diminishing its quietness. Nothing was ever, nor could be ever invented, fitter for its purpose, or more easily cut. From the arch it therefore found its way into every position where the edge of a piece of stone projected, and became, from its constancy of occurrence in the latest Gothic as well as the earliest Byzantine, most truly deserving of the name of the “Venetian Dentil.” Its complete intention is now, however, only to be seen in the pictures of Gentile Bellini and Vittor Carpaccio; for, like most of the rest of the mouldings of Venetian buildings, it was always either gilded or painted—often both, gold being laid on the faces of the dentils, and their recesses colored alternately red and blue.
§ XIV. Observe, however, that the reason above given for the universality of this ornament was by no means the reason of its invention . The Venetian dentil is a particular application (consequent on the incrusted character of Venetian architecture) of the general idea of dentil, which had been originally given by the Greeks, and realised both by them and by the Byzantines in many laborious forms, long before there was need of them for arch armor; and the lower half of Plate IX.will give some idea of the conditions which occur in the Romanesque of Venice, distinctly derived from the classical dentil; and of the gradual transition to the more convenient and simple type, the running-hand dentil, which afterwards became the characteristic of Venetian Gothic. No. 13 76is the common dentiled cornice, which occurs repeatedly in St. Mark’s; and, as late as the thirteenth century, a reduplication of it, forming the abaci of the capitals of the Piazzetta shafts. Fig. 15 is perhaps an earlier type; perhaps only one of more careless workmanship, from a Byzantine ruin in the Rio di Ca’ Foscari: and it is interesting to compare it with fig. 14 from the Cathedral of Vienne, in South France. Fig. 17, from St. Mark’s, and 18, from the apse of Murano, are two very early examples in which the future true Venetian dentil is already developed in method of execution, though the object is still only to imitate the classical one; and a rude imitation of the bead is joined with it in fig. 17. No. 16 indicates two examples of experimental forms: the uppermost from the tomb of Mastino della Scala, at Verona; the lower from a door in Venice, I believe, of the thirteenth century: 19 is a more frequent arrangement, chiefly found in cast brick, and connecting the dentils with the dogteeth: 20 is a form introduced richly in the later Gothic, but of rare occurrence until the latter half of the thirteenth century. I shall call it the gabled dentil. It is found in the greatest profusion in sepulchral Gothic, associated with several slight variations from the usual dentil type, of which No. 21, from the tomb of Pietro Cornaro, may serve as an example.
§ XV. All the forms given in Plate IX.are of not unfrequent occurrence: varying much in size and depth, according to the expression of the work in which they occur; generally increasing in size in late work (the earliest dentils are seldom more than an inch or an inch and a half long: the fully developed dentil of the later Gothic is often as much as four or five in length, by one and a half in breadth); but they are all somewhat rare, compared to the true or armor dentil, above described. On the other hand, there are one or two unique conditions, which will be noted in the buildings where they occur. 77The Ducal Palace furnishes three anomalies in the arch, dogtooth, and dentil: it has a hyperbolic arch, as noted above, Chap. X., § XV.; it has a double-fanged dogtooth in the rings of the spiral shafts on its angles; and, finally, it has a dentil with concave sides, of which the section and two of the blocks, real size, are given in Plate XIV. The labor of obtaining this difficult profile has, however, been thrown away; for the effect of the dentil at ten feet distance is exactly the same as that of the usual form: and the reader may consider the dogtooth and dentil in that plate as fairly representing the common use of them in the Venetian Gothic.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «The Stones of Venice (Vol. 1-3)»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «The Stones of Venice (Vol. 1-3)» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «The Stones of Venice (Vol. 1-3)» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












