§ II. The gunwales of the Venetian heavy barges being liable to somewhat rough collision with each other, and with the walls of the streets, are generally protected by a piece of timber, which projects in the form of the fillet, a , Fig. LI.; but which, like all other fillets, may, if we so choose, be considered as composed of two angles or edges, which the natural and most wholesome love of the Venetian boatmen for ornament, otherwise strikingly evidenced by their painted sails and glittering flag-vanes, will not suffer to remain wholly undecorated. The rough service of these timbers, however, will not admit of rich ornament, and the boatbuilder usually contents himself with cutting a series of notches in each edge, one series alternating with the other, as represented at 1, Plate IX.
§ III. In that simple ornament, not as confined to Venetian boats, but as representative of a general human instinct to hack at an edge, demonstrated by all school-boys and all idle possessors of penknives or other cutting instruments on both sides of the Atlantic;—in that rude Venetian gunwale, I say, is the germ of all the ornament which has touched, with its rich successions of angular shadow, the portals and archivolts of nearly every early building of importance, from the North Cape to the Straits of Messina. Nor are the modifications of the first suggestion intricate. All that is generic in their character may be seen on Plate IX.at a glance.
IX.
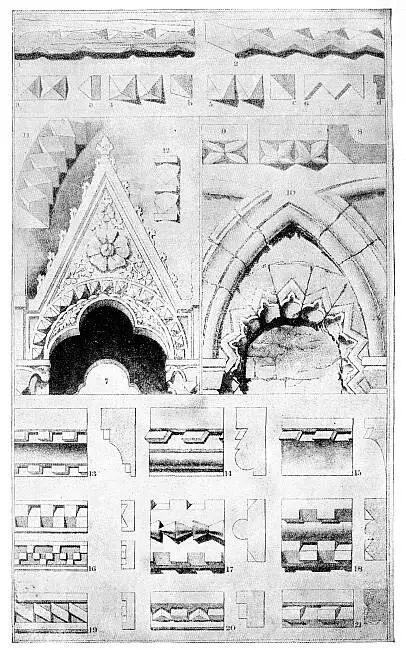
EDGE DECORATION.
§ IV. Taking a piece of stone instead of timber, and enlarging the notches, until they meet each other, we have the condition 2, which is a moulding from the tomb of the Doge Andrea Dandolo, in St. Mark’s. Now, considering this moulding as composed of two decorated edges, each edge will be reduced, by the meeting of the notches, to a series of four-sided pyramids (as marked off by the dotted lines), which, the notches here being shallow, will be shallow pyramids; but by deepening the notches, we get them as at 3, with a profile a , more or less steep. This moulding I shall always call “the plain dogtooth;” it is used in profusion in the Venetian and Veronese Gothic, generally set with its front to the spectator, as here at 3; but its effect may be much varied by placing it obliquely (4, and profile as at b ); or with one side horizontal (5, and profile c ). Of these three conditions, 3 and 5 are exactly the same in reality, only differently placed; but in 4 the pyramid is obtuse, and the inclination of its base variable, the upper side of it being always kept vertical. It is comparatively rare. Of the three, the last, 5, is far the most brilliant in effect, giving in the distance a zigzag form to the high light on it, and a full sharp shadow below. The use of this shadow is sufficiently seen by fig. 7 in this plate (the arch on the left, the number beneath it), in which these levelled dogteeth, with a small interval between each, are employed to set off by their vigor the delicacy of floral ornament above. This arch is the side of a niche from the tomb of Can Signorio della Scala, at Verona; and the value, as well as the distant expression of its dogtooth, may be seen by referring to Prout’s beautiful drawing of this tomb in his “Sketches in France and Italy.” I have before observed that this artist never fails of seizing the true and leading expression of whatever he touches: he has made this ornament the leading feature of the niche, expressing it, as in distance it is only expressible, by a zigzag.
§ V. The reader may perhaps be surprised at my speaking so highly of this drawing, if he take the pains to compare Prout’s symbolism of the work on the niche with the facts as they stand here in Plate IX.But the truth is that Prout has rendered the effect of the monument on the mind of the passer-by;—the effect it was intended to have on every man who turned the corner of the street beneath it: and in this sense there is actually more truth and likeness 74in Prout’s translation than in my fac-simile, made diligently by peering into the details from a ladder. I do not say that all the symbolism in Prout’s Sketch is the best possible; but it is the best which any architectural draughtsman has yet invented; and in its application to special subjects it always shows curious internal evidence that the sketch has been made on the spot, and that the artist tried to draw what he saw, not to invent an attractive subject. I shall notice other instances of this hereafter.
§ VI. The dogtooth, employed in this simple form, is, however, rather a foil for other ornament, than itself a satisfactory or generally available decoration. It is, however, easy to enrich it as we choose: taking up its simple form at 3, and describing the arcs marked by the dotted lines upon its sides, and cutting a small triangular cavity between them, we shall leave its ridges somewhat rudely representative of four leaves, as at 8, which is the section and front view of one of the Venetian stone cornices described above, Chap. XIV., § IV., the figure 8 being here put in the hollow of the gutter. The dogtooth is put on the outer lower truncation, and is actually in position as fig. 5; but being always looked up to, is to the spectator as 3, and always rich and effective. The dogteeth are perhaps most frequently expanded to the width of fig. 9.
§ VII. As in nearly all other ornaments previously described, so in this—we have only to deepen the Italian cutting, and we shall get the Northern type. If we make the original pyramid somewhat steeper, and instead of lightly incising, cut it through, so as to have the leaves held only by their points to the base, we shall have the English dogtooth; somewhat vulgar in its piquancy, when compared with French mouldings of a similar kind. 75It occurs, I think, on one house in Venice, in the Campo St. Polo; but the ordinary moulding, with light incisions, is frequent in archivolts and architraves, as well as in the roof cornices.
§ VIII. This being the simplest treatment of the pyramid, fig. 10, from the refectory of Wenlock Abbey, is an example of the simplest decoration of the recesses or inward angles between the pyramids; that is to say, of a simple hacked edge like one of those in fig. 2, the cuts being taken up and decorated instead of the points . Each is worked into a small trefoiled arch, with an incision round it to mark its outline, and another slight incision above, expressing the angle of the first cutting. I said that the teeth in fig. 7 had in distance the effect of a zigzag: in fig. 10 this zigzag effect is seized upon and developed, but with the easiest and roughest work; the angular incision being a mere limiting line, like that described in § IX. of the last chapter. But hence the farther steps to every condition of Norman ornament are self evident. I do not say that all of them arose from development of the dogtooth in this manner, many being quite independent inventions and uses of zigzag lines; still, they may all be referred to this simple type as their root and representative, that is to say, the mere hack of the Venetian gunwale, with a limiting line following the resultant zigzag.
§ IX. Fig. 11 is a singular and much more artificial condition, cast in brick, from the church of the Frari, and given here only for future reference. Fig. 12, resulting from a fillet with the cuts on each of its edges interrupted by a bar, is a frequent Venetian moulding, and of great value; but the plain or leaved dogteeth have been the favorites, and that to such a degree, that even the Renaissance architects took them up; and the best bit of Renaissance design in Venice, the side of the Ducal Palace next the Bridge of Sighs, owes great part of its splendor to its foundation, faced with large flat dogteeth, each about a foot wide in the base, with their points truncated, and alternating with cavities which are their own negatives or casts.
Читать дальше













