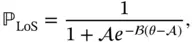where 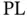 is the distance‐dependent path loss,
is the distance‐dependent path loss, 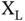 is the large‐scale fading consisting of power variation on a large scale due to the environment, and
is the large‐scale fading consisting of power variation on a large scale due to the environment, and 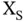 is the small‐scale fading. Parameters of channel model, such as path loss exponent and LoS probability, are dependent on the altitude level because propagation conditions change at different altitudes. The airspace is often segregated into three propagation echelons or slices as follows:
is the small‐scale fading. Parameters of channel model, such as path loss exponent and LoS probability, are dependent on the altitude level because propagation conditions change at different altitudes. The airspace is often segregated into three propagation echelons or slices as follows:
Terrestrial channel: For suburban and urban environments, altitude is between 10 and 22.5 m, respectively [7]. In this case, the terrestrial channel models can be used to model AG propagation because the airborne UAV is below the rooftop level. As a result, NLoS is the dominant component in the propagation.
Obstructed AG channel: For suburban and urban environments, altitude is 10–40 m and 22.5–100 m, respectively. In this case, LoS probability is higher than that of the terrestrial channels.
High‐altitude AG channel: All channels are in LoS for the altitude ranges between 100 and 300 m or above. Consequently, the propagation is similar to that in the free space case. Moreover, no shadowing is experienced for these channels.
2.4.1.1 Path Loss and Large‐Scale Fading
Air‐to‐Air ChannelFree space path loss model is the simplest channel model to represent the AA propagation at a relatively high altitude. Thus, the received power is given by [6]
(2.2) 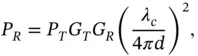
where  denotes the transmitted signal power,
denotes the transmitted signal power, 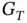 and
and 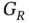 represent the gain of the transmitter and receiver antennas, respectively,
represent the gain of the transmitter and receiver antennas, respectively, 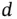 is the ground distance between the transmitter and receiver, and
is the ground distance between the transmitter and receiver, and 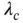 is the carrier wavelength. Path loss exponent
is the carrier wavelength. Path loss exponent 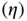 is the rate of distance‐dependent power loss, where
is the rate of distance‐dependent power loss, where 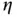 varies with environments. In Eq. ( 2.2),
varies with environments. In Eq. ( 2.2), 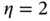 for free space propagation. Therefore, the distance‐dependent path loss expression can be generalized as
for free space propagation. Therefore, the distance‐dependent path loss expression can be generalized as
(2.3) 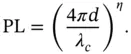
Air‐to‐Ground ChannelIn urban environment, the AG channel may not experience complete free space propagation. In the existing literature on UAV communications, the log‐distance model is the prominently used path loss model due to its simplicity and applicability when environmental parameters are difficult to define. Therefore, path loss in dB is given by
(2.4) 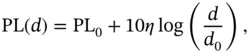
where 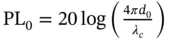 is the path loss for the reference distance
is the path loss for the reference distance 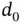 . For the same propagation distance between the ground device and the UAV, large‐scale variations are different at different locations within the same environment because the materials of obstacles vary from each other, which affects the radio signal propagation. As a result, at any distance
. For the same propagation distance between the ground device and the UAV, large‐scale variations are different at different locations within the same environment because the materials of obstacles vary from each other, which affects the radio signal propagation. As a result, at any distance 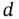 ,
, 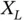 in Eq. ( 2.1) is the shadow fading measured in dB and modeled as the normal random variable with variance
in Eq. ( 2.1) is the shadow fading measured in dB and modeled as the normal random variable with variance 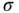 in dB. This model is extensively applied for modeling of the terrestrial channels. Table 2.2lists some measurement campaigns for the estimations of path loss and large‐scale effects.
in dB. This model is extensively applied for modeling of the terrestrial channels. Table 2.2lists some measurement campaigns for the estimations of path loss and large‐scale effects.
Another popular channel model to characterize the AG propagation in UAV communications is the probabilistic path loss model in [4] and [17]. In [17], the path loss between the ground device and the UAV is dependent on the position of the UAV and the propagation environments (e.g. suburban, urban, dense‐urban, high‐rise). Consequently, during the AG radio propagation, the communication link can be either LoS or NLoS depending on the environment. Many of the existing works [18–35] on UAV communications adopted the probabilistic path loss model of [4] and [17]. In these works, the probability of occurrence of LoS and NLoS links are functions of the environmental parameters, height of the buildings, and the elevation angle between the ground device and the UAV. This model is based on environmental parameters defined in the recommendations of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). In particular, ITU‐R provides statistical parameters related to the environment that determine the height, number, and density of the buildings or obstacles. For instance, in [36], the height of the buildings can be modeled by using the Rayleigh distribution. The average path loss for the AG propagation in [17] is given as
(2.5) 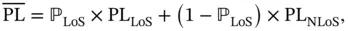
where 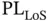 and
and 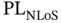 are the LoS and NLoS path loss, respectively, for the free space propagation.
are the LoS and NLoS path loss, respectively, for the free space propagation. 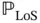 is the LoS probability given as
is the LoS probability given as
(2.6) 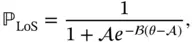
Читать дальше

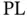 is the distance‐dependent path loss,
is the distance‐dependent path loss, 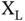 is the large‐scale fading consisting of power variation on a large scale due to the environment, and
is the large‐scale fading consisting of power variation on a large scale due to the environment, and 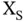 is the small‐scale fading. Parameters of channel model, such as path loss exponent and LoS probability, are dependent on the altitude level because propagation conditions change at different altitudes. The airspace is often segregated into three propagation echelons or slices as follows:
is the small‐scale fading. Parameters of channel model, such as path loss exponent and LoS probability, are dependent on the altitude level because propagation conditions change at different altitudes. The airspace is often segregated into three propagation echelons or slices as follows: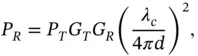
 denotes the transmitted signal power,
denotes the transmitted signal power, 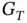 and
and 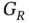 represent the gain of the transmitter and receiver antennas, respectively,
represent the gain of the transmitter and receiver antennas, respectively, 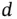 is the ground distance between the transmitter and receiver, and
is the ground distance between the transmitter and receiver, and 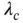 is the carrier wavelength. Path loss exponent
is the carrier wavelength. Path loss exponent 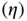 is the rate of distance‐dependent power loss, where
is the rate of distance‐dependent power loss, where 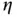 varies with environments. In Eq. ( 2.2),
varies with environments. In Eq. ( 2.2), 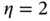 for free space propagation. Therefore, the distance‐dependent path loss expression can be generalized as
for free space propagation. Therefore, the distance‐dependent path loss expression can be generalized as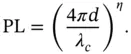
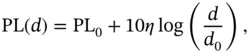
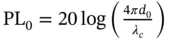 is the path loss for the reference distance
is the path loss for the reference distance 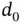 . For the same propagation distance between the ground device and the UAV, large‐scale variations are different at different locations within the same environment because the materials of obstacles vary from each other, which affects the radio signal propagation. As a result, at any distance
. For the same propagation distance between the ground device and the UAV, large‐scale variations are different at different locations within the same environment because the materials of obstacles vary from each other, which affects the radio signal propagation. As a result, at any distance 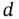 ,
, 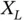 in Eq. ( 2.1) is the shadow fading measured in dB and modeled as the normal random variable with variance
in Eq. ( 2.1) is the shadow fading measured in dB and modeled as the normal random variable with variance 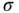 in dB. This model is extensively applied for modeling of the terrestrial channels. Table 2.2lists some measurement campaigns for the estimations of path loss and large‐scale effects.
in dB. This model is extensively applied for modeling of the terrestrial channels. Table 2.2lists some measurement campaigns for the estimations of path loss and large‐scale effects.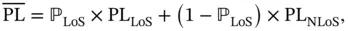
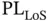 and
and 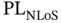 are the LoS and NLoS path loss, respectively, for the free space propagation.
are the LoS and NLoS path loss, respectively, for the free space propagation. 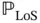 is the LoS probability given as
is the LoS probability given as