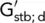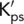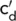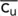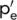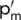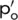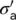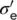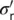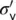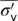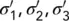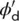The content of the book aligns to the subjects typically covered in all university geotechnics courses. Teachers should find the content and teaching resources helpful for the own needs, and students will find that the book covers all courses in all years of their degree – all written in an easy‐to‐follow style.
In addition to Dr Aboul Hosn, I must also express my thanks to Dr Andrew Bond (past Chair TC250/SC7 – Eurocode 7) and to Dr Daniel Barreto (Edinburgh Napier University) for answering the various questions I posed to them as I wrote this edition.
Ian Smith is a freelance Geotechnical and Educational consultant, and Professor of Geotechnical Engineering and Leader of the Built Environment Education at Heriot Watt University, Edinburgh. He has taught Geotechnical Engineering for 25 years at various universities across the globe, having spent some years beforehand working in the site investigation industry. He was Head, then Dean, of the School of Engineering and the Built Environment at Edinburgh Napier University before leaving to set up his own consultancy in 2017. He is an authority on the use of Eurocode 7 in geotechnical design, and has instructed designers and academics in the use of the code throughout the UK, Europe and in China. He is also Visiting Professor at three universities in China and is regularly invited to teach geotechnical engineering at universities across Europe and Asia.
The following is a list of the more important symbols used in the text.
Notation specific to the second generation of Eurocode 7 are indicated where appropriate.
| A |
Area, pore pressure coefficient |
| A' |
Effective foundation area |
| A b |
Area of base of pile |
| A s |
Area of surface of embedded length of pile shaft |
| B |
Width, diameter, pore pressure coefficient, foundation width |
| B' |
Effective foundation width |
| C |
Cohesive force, constant |
| C a |
Area ratio |
| C C |
Compression index, soil compressibility, coefficient of curvature |
| C d,SLS |
Eurocode 7 serviceability limit state limiting design value |
| C N |
SPT overburden correction factor |
| C r |
Static cone resistance |
| C s |
Constant of compressibility |
| C u |
Uniformity coefficient |
| C v |
Void fluid compressibility |
| C w |
Adhesive force |
| D |
Diameter, depth factor, foundation depth, embedded length of pile |
| D w |
Depth of groundwater table |
| D r |
Relative density |
| D 1, D 2 |
Cutting shoe diameters |
| D 10, D 30, D 60 |
Effective particle sizes (10, 30, 60%) |
| E |
Modulus of elasticity, efficiency of pile group |
 |
One‐dimensional modulus of elasticity |
| E d |
Eurocode 7 design value of effect of actions |
| E dst;d |
Eurocode 7 design value of effect of destabilising actions |
| E stb;d |
Eurocode 7 design value of effect of stabilising actions |
| E M |
Pressuremeter modulus |
| E m |
Eurocode 7 design value of modulus of elasticity |
| E r |
SPT energy ratio |
| F |
Factor of safety |
| F b |
Factor of safety on pile base resistance |
| F c;d |
Eurocode 7 design axial compression load on a pile |
| F d |
Eurocode 7 design value of an action |
| F rep |
Eurocode 7 representative value of an action |
| F s |
Factor of safety on pile shaft resistance |
| G; G' |
Shear modulus; effective shear modulus |
| G k; G d |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) characteristic permanent action; design permanent action |
| G dst;d |
Eurocode 7 design value of destabilising permanent vertical action (uplift) |
| G s |
Particle specific gravity |
| G stb;d |
Eurocode 7 design value of stabilising permanent vertical action (uplift) |
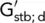 |
Eurocode 7 design value of stabilising permanent vertical action (heave) |
| G wk |
Eurocode 7 (2 ndG) characteristic value of G w |
| G w,rep |
Eurocode 7 (2 ndG) representative value of G w |
| G wk;inf |
Eurocode 7 (2 ndG) inferior (lower) characteristic value of G w |
| G wk;sup |
Eurocode 7 (2 ndG) superior (upper) characteristic value of G w |
| H |
Thickness, height, horizontal load |
| I |
Index, moment of inertia |
| I D |
Density index |
| I L |
Liquidity index |
| I P |
Plasticity index, immediate settlement coefficient |
| I σ |
Vertical stress influence factor |
| K |
Boussinesq Influence factor, ratio of σ 3/ σ 1, bulk/volumetric modulus |
| K' |
Effective bulk/volumetric modulus |
| K a |
Coefficient of active earth pressure |
| K F |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) action consequence factor |
| K M |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) material consequence factor |
| K 0 |
Coefficient of earth pressure at rest |
| K p |
Coefficient of passive earth pressure |
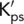 |
Effective plane strain bulk/volumetric modulus |
| K s |
Pile constant |
| L |
Length |
| L' |
Effective foundation length |
| M |
Moment, slope projection of critical state line, mass, mobilisation factor |
| M s |
Mass of solids |
| M w |
Mass of water |
| N |
Number, stability number, uncorrected blow count in SPT |
| N 60 |
Number of blows from the SPT corrected to energy losses |
| (N 1) 60 |
Number of blows from the SPT corrected to energy losses, rod length and normalised for effective vertical overburden stress |
| N c, N q, N γ |
Bearing capacity coefficients |
| N p |
Immediate settlement coefficient |
| P |
Force |
| P a |
Thrust due to active earth pressure |
| P p |
Thrust due to passive earth pressure |
| P w |
Thrust due to water or seepage forces |
| Q |
Total quantity of flow in time t, applied surface line load |
| Q b |
Ultimate soil strength at pile base |
| Q k; Q d |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) characteristic variable action; design variable action |
| Q s |
Ultimate soil strength around pile shaft |
| Q u |
Ultimate load carrying capacity of pile |
| R |
Radius, reaction |
| R b;cal |
Eurocode 7 calculated value of pile base resistance |
| R b;k |
Eurocode 7 characteristic value of pile base resistance |
| R b,rep |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) representative base resistance |
| R c |
Eurocode 7 compressive resistance of ground against a pile at ultimate limit state |
| R c;cal |
Eurocode 7 calculated value of R c |
| R c;d |
Eurocode 7 design value of R c |
| R cd |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) design value of R c |
| R c;k |
Eurocode 7 characteristic value of R c |
| R c;m |
Eurocode 7 measured value of R c |
| R c,rep |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) representative total pile resistance |
| R d |
Eurocode 7 design resisting force |
| R o |
Overconsolidation ratio (one‐dimensional) |
| R p |
Overconsolidation ratio (isotropic) |
| R s;cal |
Eurocode 7 calculated value of pile shaft resistance |
| R s;k |
Eurocode 7 characteristic value of pile shaft resistance |
| R s,rep |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) representative shaft resistance |
| S |
Vane shear strength |
| S dst;d |
Eurocode 7 design value of destabilising seepage force |
| S r |
Degree of saturation |
| S t |
Sensitivity |
| T |
Time factor, tangential force, surface tension, vane torque |
| T d |
Eurocode 7 design value of total shearing resistance around structure |
| U |
Average degree of consolidation |
| U z |
Degree of consolidation at a point at depth z |
| V |
Volume, vertical load |
| V a |
Volume of air, percentage air voids |
| V dst;d |
Eurocode 7 design value of destabilising vertical action on a structure |
| V s |
Volume of solids |
| V v |
Volume of voids |
| V w |
Volume of water |
| W |
Weight |
| W s |
Weight of solids |
| W w |
Weight of water |
| X d |
Eurocode 7 design value of a material property |
| X k |
Eurocode 7 representative value of a material property Eurocode 7 (2nd G) characteristic value of a material property |
| X rep |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) representative value of a material property |
| Z |
Section modulus |
| a |
Area, wall adhesion, intercept of MCV calibration line with w‐axis |
| b |
Width, slope of MCV calibration line |
| c |
Unit cohesion |
| c ' |
Unit cohesion with respect to effective stresses |
| c b |
Undisturbed soil shear strength at pile base |
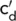 |
Eurocode 7 design value of effective cohesion |
| c r |
Residual value of cohesion |
| c u |
Undrained unit cohesion |
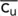 |
Average undrained shear strength of soil |
| c u;d |
Eurocode 7 design value of undrained shear strength |
| c v |
Coefficient of consolidation |
| c w |
Unit cohesion between wall and soil |
| d |
Pile penetration, pile diameter, particle size |
| d c, d q, d γ |
Depth factors |
| e |
Void ratio, eccentricity |
| f |
Settlement coefficient |
| f s |
Ultimate skin friction for piles |
| g |
Gravitational acceleration |
| h |
Hydraulic head, height, head loss |
| h c |
Capillary rise, tension crack depth |
| h e |
Equivalent height of soil |
| h w |
Excess head |
| i |
Hydraulic gradient |
| i c |
Critical hydraulic gradient |
| i c, i q, i γ |
Inclination factors |
| k |
Coefficient of permeability |
| l |
Length, length of flow path |
| m |
Stability coefficient |
| m B, m L |
Eurocode 7 load inclination factor parameters |
| m v |
Coefficient of volume compressibility |
| n |
Porosity, stability coefficient |
| p |
Pressure, mean pressure, mean normal stress |
| p' |
Mean normal effective stress |
| p a |
Active earth pressure |
| p c |
Preconsolidation pressure (one‐dimensional) |
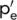 |
Equivalent consolidation pressure (isotropic) |
| p LM |
Pressuremeter limit pressure |
| p 0 |
Earth pressure at rest |
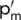 |
Preconsolidation pressure (isotropic) |
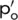 |
Effective overburden pressure |
| p p |
Passive earth pressure |
| q |
Unit quantity of flow, deviator stress, uniform surcharge, bearing pressure |
| q' |
Effective deviator stress |
| q a |
Allowable bearing pressure |
| q u |
Ultimate bearing capacity |
| q u net |
Net ultimate bearing capacity |
| r |
Radius, radial distance, finite difference constant |
| r u |
Pore pressure ratio |
| s |
Suction value of soil, stress parameter, settlement |
| s c, s q, s γ |
Shape factors |
| s w |
Corrected drawdown in pumping well |
| t |
Time, stress parameter |
| u, u w |
Pore water pressure |
| u a |
Pore air pressure, pore pressure due to σ 3in a saturated soil |
| u d |
Pore pressure due to ( σ 1− σ 3) in a saturated soil |
| u dst;d |
Eurocode 7 design value of destabilising total pore water pressure |
| u i |
Initial pore water pressure |
| u t |
Pore water pressure at toe of sheet pile wall |
| v |
Velocity, specific volume |
| w |
Water, or moisture, content |
| w L |
Liquid limit |
| w P |
Plastic limit |
| w s |
Shrinkage limit |
| x |
Horizontal distance |
| y |
Vertical, or horizontal, distance |
| z |
Vertical distance, depth |
| z a |
Depth of investigation points |
| z o |
Depth of tension crack |
| z w |
Depth below water table |
| α |
Angle, pile adhesion factor, slope of K fline |
| β |
Slope angle |
| Γ |
Eurocode 7 over‐design factor, specific volume at ln p' = 0 |
| γ |
Unit weight (weight density), shear strain |
| γ ' |
Submerged, buoyant or effective unit weight (effective weight density) |
| γ A;dst |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: accidental action – unfavourable |
| γ b |
Bulk unit weight (bulk weight density), Eurocode 7 partial factor: pile base resistance |
| γ c' |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: effective cohesion |
| γ cu |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: undrained shear strength |
| γ d |
Dry unit weight (dry weight density) |
| γ E |
Eurocode 7 partial factor for effects of actions,Eurocode 7 (2nd G) partial factor for unfavourable effects of actions |
| γ E,fav |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) partial factor for favourable effects of actions |
| γ F |
Eurocode 7 partial factor for an action |
| γ G |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) partial factor for permanent unfavourable/destabilising action |
| γ G;dst |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: permanent action – unfavourable |
| γ G,fav |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) partial factor for permanent favourable action |
| γ G;stb |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: permanent action – favourable |
| γ G,w |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) partial factor for unfavourable/destabilising water action |
| γ G,w,stb |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) partial factor for stabilising water action |
| γ M |
Eurocode 7 partial factor for a soil parameter |
| γ Q |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) partial factor for variable (unfavourable) action |
| γ Q;dst |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: variable action – unfavourable |
| γ Q,w |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) partial factor for unfavourable water action |
| γ qu |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: unconfined compressive strength |
| γ R |
Eurocode 7 partial factor for a resistance |
| γ Rb |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) pile design base resistance factor |
| γ Rc |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) pile design total resistance factor |
| γ Rd |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) pile design model factor |
| γ Re |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: earth resistance |
| γ Rh |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: sliding resistance |
| γ Rs |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) pile design shaft resistance factor |
| γ Rv |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: bearing resistance |
| γ s |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: pile shaft resistance |
| γ sat |
Saturated unit weight (saturated weight density) |
| γ t |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: pile total resistance |
| γ tanδ |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) partial factor: ground/structure interface friction |
| γ tanϕ |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) partial factor: angle of shearing resistance |
| γ ts |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) partial factor: effective shear strength |
| γ w |
Unit weight of water (weight density of water) |
| γ γ |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: weight density |
| γ ϕ' |
Eurocode 7 partial factor: angle of shearing resistance |
| δ𝛿 |
Ground–structure interface friction angle |
| ε |
Strain |
| η |
Dynamic viscosity of water, conversion factor |
| θ |
Angle of failure plane to major principal plane, angle subtended at centre of slip circle |
| κ |
Slope of swelling line |
| λ |
Slope of normal consolidation line, SPT rod length correction factor |
| μ |
Settlement coefficient, one micron |
| ν |
Poisson's ratio |
| ξ m |
Eurocode 7 (2nd G) pile design correlation factor |
| ξ 1, ξ 2 |
Eurocode 7 correlation factors to evaluate results of static pile load tests |
| ξ 3, ξ 4 |
Eurocode 7 correlation factors to derive pile resistance from ground investigation results |
| ρ |
Density, settlement |
| ρ' |
Submerged, buoyant or effective density |
| ρ b |
Bulk density |
| ρ c |
Consolidation settlement |
| ρ d |
Dry density |
| ρ i |
Immediate settlement |
| ρ s |
Particle density |
| ρ sat |
Saturated density |
| ρ w |
Density of water |
| σ |
Total normal stress |
| σ' |
Effective normal stress |
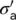 |
Total, effective axial stress |
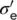 |
Equivalent consolidation pressure (one‐dimensional) |
σ r, 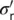 |
Total, effective radial stress |
| σ stb;d |
Eurocode 7 design value of stabilising total vertical stress |
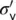 |
Effective overburden pressure |
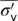 |
Average effective overburden pressure |
| σ 1, σ 2, σ 3 |
Total major, intermediate and minor stress |
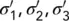 |
Effective major, intermediate and minor stress |
| τ |
Shear stress |
| ϕ' |
Angle of shearing resistance with respect to effective stresses |
| ϕ cv |
Critical state, or constant volume, angle of shearing resistance |
| ϕ cv;d |
Design value of critical state angle of shearing resistance |
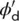 |
Design value of ϕ' |
| ϕ u |
Angle of shearing resistance with respect to total stresses (=0) |
| ψ |
Angle of back of wall to horizontal, Eurocode 7 correlation factor |