Polymer Composites for Electrical Engineering
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Polymer Composites for Electrical Engineering» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Polymer Composites for Electrical Engineering
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Polymer Composites for Electrical Engineering: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Polymer Composites for Electrical Engineering»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Polymer Composites for Electrical Engineering
Polymer Composites for Electrical Engineering
Polymer Composites for Electrical Engineering — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Polymer Composites for Electrical Engineering», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Xueling Yao School of Electrical Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
Yunhe Zhang Key Laboratory of High Performance Plastics (Jilin University), Ministry of Education. College of Chemistry, Jilin University, Changchun, P. R. China
Yutong Zhao Key Laboratory of Smart Grid of Education Ministry, School of Electrical and Information Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China
Jia Zhidong Engineering Laboratory of Power Equipment Reliability in Complicated Coastal Environments, Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School, Tsinghua University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Yao Zhou Department of Materials Science and Engineering, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA
Lixue Zhu Key Laboratory of High Performance Plastics (Jilin University), Ministry of Education. College of Chemistry, Jilin University, Changchun, P. R. China
Preface
Power grid is an indispensable infrastructure in modern society. With the increasingly severe climate change, the transmission of clean energy becomes more and more important, which puts forward higher requirements for the safe operation of power grid and power supply quality. On the other hand, the sending end of clean energy is far away from the receiving end of big cities and industrial areas, so it is necessary to develop Ultra‐High Voltage (UHV), long‐distance and large capacity transmission technology, as well as distributed generation technology to form modern smart micro grids.
To effectively improve the performance of power grid, especially the acceptance of clean energy by UHV power grid, advanced smart power equipment is needed. The performance of power equipment made of traditional materials is restricted by the electrical characteristics of materials, so it is difficult to meet the development needs of smart grid. Therefore, it is necessary to develop emerging high‐performance power equipment materials.
Although metal materials, ceramic materials, and polymer materials are widely used in power equipment, composite materials are more widely used. This is mainly because polymer composites not only have the characteristics of easy processing, lightweight, and low cost of polymers but also have the versatility of other components, which account for an increasing proportion in power equipment. In recent years, with the wide use of clean energy and the development of UHV flexible direct current (DC) transmission technology, some emerging polymer composites (especially nanocomposites) have appeared and been used in engineering practice. Therefore, polymer composites for electrical engineering have been developed rapidly.
This book consists of 13 chapters, which are all contributed by well‐recognized experts in electrical engineering or composite materials. Chapters 1and 2review the electrical and thermal energy storage of polymer composites, respectively, and Chapters 3and 4deal with the thermal properties of polymer composites in electrical engineering, including high temperature endurance and fire‐retardant performance. Chapters 5, 6, 9, 10, and 12focus on the applications of polymer composites in power cables, capacitors, motors, generators, and switchgears. The polymer composites for electric stress control and outer door insulation applications are covered in Chapters 7and 8, respectively. Chapter 11provides a detailed overview on design, analysis, and performance of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites in lightning environment. Chapter 13reviews the preparation, processing, and application of glass fiber reinforced polymer composites in electrical engineering.
As such, this book is well‐structured with basics and application to transfer sufficient coordinated knowledge not only to experts in electrical engineering and material science but also to university students who intend to work in this field in near future.
We greatly thank all contributors for bringing this wonderful book to the community, which is the first comprehensive book focusing on the design, fabrication, processing, analysis, and applications of polymer composites in electrical engineering. Xingyi Huang, one of the coeditors, would like to thank Shanghai Key Laboratory of Electrical Insulation and Thermal Aging and National Natural Science Foundation of China for their long‐time support.
1 Polymer Composites for Electrical Energy Storage
Yao Zhou
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA
1.1 Introduction
Electrical energy storage in dielectric materials that involves the movement and separation of opposite charges between the two electrodes under the applied electric field is ubiquitous in electrical engineering. The electrostatic capacitors are widely employed in the power electronic devices in various applications, including grid‐connected wind farm and photovoltaic, hybrid electric vehicle, medical defibrillator, electric power transmission, etc. [1–4]. Polymer dielectrics have been widely adopted in electrostatic capacitors because of their high breakdown strength, light weight, ease of processing, low cost, and excellent flexibility [5–10]. However, the relatively low dielectric constant restricts the application of polymer dielectrics because of the low discharged energy density [11]. To overcome this issue, a polymer composite approach has been proposed to combine the advantages of polymers and inorganic nanofillers to attain both high dielectric constant and high breakdown strength, as well as low energy loss [12–14].
Over the past decades, great achievements have been made in developing high performance polymer composites for electrical energy storage application. A variety of material structure designs and processing strategies have been proposed to increase the energy density of the polymer composites. This chapter provides a comprehensive understanding of the fundamentals and recent development in the field of polymer composites for electrical energy storage. The strategies of achieving high electrical energy storage performance such as controlling the nanofiller dimension and morphology, controlling the nanofiller distribution and orientation, modifying the nanofiller/polymer interface, introducing multiple nanofillers, and constructing multilayer‐structured composites are particularly discussed.
1.2 General Considerations
In general, the stored electrical energy density ( U s) in the dielectric materials can be expressed as
(1.1) 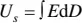
where E is the applied electric field and D is the electric displacement [15]. To measure the stored energy density, discharged energy density ( U d), and charge/discharge efficiency ( η ) of the dielectrics, the electric displacement ( D ) is measured as a function of applied electric field ( E ) during the charging and discharging processes, which is also called as the D ‐ E loop. The schematic of typical D ‐ E loop of the dielectric material is shown in Figure 1.1. The stored energy density can be calculated by integrating the area bounded by the charging curve, the D ‐axis, and the horizontal line y = D max. Similarly, the discharged energy density can be calculated by integrating the area bounded by the discharging curve, the D ‐axis, and the horizontal line y = D max. The energy loss ( U l) during the charge/discharge circle can be represented by the area bounded by the charging and discharging curves. Apparently, the stored energy density equals to the discharged energy density plus the energy loss, that is, U s= U d+ U l. The charge/discharge efficiency is defined as η = U d/ U s× 100%. For linear dielectrics, the electric displacement increases linearly with the applied electric field, i.e. D = ε 0 ε r E , where ε 0is the vacuum dielectric constant (8.85 × 10 −12F/m) and ε ris the relative dielectric constant of the dielectric material [16–18]. As a result, the stored energy density of linear dielectrics can be simplified as
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Polymer Composites for Electrical Engineering»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Polymer Composites for Electrical Engineering» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Polymer Composites for Electrical Engineering» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












