Rui Li - Soft-Switching Technology for Three-phase Power Electronics Converters
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Rui Li - Soft-Switching Technology for Three-phase Power Electronics Converters» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Soft-Switching Technology for Three-phase Power Electronics Converters
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Soft-Switching Technology for Three-phase Power Electronics Converters: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Soft-Switching Technology for Three-phase Power Electronics Converters»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Discover foundational and advanced topics in soft-switching technology, including ZVS three-phase conversion Soft-Switching Technology for Three-phase Power Electronics Converters,
Soft-Switching Technology for Three-phase Power Electronics Converters
Soft-Switching Technology for Three-phase Power Electronics Converters — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Soft-Switching Technology for Three-phase Power Electronics Converters», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
3 Chapter 3Figure 3.1 Soft‐switching converter: (a) with DC‐side resonance; (b) with AC...Figure 3.2 SPWM: (a) modulation signals and carrier; (b) PWM waveform in a s...Figure 3.3 Two types of switching commutations of phase‐ a switch leg: (a) Ty...Figure 3.4 Phase current polarity vs. Type 2 commutation edge: (a) filter cu...Figure 3.5 Phase current polarity vs. Type 2 commutation edge with non‐unit ...Figure 3.6 PWM scheme vs. EA‐PWM scheme: (a) three‐phase filter currents; (b...Figure 3.7 Active‐clamping ZVS three‐phase converter.Figure 3.8 Active‐clamping three‐phase converter with CAC auxiliary circuit....Figure 3.9 Modulation signals and filter current waveforms.Figure 3.10 Typical waveforms in a switching period.Figure 3.11 Initial state before time t 0.Figure 3.12 Stage 1[ t 0, t 1].Figure 3.13 Stage 2[ t 1, t 2]: first resonance.Figure 3.14 Stage 3[ t 2, t 3]: resonant inductor discharging duration 1.Figure 3.15 Stage 4[ t 3, t 4]: resonant inductor discharging duration 2.Figure 3.16 Stage 5[ t 4, t 5]: current boost stage with three leg short‐circui...Figure 3.17 Stage 6[ t 5, t 6]: second resonance.Figure 3.18 Stage 7[ t 6, t 7]: PWM duration with state 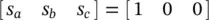 .Figure 3.19 Stage 8[ t 7, t 8]: Type 1 commutation.Figure 3.20 Stage 9[ t 8, t 9].Figure 3.21 Stage 10[ t 9, t 10]: Type 1 commutation.Figure 3.22 Stage 11 [ t 10, t 11]: PWM duration with state
.Figure 3.19 Stage 8[ t 7, t 8]: Type 1 commutation.Figure 3.20 Stage 9[ t 8, t 9].Figure 3.21 Stage 10[ t 9, t 10]: Type 1 commutation.Figure 3.22 Stage 11 [ t 10, t 11]: PWM duration with state 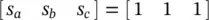 .Figure 3.23 Stage 12 [ t 11, t 12]: Type 1 commutation.Figure 3.24 Stage 13 [ t 12, t 13]: PWM duration with state
.Figure 3.23 Stage 12 [ t 11, t 12]: Type 1 commutation.Figure 3.24 Stage 13 [ t 12, t 13]: PWM duration with state 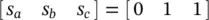 .Figure 3.25 Circuit of the first resonant stage: (a) circuit state; (b) equi...Figure 3.26 The circuit of the second resonant stage: (a) circuit state; (b)...Figure 3.27 Midpoint voltages of three‐phase active‐clamping converter with ...Figure 3.28 Phase‐a modulation signal at DPWM: (a) m a= 0.9; (b)
.Figure 3.25 Circuit of the first resonant stage: (a) circuit state; (b) equi...Figure 3.26 The circuit of the second resonant stage: (a) circuit state; (b)...Figure 3.27 Midpoint voltages of three‐phase active‐clamping converter with ...Figure 3.28 Phase‐a modulation signal at DPWM: (a) m a= 0.9; (b) 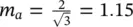 .Figure 3.29 Typical three‐phase modulation signals of DPWM.Figure 3.30
.Figure 3.29 Typical three‐phase modulation signals of DPWM.Figure 3.30 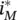 at θ =0.Figure 3.31
at θ =0.Figure 3.31 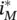 at θ = −π/3 and θ = π/3.Figure 3.32
at θ = −π/3 and θ = π/3.Figure 3.32 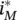 at θ = π.Figure 3.33
at θ = π.Figure 3.33 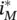 at θ = 2π/3 and θ = 4π/3.Figure 3.34 ZVS range of CAC converter: (a) with CPWM; (b) with DPWM.Figure 3.35 ZVS range of MVAC converter: (a) with CPWM; (b) with DPWM.Figure 3.36 Control diagram of three‐phase ZVS CAC converter.Figure 3.37 Typical waveforms of gate drive signals.Figure 3.38 Three‐phase converter with CAC auxiliary circuit.Figure 3.39 Grid voltages and grid currents waveforms of unit power factor h...Figure 3.40 SVM hexagon with 12 sectors.Figure 3.41 Composition of the reference vector in sector 1‐1.Figure 3.42 Vectors available in sector 1‐1. (a) Nonzero vector
at θ = 2π/3 and θ = 4π/3.Figure 3.34 ZVS range of CAC converter: (a) with CPWM; (b) with DPWM.Figure 3.35 ZVS range of MVAC converter: (a) with CPWM; (b) with DPWM.Figure 3.36 Control diagram of three‐phase ZVS CAC converter.Figure 3.37 Typical waveforms of gate drive signals.Figure 3.38 Three‐phase converter with CAC auxiliary circuit.Figure 3.39 Grid voltages and grid currents waveforms of unit power factor h...Figure 3.40 SVM hexagon with 12 sectors.Figure 3.41 Composition of the reference vector in sector 1‐1.Figure 3.42 Vectors available in sector 1‐1. (a) Nonzero vector 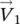 :state 100....Figure 3.43 Type 2 commutations between vectors in sector 1‐1.Figure 3.44 Converter state changing roadmap for vector sequence:
:state 100....Figure 3.43 Type 2 commutations between vectors in sector 1‐1.Figure 3.44 Converter state changing roadmap for vector sequence: 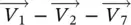 .Figure 3.45 Waveforms of three‐phase switch bridge state, auxiliary switch s...Figure 3.46 Active clamped three‐phase converters: (a) with CAC; (b) with MV...
.Figure 3.45 Waveforms of three‐phase switch bridge state, auxiliary switch s...Figure 3.46 Active clamped three‐phase converters: (a) with CAC; (b) with MV...
4 Chapter 4Figure 4.1 Circuit topology of the CAC rectifier.Figure 4.2 Vector representation in complex plane with αβ coordina...Figure 4.3 Topology of the three‐phase converter.Figure 4.4 Sectors and voltage vectors in space complex plane.Figure 4.5 Two kinds of space vector sequences. (a) Symmetrical voltage vect...Figure 4.6 Switching commutation process of a leg in three‐phase rectifier. ...Figure 4.7 Driving logic and key waveforms of a leg in three‐phase converter...Figure 4.8 The voltage and current waveforms in a utility cycle.Figure 4.9 Sectors in space vector diagram.Figure 4.10 The dendrogram analysis of switching commutation sequences betwe...Figure 4.11 Three kinds of space vector sequences with one Type 2 commutatio...Figure 4.12 Switching state of the CAC circuit: (a) S 7's on‐state; (b) S 7's ...Figure 4.13 Switch commutation processes of CAC rectifier in sector 1‐1. (a)...Figure 4.14 Key waveforms in sector 1‐1.Figure 4.15 Driving logic and key waveforms in sector 1‐1.Figure 4.16 Equivalent circuit of stage 1: the initial stage.Figure 4.17 Equivalent circuit of stage 2: the first resonance stage.Figure 4.18 Equivalent circuit of stage 3: the freewheeling stage.Figure 4.19 Equivalent circuit of stage 4: the second resonance stage.Figure 4.20 Equivalent circuit of stage 5: the second steady stage.Figure 4.21 Equivalent circuit of stage 6: the Type 1 commutation stage.Figure 4.22 Equivalent circuit of stage 7: the third steady stage.Figure 4.23 Equivalent circuit of stage 8: the Type 1 commutation stage.Figure 4.24 Resonance circuit and its equivalent circuit of stage 2 ( t 1– t 2):...Figure 4.25 Equivalent circuit of stage 4 ( t 3– t 4): (a) circuit state of the ...Figure 4.26 Gate signal derivation in sector 1‐1.Figure 4.27 Control block diagram of the rectifier.Figure 4.28 Topology of the CAC rectifier.Figure 4.29 λ 7versus Z r.Figure 4.30 i res/ I mversus resonant impedance Z r.Figure 4.31 Resonant impedance Z rversus resonant parameters.Figure 4.32 CM200DU‐24NFH IGBT turn‐off loss under ZVS conditions.Figure 4.33 Recommended resonant parameters area.Figure 4.34 The 40 kW ZVS rectifier prototype.Figure 4.35 Bus bar and structure 40 kW ZVS rectifier prototype.Figure 4.36 Output current and grid voltageFigure 4.37 Voltage and current waveforms of the bridge switch.Figure 4.38 Voltage and current waveforms of the bridge switch’s antiparalle...Figure 4.39 Voltage and current waveforms of the auxiliary switch.Figure 4.40 Voltage across C cland current through L r.Figure 4.41 Voltage and current waveforms of the bridge switch S 1in a line ...Figure 4.42 Measured efficiency.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Soft-Switching Technology for Three-phase Power Electronics Converters»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Soft-Switching Technology for Three-phase Power Electronics Converters» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Soft-Switching Technology for Three-phase Power Electronics Converters» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.











