Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Organizational Transformation
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Organizational Transformation» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Organizational Transformation
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Organizational Transformation: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Organizational Transformation»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Discusses the impact of AI on organizational transformation which is a mix of computational techniques and management practices, with in-depth analysis about the role of automation & data management, and strategic management in relation to human capital, procurement & production, finance, and marketing.
Audience
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Organizational Transformation — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Organizational Transformation», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
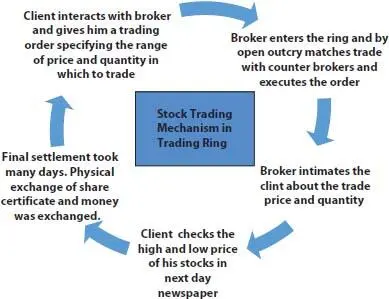
5 5. Physical Exchange of Share Certificates and Money: Share certificates existed in physical form in hard copy, had to be sealed with company stamp, and had to be posted from one owner to another in case of a trade. Same was the case with money; it actually changed hands between clients, brokers, stock exchanges, etc. [2]. So, the whole process was very lengthy and time taking which also resulted in loss and theft of share certificates and money.
6 6. Localized Functioning of Exchanges: There were a lot of stock exchanges; literally, at all centers of trade, otherwise people of that city could not trade efficiently. Companies had to be listed on each stock exchange to create volume and presence at all places. It all gave rise to complexities and also gave way for scams and frauds.
7 7. No Participation of Tiers II & III and Rural India: Since information flow was very less, so people in smaller cities and towns had no idea about the working of stock exchanges. They either thought of it as a place of making big money or a hoax to lose money. So, the actual participation was not there by the people of smaller places.
8 8. Long Trading Cycles: Today, a trade squares up in T+2 days that means that with 3 working days after a trade has been executed, the seller gets the money in his account and shares from his DP are transferred to the buyers account, and at buyers end, he gets the shares in his DP and money from his account gets deducted. This all happens in 2 days, but back in ring trading days, all took T+5 days at least, actual receiving of share certificates may have taken even longer than that.
2.4 Generation 2: Shifting to Online Platform
This was the era of big transformation in stock broking. All the systems which used to happen manually were shifted to computers and online trading was started [3]. Online trading replaced ring-based trading and made physical stock exchanges less important in stock trading since it made share trading possible from any place anywhere. Online share trading was initiated in India in the year 2000 by NSE (National Stock Exchange) after getting the sanction from regulatory authority the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). Online trading was proposed in a committee set up by SEBI on Internet Trading and services and was approved in January 2000. This transformation from manual to computer-based trading gave way for more transparent execution of working of stock exchanges [5]. It also augmented the speed at which trades were executed and completed. It also induced convenience and security in share trading for investors. This simplicity and a sense of security made more and more people to participate in stock broking which led to a tremendous growth in retail participation [6]. There were few major changes that appeared in this age which are as follows:
1 1. Only Two Stock Exchanges Prevailed: We discussed earlier that almost every major city of India had a stock exchange of its own and companies were listed on them. By 1990s, there were 24 stock exchanges in India in all major cities. But when everything shifted online the physical exchanges became just buildings as the broking was consolidated and all the companies listed themselves only on two major exchanges, namely, BSE and NSE. The sensitivity index on stock markets is the barometer of the stocks, low and high cumulative of major stocks listed on that exchanges. BSE has SENSEX with 30 stocks and NSE has NIFTY with 50 stocks. It was in January 1986 that BSE’s sensitivity index SENSEX was launched. It was the first stock market index which came into being. Its base year was set as 1978–1979. The underlying principle for selecting companies that would go in SENSEX or NIFTY are trading frequency, market capitalization, trading history, listing history, and industry representation. In March 1995, BSE ended its 120 years history of floor trading and shifted to computerized trading operations and then began the screen-based trading system nationwide. NSE came into force in November 1992. It was set up to accommodate to medium sized companies. In June 1994, NSE commenced operation in wholesale debt market segment. In November 1994, NSE shifted to screen-based trading format for the first time in India. Sensitivity index of NSE, NIFTY, was created in April 1996. It consists of top 50 scripts with highest market capitalization and it is an indicator of all the major companies in the NSE. NSE also has NIBIS (NSE’s Internet-Based Information System) for online real-time diffusion of trading related information on the Internet.
2 2. Online Trading Software: The biggest challenge in online trading was to make it error free, transparent, and easily accessible. For this purpose, NSE was the primary stock exchange in India which started providing pan India screen-based, order-driven, trading system. The trading system at NSE is known as the National Exchange for Automated Trading (NEAT) system. It is an online, fully computerized, nameless, order-driven system with nationwide presence. Another package offered by NSE is “NEAT Plus”. Neat Plus provides a novel service to the subscribers which makes them trade in more than one stock exchange simultaneously. To ensure that that the system does not collapse due to over burden, NSE undertakes periodic testing and capacity enhancements as soon as its users and trading volume increases. NEAT also provides realtime data sharing on trading volumes and thus traders and investors can factor in the second to second changes in their Trades. BSE also has a system just like NEAT which is called as BOLT. BSE Online Trading (BOLT) is also a computerized, screen-based trading platform which can be used to punch in orders from anywhere, anytime during trading hours. It has a turnover capacity of 8 million orders each day. The BSE has also pioneered a nationalized exchange-based internet order punching system, to facilitate investors from all over the world to trade in scripts listed on BSE.
3 3. Depositories: Two major depositories were made to keep a record of stock holdings and their owners and also to keep a track of buying and selling activities by these depository account holders. NSDL (National Securities Depositories Ltd.) and CDSL (Central Depositories Services Ltd.) were the two biggest depositories which hold the maximum accounts of the nation [7].
4 4. T + 2 Rolling Day Settlement: [8] Rolling settlement is a settlement process where a trade executed in the stock market is settled in trading day plus 2 more working days. In the ring trading system, this process used to take days at minimum 5–6 days, but in online trading with the help of [9] depositories and back accounts and their sync with the stock exchanges, the time to complete the process of transferring shares from the account of seller to buyer and also monetary transaction of money from seller to buy’s account took only 2 days after the day of trading. This increased liquidity to a large extent as the money exchanged hands quickly.
5 5. Investor Registration Norms: The two major parties in stock broking are the investors and the brokers. The registration norms for both parties were made stricter. Brokers could not be registered unless they passed exams from NCFM to show that they have required knowledge of stock broking and its process. The clients could not trade unless they presented documents of their address, identity, and financial standing. These strict norms were not there earlier. These helped in making the stock broking forgery free.
6 6. Order Verification by SEBI: In this stage, a very elaborative order verification system was put in place. The brokers were directed very strictly that they need to get the order slips signed by the clients on a daily basis, and also after the end of each day, they were required to make a call to the clients and tell them the exact order which was executed on behalf of him. Stock exchanges and DPs were also advised to keep sending the order details and statements on a regular basis. All this helped in making the system very transparent and full proof where investors do not feel cheated. This all led to more satisfaction in the clients/investors [10].
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Organizational Transformation»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Organizational Transformation» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Organizational Transformation» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












