Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
This book discusses how the industrial internet will be augmented through increased network agility, integrated artificial intelligence (AI) and the capacity to deploy, automate, orchestrate, and secure diverse user cases at hyperscale.
Audience
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Big Data is the driving technology of IoT, related to data are currently the great creators and destroyers of business value. Since the IoT devices connected to the network are constantly sending, receiving, exchanging, and crossing data, i.e., constantly producing data. As a result, the accumulation, analysis, and use of Big Data are more significant, especially for companies, which have the most expressive production of data with IoT, as it has a large number of objects that can be connected or already connected. In addition, with data and information in hand, companies make fewer mistakes, produce more, and win more customers. To make sense (means of storing, tracking, analyzing, and making use of this large amount) of all this data (information), Big Data analysis has a fundamental role, which is critical for companies of all sizes [19, 40].
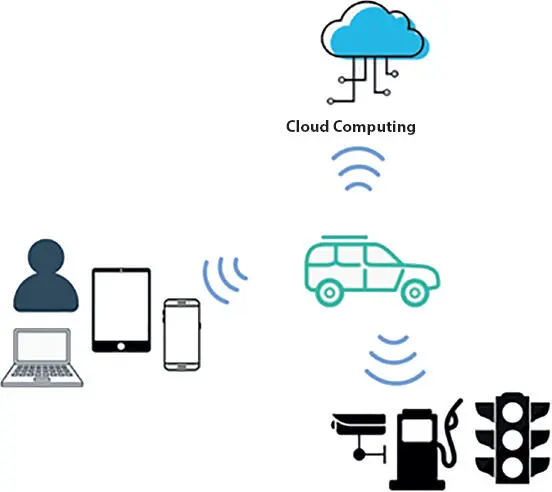
Figure 1.6 Connection to the car’s illustration.
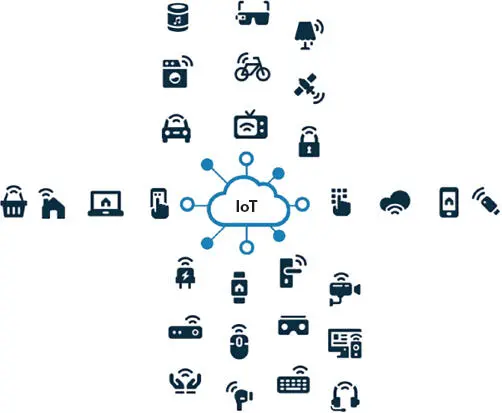
Figure 1.7 IoT devices.
Still pondering the seven main attributes that define and differentiate a normal object or device from an item that is part of the great mass of IoT connectivity, these devices and systems include sensors that track and measure activity worldwide. Internet connectivity will be in the item itself (thing/device), probably collecting information over time through sensors, exchanging messages, and files with a Cloud platform. Like any computer, the devices will have some built-in processing power, even if only to analyze and transmit data. Although many of the IoT devices are not yet equipped with special features to become really powerful in processing [41–43].
Efficient energy consumption is related to these devices being able to operate for a certain time or more on their own, using stored energy or staying connected only while used. Cost x benefit ratio is linked to the premise that several objects with sensors (must be relatively inexpensive to purchase and implant) distributed on a large scale to be really efficient, as in the case of food products in supermarkets that must have an indication of validity. Quality and reliability are related that many of the devices must operate exposed to harsh climates for long periods of time [41–43].
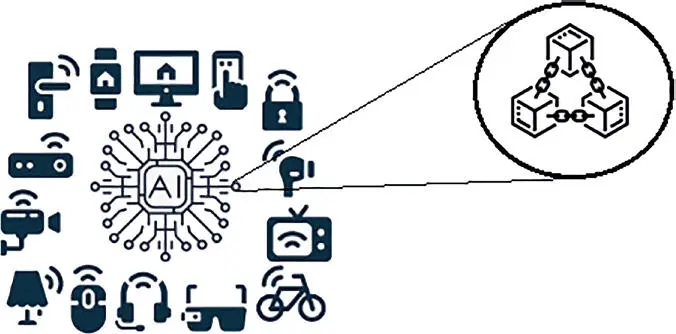
Figure 1.8 IoT and blockchain illustration.
Security is given that IoT machines and devices transmit private and detailed information, such as that related to the user’s health, still reflecting that the change from previously inert objects to a reality based on connectivity transforms businesses, products, and workflows to suit consumer trends and needs. In this respect, blockchain technology can promote more digital security ( Figure 1.8), so that objects connected to networks are not hacked [41–43].
However, the main potential of IoT is to carry out communication between objects, and people are given the practical nature, via the internet, “things” exchange signals with each other, i.e., mobile and fixed objects gain autonomy to interact with each other and with users. One of the greatest examples of this digital transformation in recent years is the increased use of IoT in homes and work relationships. Another technology that enhances the growth of IoT is AI, guaranteeing more autonomy and learning for objects connected to the internet [44].
1.3 IoT Ecosystem
IoT is basically things, i.e., it is all types of equipment/device/sensor that can be connected in different ways, from a truck to monitor the displacement of product transport fleets, use of sensors in tractors that measure the soil situation and send data to systems responsible for processing this information, and make suggestions for the best areas or times for planting, a boiler temperature sensor in a factory, or the adoption of devices at home, such as thermometers, energy consumption regulators, or home appliance managers, who allow the householder to control this equipment remotely, or even microsensors that monitor the status of patients remotely in hospitals or outside them [45].
In IoT, it is consistent with an environment whose rules deal with both connection and intelligent data collection and processing, since applications allow the coordinated and intelligent use of devices to control various activities, from monitoring with cameras and sensors to managing spaces and of productive processes. The IoT ecosystem is a system composed of a digital space of interaction including digital tools related to data analysis and modeling, as well as digital elements that integrate and interact within it. It is through these interactions and the exchange of information that AI allows these elements to work in an integrated manner, composing an intelligence potential far superior to what each of its elements has separately. The IoT ecosystem involves different agents and processes, such as smart objects [sensors, appliances, cars ( Figure 1.9), and factory automation equipment], smart modules (processors and memories), connectivity services (access to the internet or private networks that connect these devices), integrators (systems that combine applications, processes, and devices), enablers (control systems, collection, and processing of data and commands involving objects), and even providers of IoT services [45, 46].
Figure 1.9 Maintenance IoT vehicle illustration.
Within an IoT ecosystem, applications that integrate IoT technologies with Big Data technologies are operated, enabling the collection and analysis in real time of large data sets, allowing the development of predictive models for a variety of situations, from consumer behavior to the prevention of factory failures, and optimizing activities on the most varied fronts of activity. IoT technology brings changes both in the development of more pervasive connectivity and in the increase of data processing, derived from the refinement of sensors that allow data collection in different environments. All of this is associated with some practical solution allowing for increased efficiency, reduced human intervention, or even new business models [45], still evaluating that the AI generates a layer to enhance the value generated by the analysis of the different information captured and combined; allowing the automation of the decision-making process and actions in specific situations; bringing significant benefits to the increase in the speed of processes, reduction of the error rate due to human interference, and reduction of costs per transaction, in addition to the possibility of greater absorption of insights at each interaction that feedback and “teach” the AI algorithms (Machine Learning as an example); and making this incrementally more efficient [31].
In the digital transformation of the industry (relating the advent of the Fourth Industrial revolution), AI associates IoT with the combination of the ecosystem for data transmission between devices and the technology for analyzing this information independently, still conceptualizing the emergence of Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT). Considering that the IoT concept is related to the various IoT devices that collect data and create a network for transmitting critical information to administrators, on the other hand, AIoT data is processed by resources that analyze the standards providing only the information necessary for making a decision and can even make the necessary decisions without human involvement [17].
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












