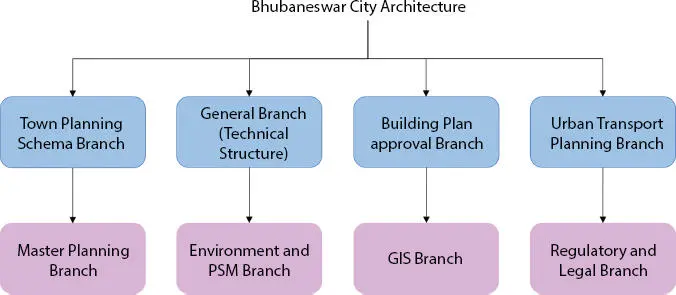
Figure 1.1 Bhubaneswar smart city structure.
1.2 Smart City Structure in India
1.2.1 Bhubaneswar City
In India, Bhubaneswar has the best infrastructural setup of smart city project. It is the city where center of economic and having more religious importance in Eastern part of India. Consistently, this city has proved its efficiency in assessment among top smart city around the globe. It plays vital role in digital communication with advanced technologies. Figure 1.1shows the Bhubaneswar smart city structure. This project included with construction engineering and green and park areas with road and development accessibility and slum accommodation.
For government entities smart city specifications are, technology for the traffic, parking, emergency response, and emergency control, digitalized payment services via command payment methods schema capital of business planning and e-governance in this smart project [2].
1.2.1.2 Healthcare and Mobility Services
The smart city’s primary focus is more on the child and elderly friendly option. Most of the homeless camp, however, defecate in the open. In an integrated safe urban transport scheme, several positive measures have been taken, including low carbon mobility program, and the e-rickshaws are introduced to reduce the carbon emission in environment and also to control the pollution-free society [2]. It is still in the planning stage, and a variety of commuters are debating that it is continuous to have the poor transport facilities.
Few centers for the skill development and the microbusiness incubators have also been developed. Most of these projects are small. Despite of that nearly 85 lakhs are unemployed in the year 2018, the rate of unemployment has soared to 6.77 from the past year percent of 4.7. In the first quarter of 2018, this state has ranked as the 7th among the state in India. In Bhubaneswar, there are 565 buses are linking the 67 wards with the help of the IT-backend support options the e-mobility attempt to update and develop the service under the Atal mission.
Vision of smart city in Pune is to redesign its streets and roads and its equal for all people. Pune Smart City overview is shown in Figure 1.2. Design of the city is based upon the universal accessibility for the elderly and physically challenged and increased focus on the pedestrians, modern world infrastructure through the creation of appropriate arrangements for underground utilities [3]. Allocation is mainly to motorized traffic, continuous excavation of roads, and weak pedestrian crossing for layout facilities.
Figure 1.2 Pune smart city overview.
This city has been developed to create an overall master plan based on a patented econometric model that will make Pune fit for the future up to 2030 comprehensive infrastructure specifications that have been completed for the next 5 years. It aims at a comprehensive range of urban options, including job opportunities creation, socio-economic growth, and beyond infrastructure and habitability [4].
1.2.2.2 Transport and Mobility
Real monitoring system of the live ongoing buses in the city is to track the location of different locations. Smart bus stops with the public information systems. This live tracking of the buses is availed through the mobile app by the people in this eco system. Around 319 signals are present in the city where the pedestrian right get the way for the emergency response system [4]. Also, advanced traffic management system by using the CCTV and the mobile GPS-based traffic system analysis is similar to Google live traffic system and intelligent road asset management system to help all.
1.2.2.3 Water and Sewage Management
New advanced technologies for water management are introduced in the smart bulk meters with the SCADA, for the commercial establishment; it used for the domestic households through the campaign along with a revised telescopic traffic.
1.3 Status of Smart Cities in India
According to the report the government of India has planned to launch 100 smart city missions (SCMs). These cities are able to provide decent roads, to build housing for everyone in the city, and also to create green spaces. Five years back, a substantial portion of the capital earmarked was no spent. A single network is yet to be completed by many smart cities. Actually, the project initial proposed for smart city was around 5,151 projects but only 3,629 have been actively pursued. In those number, only 25% of the projects are only have been completed [6]. But in the terms of value, the proportion of work done is just 11% of the total.
1.3.1 Funding Process by Government
Over 5 years, the central government has allocated Rs 48,000 crore to the mission. That amounts to an average of Rs 96 crore per city per year, maybe enough in many cities to create a sewage drain. An equivalent amount would have to be contributed by the states and urban local bodies of amount 96 crore. The city administration had to raise the remainder of the necessary financing through a host of sources-public-private partnerships, grants, resource monetization, and the likes. While renowned planners have created the smart city ideas, with the financial arrangements planned out in advance, most urban local authorities are struggling to raise the funds needed. While several bodies have raised concerns that the financing of the central government is insufficient, the government itself is not sympathetic [5, 6] and funds raised by government of India as shown in Figure 1.3. That any of the 30 cities will have no trouble collecting funds because they have A++ credit scores.
Pune is an smart example that has successfully launched a municipal bond, documenting its own process and replicating the success of the other cities.
The source of funds may vary in different countries; the sources of the smart city projects are provided by government and the private organizations; they are state government and the urban local bodies and central government. Public-private partnership organizations, convergence with the other government mission resources, and also load providers are all contributing in this mission progress. Analysts think that national transformative projects such as the Smart Cities Mission will take time to implement in a vast country like India. The mission is also suffering from the lack of urban planners.
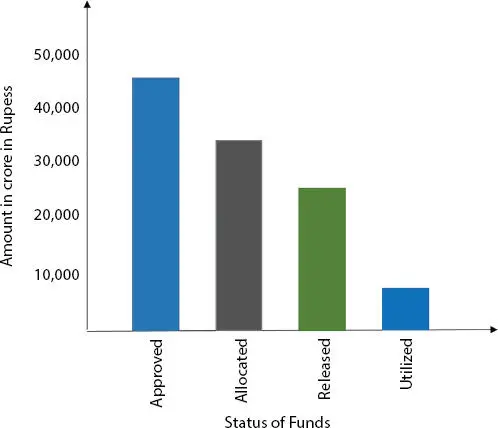
Figure 1.3 Funds raised by government of India.
1.4 Analysis of Smart City Setup
The vision of a community and the priorities of people form an important aspect of the planning of smart cities. Since each city has distinct strength and the disadvantages, it is possible that their respective approaches to creating a smart city will vary. Here are some attempt to analyze the possible variation of the city setup by economical-based setup architecture [6]. Cities can be turned smart with any mixture of different smart components. A city does not need to be branded as smart for all the components. The number of smart components depends on the cost and available technologies.
Читать дальше















