Key concepts in cognitive psychology come into play during visual recognition, and having some understanding of how the brain processes visual information can be helpful in training the eye to see ( Table 1). In figure–ground separation, the brain focuses on a perceived figure and tends to ignore the background. Thus, an important initial step in diagnosing disease when viewing microscopic slides is to train the brain to accurately identify the most important features (“figure”). In order to make sense of visual stimuli, the brain also automatically groups information. With all else being equal, similar objects will be grouped together, closer objects will be grouped together, and objects perceived as having a similar color/texture or common enclosure (“common region”) will be grouped together. Clues such as body site (Figure 4) and absence of obvious pathology (Figure 5 and Table 2) can also be useful.
Table 1 Visual recognition in dermatopathology as related to cognitive psychology.
| Dermatopathology |
|
Cognitive psychology concept |
| Overview (2×/4× ocular) |
“Tumor” versus “rash”ArchitectureBody siteCell type |
GestaltFigure–ground separationGrouping |
| Higher magnification (10×/20×/40× ocular) |
Confirm cell type/morphologyFiner details of architecture |
Grouping using finer detailsSimilarityProximityCommon region |
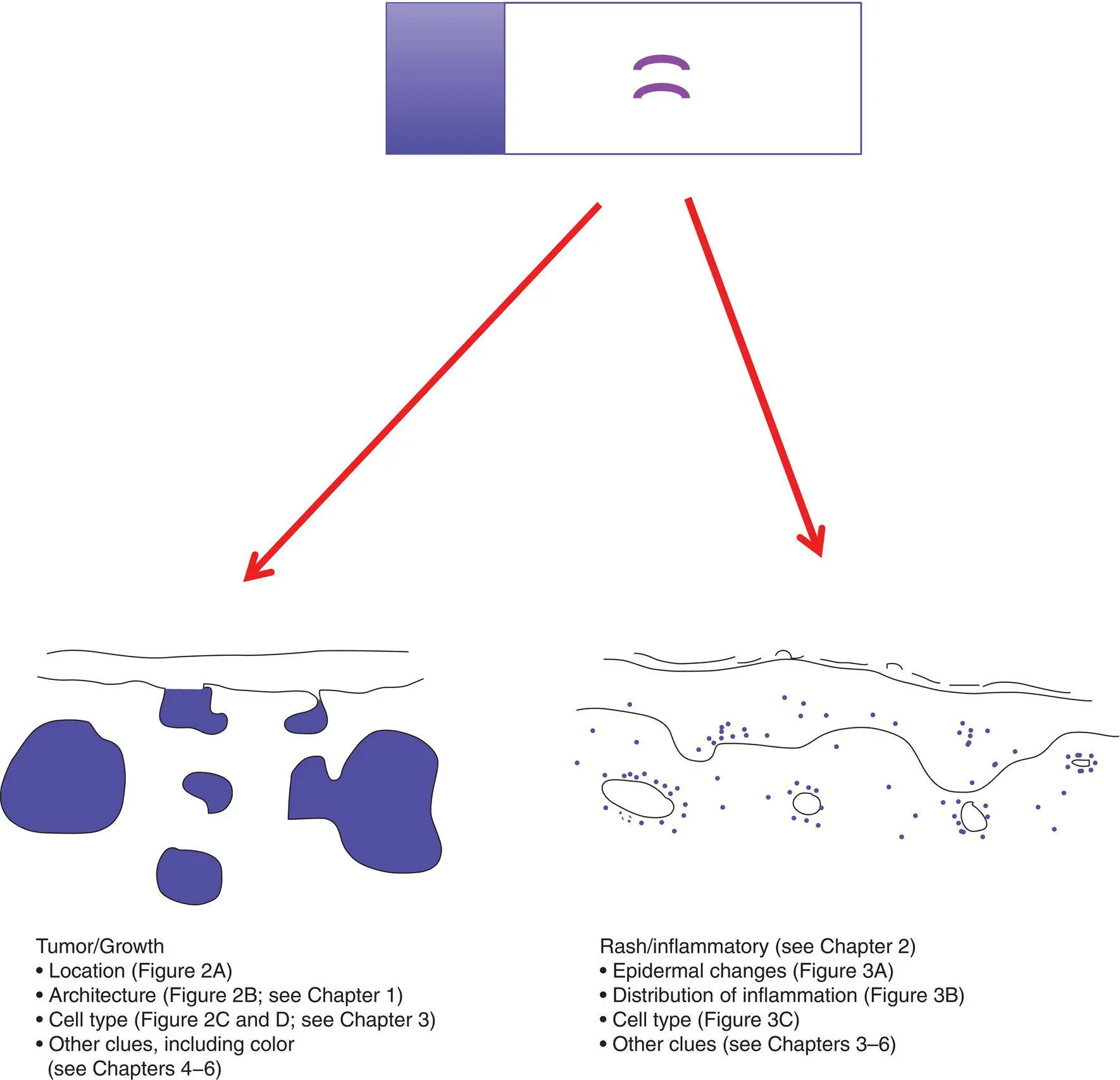
Figure 1 Gestalt impression of a slide
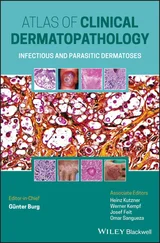
A major initial breakpoint in evaluating a specimen on a slide is the determination of the type of process: tumor/growth versus rash/inflammatory
NoteIn some cases, it is not readily apparent if the process is a tumor or an inflammatory process (examples include mycosis fungoides, a form of cutaneous T‐cell lymphoma, as well as deep fungal infections, which can induce florid epidermal hyperplasia mimicking a squamous cell carcinoma).
Figure 2(A)Location of the tumor
Important characteristics to consider for a tumor/growth include location (A), architecture (B), cell type (C), and benignancy versus malignancy (D). The eye can be trained to focus in on the blue areas (figure–ground separation; grouping)
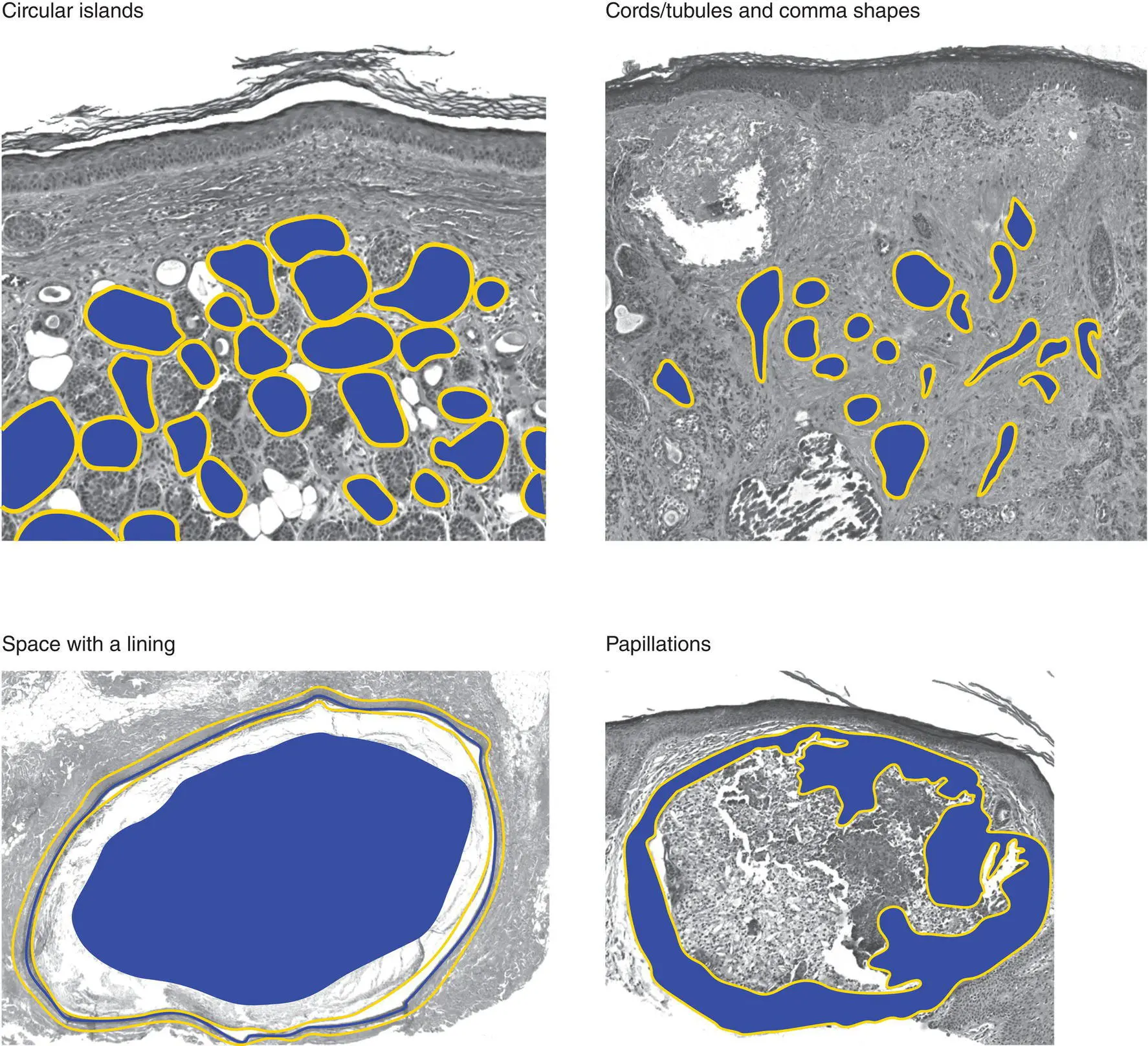
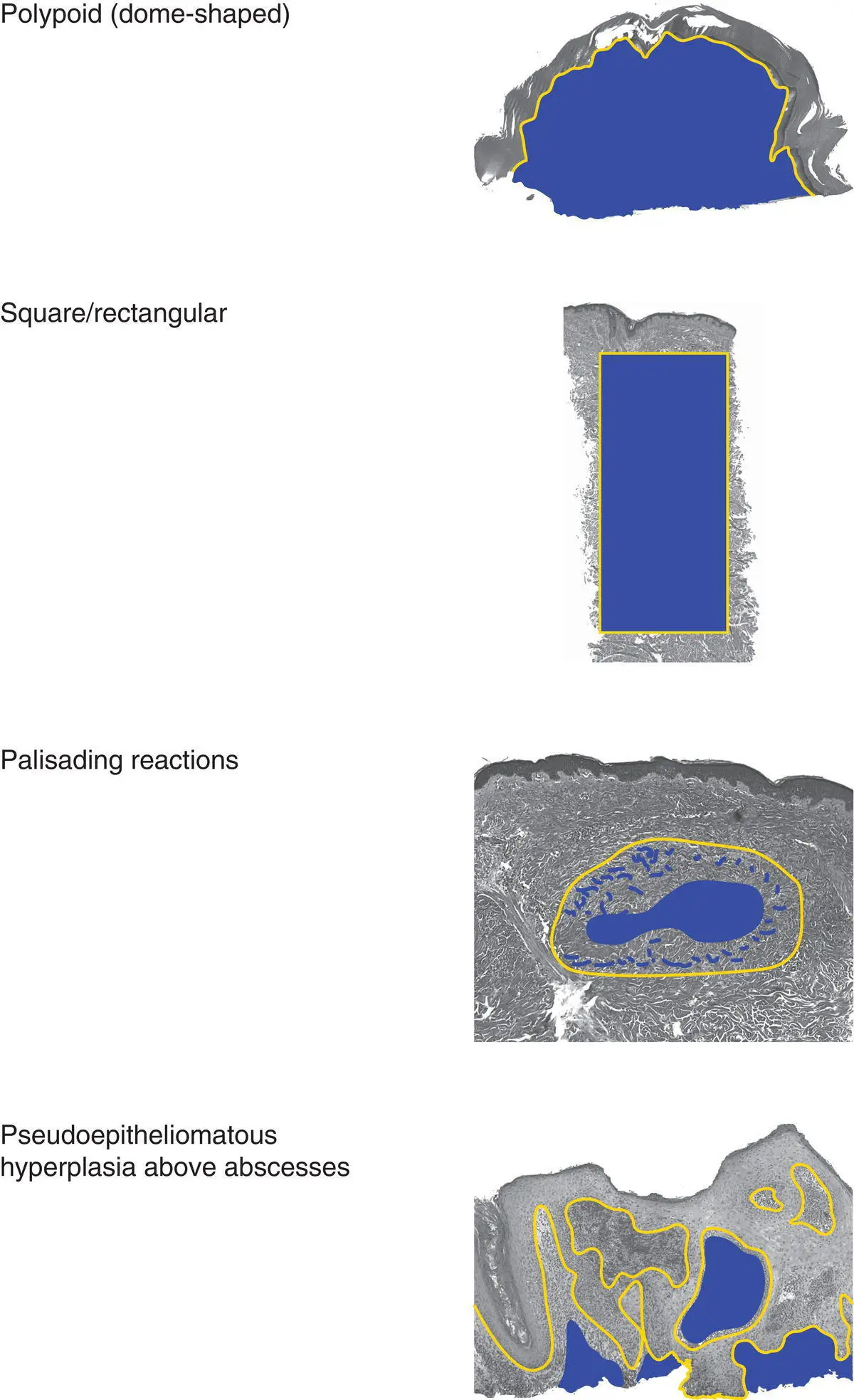
Figure 2(B)Architecture of an epidermal tumor/process
Dermal tumors can have various architectural patterns
NoteBenign tumors are often symmetric with a pushing border, and malignant tumors may be asymmetric and infiltrative.

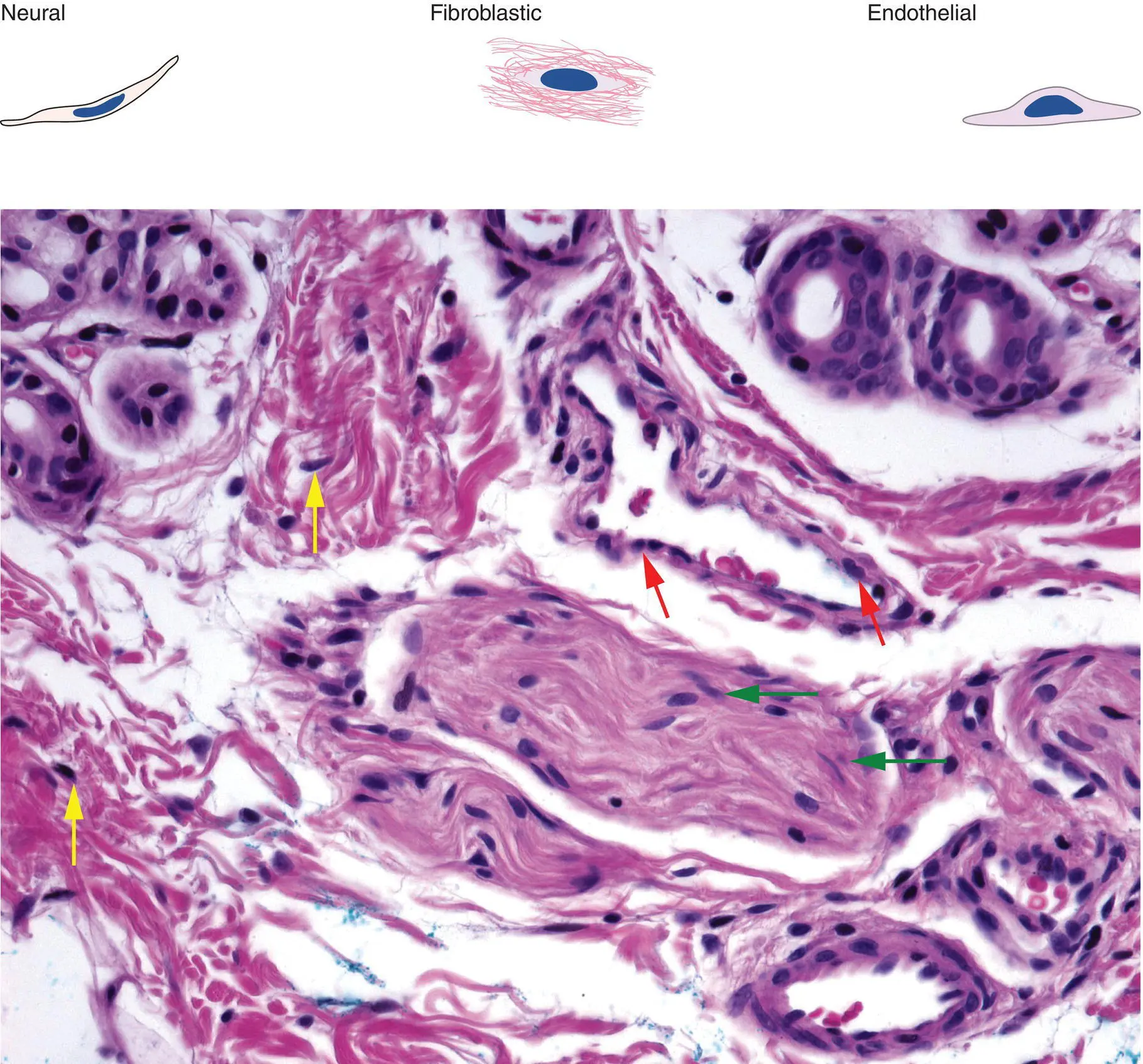
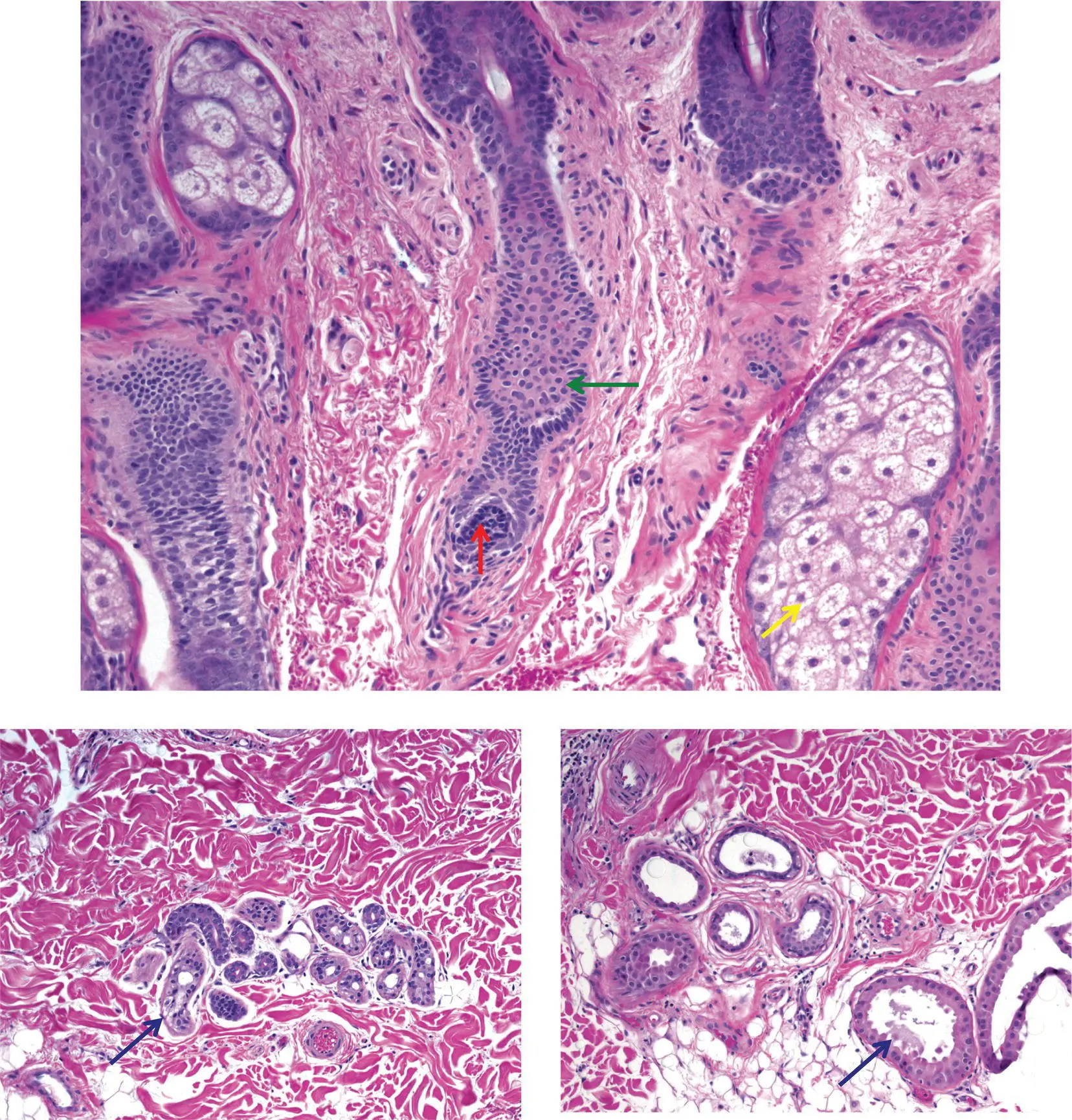
Figure 2(C)Different tumors are predominantly composed of a particular cell type
Keratinocytic: rectangular/polygonal shape, intercellular bridges, round nucleus and small nucleolus
Melanocytic: may be nested/clustered; nevomelanocytes (red arrow): oval nuclei, small nucleolus, pseudonuclear inclusions or melanin pigment may be evident; dendritic melanocyte (green arrow): thin cytoplasmic processes extending away from cell center
Smooth muscle: spindle cell with abundant cytoplasm, perinuclear clear space, cigar‐shaped nucleus
Adipocytic: thin membrane with compressed nucleus
Neural: spindle cell with tapered nucleus, pink cytoplasm (green arrows)
Fibroblast: spindle cell with oval nucleus (yellow arrows)
Endothelial: blue nuclei surrounding vascular spaces (red arrows)
Hair follicle: matrical cells are round to oval and dark blue (red arrow); outer root sheath cells are pale pink (green arrow)
Sebocytes: bubbly cytoplasm (yellow arrow) and central nucleus that may be star‐shaped (scalloped)
Eccrine gland and duct: the gland has clear cells (blue arrow); the duct has an eosinophilic pink cuticle
Apocrine gland and duct: the gland often shows decapitation secretion (black arrow)
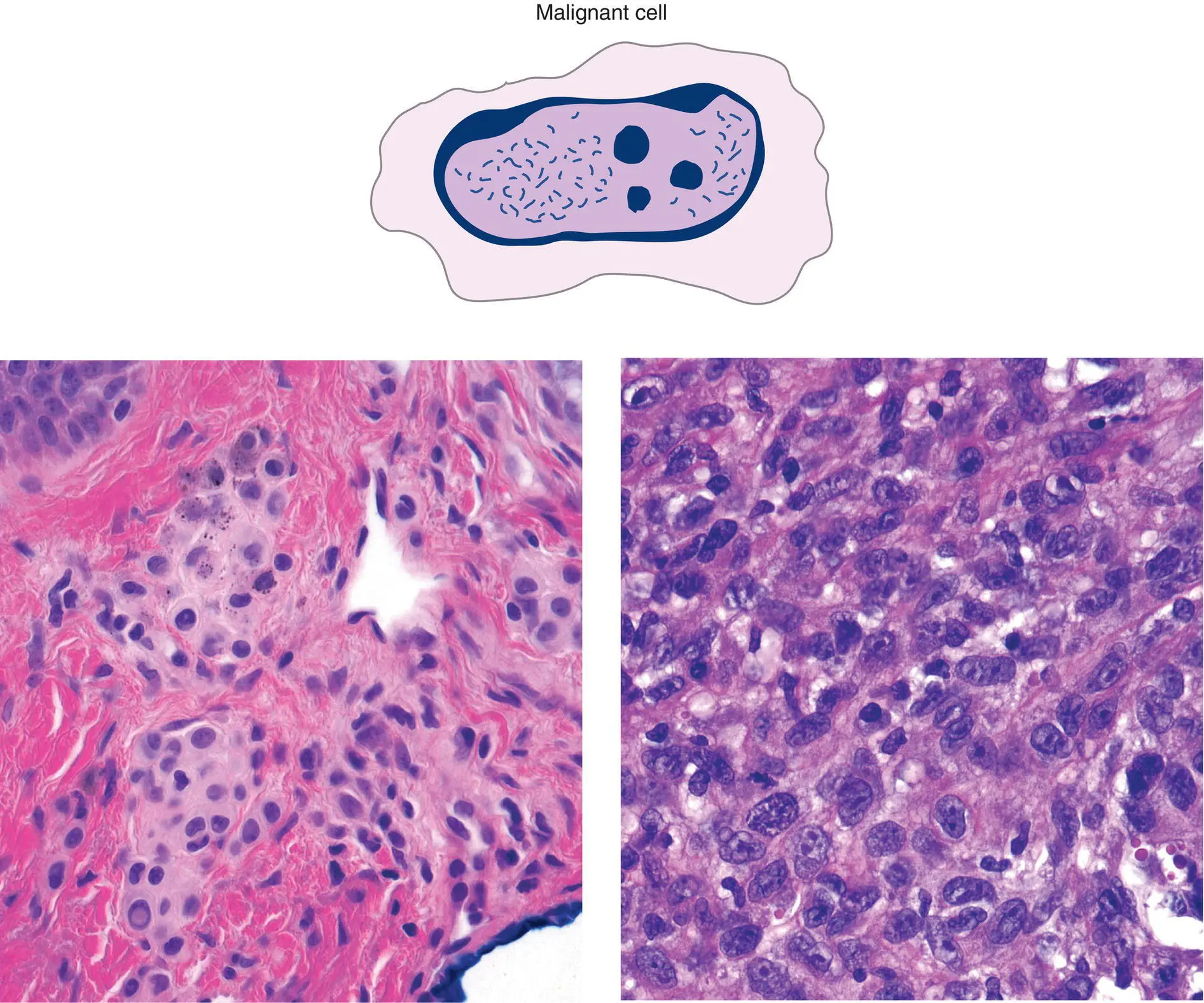
Figure 2(D)Cytologic features are important in pointing toward a benign versus malignant tumor
Malignant cells have high nuclear:cytoplasmic ratio, irregular chromatin pattern, irregular nuclear contours, irregular nucleolar shape and size
Primarily nuclear details suggest cytologic malignancy
Cytoplasmic features point to differentiation: keratinocytes – eosinophilic, hyalinized cytoplasm, melanocytes – fine brown pigment
| Benign nevomelanocytes (left) |
versus |
Melanoma cells (right) |
| Small nucleus, abundant cytoplasm |
|
Large nucleus, relatively little cytoplasm |
| Smooth nuclear border |
|
Irregular nuclear border |
| Chromatin pattern nondescript |
|
Irregular, chunky nuclear contents (chromatin) |
| Inconspicuous nucleolus |
|
1 or more large, purple nucleoli |
“Rash”: key concepts
The eye can be trained to focus in on the blue areas (figure–ground separation; grouping)
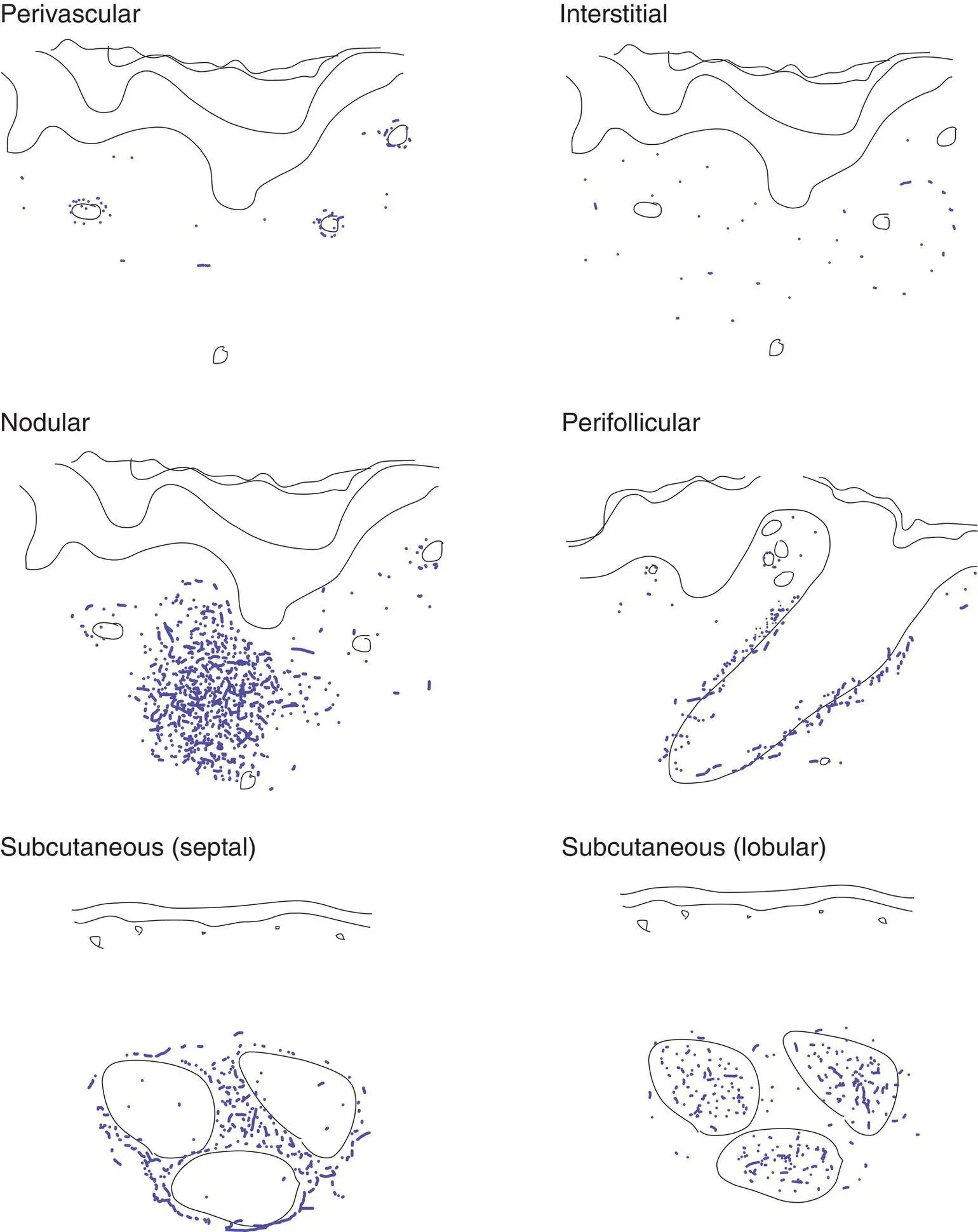
Key features include epidermal changes (A), distribution of inflammation (B), and inflammatory cell type (C)
Parakeratosis is often present in spongiotic and papulosquamous disorders; dry parakeratosis without serum but with neutrophils is suggestive of psoriasis
Simplistically, a dermatitis can be categorized as spongiotic, papulosquamous, or interface
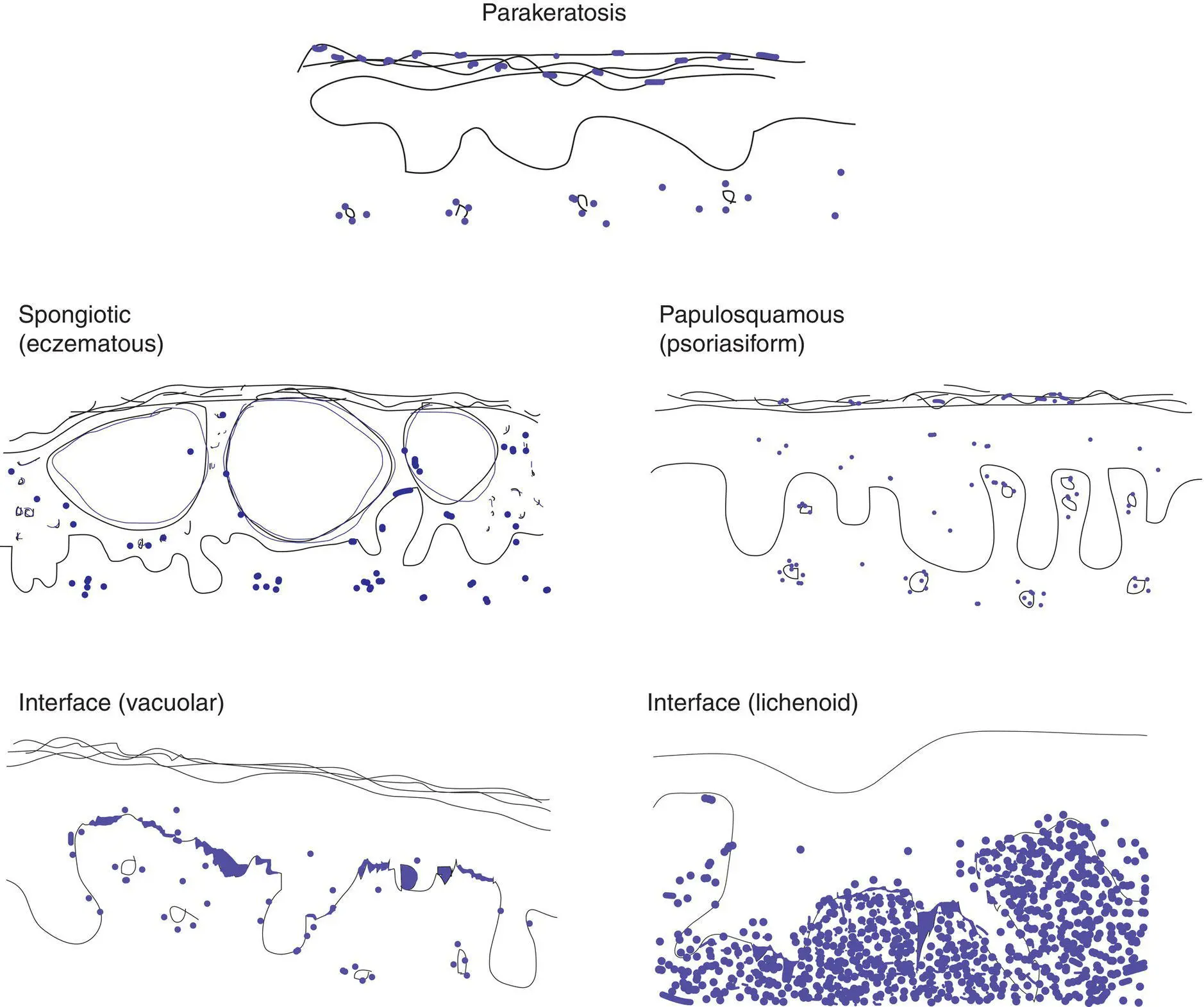
Figure 3(A) Key epidermal changes
Parakeratosis: retained nuclei in the stratum corneum
Spongiosis: increased intercellular spaces and sometimes vesicles
Papulosquamous: thickened epidermis with parakeratosis
Interface (vacuolar): spaces in basal cells, which may be polygonal (squamatized), lymphocytes at junction
Interface (lichenoid): dense band of lymphocytes between epidermis and dermis with necrotic keratinocytes
Читать дальше