
“Management Accounting.” is based on the idea that all accounting/controlling considerations in an enterprise are always focused on the Big Picture – the comprehensive overview or comprehensive presentation of these business activities as a whole. All business activities are always analyzed and evaluated with reference to this overall connection.
For this reason there are substantial differences in “Management Accounting.” compared to classical textbooks on accounting/controlling or to standard literature in the field of accounting/controlling.
In order to give a total, general overview of the connections in accounting – independent of national and international trade and tax laws – neither references to legal texts are given nor paragraphs or legal regulations are mentioned.
Concentrating on the connections, certain specific parts which are of importance to specialists in accounting are excluded and avoided on purpose, because for newcomers in accounting they usually produce fear of approach.
In this context, in “Management Accounting.”, a kind of presentation has been chosen to show the connections between balance sheet and profit/loss account, so that only the final effects of economic activities are considered directly in balance sheet and profit/loss account, whereas the usual presentation of detailed account items and entry formulas is completely avoided.
The approach that is used in “Management Accounting.” focuses on two central connections which form the basic structure of presenting the economic activities in accounting/controlling of an enterprise:
The first of these two connections is the basic connection between Balance Sheet and Profit/Loss Account.
The second decisive connection is based on the interaction of the components result (profit or loss respectively), liquidity (solvency) and balance sheet which – with a view to the future – are presented through the elements Profit Plan, Finance Plan and Budgeted Balance Sheet.
Combining the two groups of topics Balance Sheet | Profit/Loss Account and Profit Plan | Finance Plan | Budgeted Balance Sheet, the circle of the effects of economic activities of an enterprise closes. The connection of accounting/controlling as a whole opens up.
The two central groups of topics which are presented in “Management Accounting.” – Balance Sheet | Profit/Loss Account and Profit Plan | Finance Plan | Budgeted Balance Sheet meet exactly at the interface between past, current and future situation:
The group of topics: Balance Sheet | Profit/Loss Account deals with the past or the current situation of the enterprise.
The group of topics: Profit Plan | Finance Plan | Budgeted Balance Sheet deals with the future development of the enterprise.
The basic elements which are used remain the same in both groups of topics, also the contents and connections. What changes is the way they are considered and the terms which are used.
In a first step, “Management Accounting. Part 1 - Balance Sheet | Profit/Loss Account” deals with the presentation of the basic contents of and the connection between the elements Balance Sheet and Profit/Loss Account. Subsequently and building on them, the connections described are presented and annotated in form of case studies.
The second fundamental connection in accounting, the central “Accounting/Controlling Overall Context”, the connection between the elements Profit Plan, Finance Plan and Budgeted Balance Sheet is shown in “Management Accounting. Part 2 - Profit Plan | Finance Plan | Budgeted Balance Sheet”.

2. Survey of the Contents

“Management Accounting.” covers the range:
- from the effects of business activities regarding the aspects of profit/loss, liquidity or solvency respectively (presented through surplus of or demand for cash) and balance sheet,
- via the central elements of accounting/controlling: Balance Sheet, Profit/Loss Account, Profit Plan, Finance Plan and Budgeted Balance Sheet,
- as well as to their development from a time-wise point of view – from the past over the current situation (each presented through Balance Sheet and Profit/Loss Account, possibly also through a Cash Flow Statement) to the future (presented through Profit Plan, Finance Plan and Budgeted Balance Sheet).
The following short overview of the elements and connections used is meant to make the structure of “Management Accounting.” easier for the reader and also to help with assigning the contents.
The following elements are presented in this overview:

The presentation of all details referring to the elements and connections mentioned here, can be found in “Management Accounting. Part 1 - Balance Sheet | Profit/Loss Account” on the one hand, and in “Management Accounting, Part 2 - Profit Plan | Finance Plan | Budgeted Balance Sheet” on the other hand, and also as an overall presentation in the textbook “Management Accounting.” which forms the basis for “Management Accounting. Part 1” and “Management Accounting. Part 2”.
2.1. Balance Sheet 
A balance sheet is always a look at the enterprise at a certain point in time. It contains permanently stock values.
The balance sheet presents – referring to a certain point in time – the goods or assets an enterprise has available at exactly this moment and in what way the enterprise is financed at this moment (with equity or debt capital / liabilities).
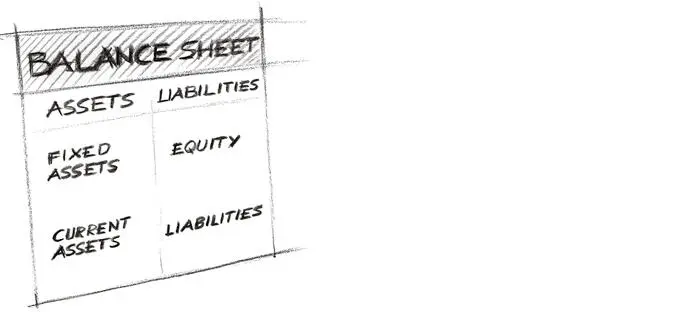
Figure 1: Balance Sheet
On the left side of the balance sheet, the assets side, the assets of an enterprise are presented, structured into fixed assets (non-current assets) and current assets. On the right side of the balance sheet, the liabilities side, the source of the financial means of the enterprise is presented, differentiating between equity and debt capital.
Detailed explanations concerning the balance sheet follow in chapter 3 - Balance Sheet | Profit/Loss Account.
2.2. Profit/Loss Account 
The profit/loss account, in contrast to the balance sheet, is a period of time-oriented reflection of an enterprise, a consideration of the economic development of an enterprise in the course of time. The profit/loss account contains permanently flow values.
In the profit/loss account the result of the business activity (the profit or loss of the enterprise respectively) is presented – in form of the difference between expense and income. The income or turnover/sales which are achieved by selling products, goods or services are compared to the arising expense in the enterprise and the result of the comparison leads to the profit or loss of the enterprise.
Читать дальше



















