Cloud Computing Solutions
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Cloud Computing Solutions» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Cloud Computing Solutions
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Cloud Computing Solutions: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Cloud Computing Solutions»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
The main purpose of this book is to include all the cloud-related technologies in a single platform, so that researchers, academicians, postgraduate students, and those in the industry can easily understand the cloud-based ecosystems.
Audience
Cloud Computing Solutions — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Cloud Computing Solutions», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
In 1997, the term “cloud computing” was introduced in academia by Ramnath Chellappa, who defined it as a “computing paradigm where the boundaries of computing will be determined by economic rationale rather than technical limits alone.” In 1999, Salesforce started conveying applications to their clients utilizing basic websites. The actual applications were undertaken and dispersed over the web; in this manner, utility-based computing began being used in the real world. Amazon started its point of reference by creating Amazon Web Services (AWS) and conveying storage services, estimations and so on in 2002. Amazon allows clients to integrate its immense online substance with their own website. Its web services and computing facility have expanded slowly upon request. In 2006, Amazon initially launched its Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) 3as a commercial internet benefit that allows small enterprises and individuals to lease infrastructure (resources, storage, memory) upon which they can carry and run their own applications. With the implementation of Amazon storage (Amazon S3), a “pay-per-use” model was also implemented. Cloud’s Google App Engine, 4 Force.com, Eucalyptus, 5Windows Azure, 6Aneka 7and a lot more of their kind are capturing the cloud business.
The next section is about cluster, grid and mobile computing.
1.2 Cluster Computing
A computer cluster can be characterized as an arrangement of several coupled computers cooperating in such a way that every machine can be viewed as a single system image (SSI). Computer clusters are developed by merging a colossal number of computer developments, including access to fast networks, low-cost MPs, and software that delivers high-performance computing.
According to Sadashiv and Kumar [4], a cluster can be defined as the collection of distributed or parallel computers attached among themselves with the help of high-speed networks such as SCI, Myrinet, Gigabit Ethernet and InfiniBand. They function collectively in the execution of data- and compute-intensive tasks that would not be feasible for a single computer to execute alone. The clusters are mostly used for load balancing (to distribute the task over the different interconnected computers), high availability of the required data, and for compute purpose. The interconnected computers are used due to their high availability as they maintain the redundant nodes which are being utilized to convey the required service when the system components fail.
The performance of the system is upgraded enough and enhanced in that case because regardless of whether one node neglects to figure out the task, there is another backup node which will be ready to convey the task and takes on the simple single purpose without any snags [5]. At the point when numerous computers are connected in a computer cluster, they can easily share computational workload as a single virtual computer. From the client’s perspective, they are numerous machines, yet they are working as a single virtual machine. The client’s demand is received and appropriated among all the independent computers to shape a computer cluster. This outcome is adjusted and reasonable computational workload is shared among various machines, enhancing and improving the computational performance of the cluster systems. Frequently clusters are used for the most part for computational purposes, and than for taking care of IO-based exercises.
1.2.1 The Architecture of Cluster Computing Environment
Figure 1.2represents the cluster where numerous independent computers, an operating system, a correspondence or networked system and an elite interconnecting medium, middleware and diverse application are incorporated. A computer is either a single or a multiprocessor system with memory, Input/Output provisions and operating system. A computer cluster for the most part alludes to at least two quantities of computers (nodes) interconnected. The nodes can remain in a specific bureau or can be physically particular and associated through fast LAN. The network interface equipment fills in as a correspondence processor; however, it transmits and gets packets of information between cluster nodes via a system/switch. Correspondence programming is in charge of fast and dependable information exchange among cluster nodes and the exterior. The cluster middleware remains in the middle of the numerous personal computers or workstations and several applications. It fills in like single system image producer and accessibility infrastructure. Programming situations offer proficient, compact and easy-to-use apparatuses for application improvement. Computer clusters are also being used for the execution of parallel and consecutive applications.
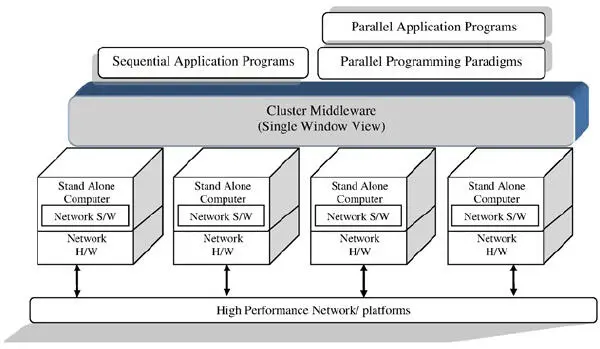
Figure 1.2: Architecture of computer cluster.
1.2.2 Components of Computer Cluster
A typical computer cluster has some prominent components which are used to do a specific task [6]. The components are as follows:
1 Multiple high-performance computers (PCs, workstations or SMPs)
2 State-of-the-art operating systems (layered or micro-kernel based)
3 High-performance networks/switches (such as Gigabit Ethernet and Myrinet)
4 Network interface cards (NICs)
5 Fast communication protocols and services (such as active and fast messages)
6 Cluster middleware (single system image (SSI) and system availability infrastructure):Hardware (such as digital (DEC) memory channel, hardware DSM, and SMP techniques),Operating system kernel or gluing layer (such as Solaris MC and GLUnix),Applications and subsystems applications (such as system management tools and electronic forms),Runtime systems (such as software DSM and parallel file system),Resource management and scheduling software, such as ISF (load sharing facility),CODINE (computing in distributed networked environments)
7 Parallel programming environments and tools (such as compilers, PVM (parallel virtual machine), and MPI (message passing interface)), and
8 Applications of sequential, parallel or distributed computing.
1.3 Grid Computing
Carl Kesselman and Ian Foster first coined the term grid computing in the 1990s, which is characterized as resource sharing and critical thinking in unique, multi-institutional virtual associations [7]. We have to contrast grid computing’s classification with cluster. While clusters use the same operating system and hardware and run locally, grids involve heterogeneous computer systems that are interconnected with one another and distributed globally. The hardware and OSs run on the machines could also be distinct from each other [5, 8].
Grid computing is a convoluted component which has progressed by means of earlier advancements in parallel, dispersed and high-performance computing (HPC) [9, 10].
The real and specific problem that underlies the Grid concept is coordinated resource sharing and problem solving in dynamic, multi-institutional virtual organizations. The sharing that we are concerned with is not primarily file exchange but rather direct access to computers, software, data, and other resources, as is required by a range of collaborative problem-solving and resource-brokering strategies emerging in industry, science, and engineering. This sharing is, necessarily, highly controlled, with resource providers and consumers defining clearly and carefully just what is shared, who is allowed to share, and the conditions under which sharing occurs. A set of individuals and/or institutions defined by such sharing rules form what we call a virtual organization (VO) [2].
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Cloud Computing Solutions»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Cloud Computing Solutions» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Cloud Computing Solutions» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












