The maximum amplitude of relative migrations close to the amplitude of absolute surface vibrations occurs at a sufficiently large value of acceleration Aω 2, when particles of an unconsolidated reservoir remain practically immobile in space.
A case of rectilinear extensional vibration of the surface displays the same patterns of vibration penetration as the considered case of circular vibrations. Solution of the problem here is more complex than in the case of circular vibration, especially for the second model, because the particle motion occurs with two long or instantaneous stops in each vibration period [5].
A different situation occurs with the vibration penetration process in individual reservoir layers in a case of transverse surface vibration of one of the layers. Experimental data indicate exponential nature of particles’ vibration amplitude decline with certain distance from the vibrating surface of one of the layers. Let us denote v a pulsating component of the reservoir particle velocity and introduce a function

where R is the velocity recovery factor at a strike, and V 0is some characteristic velocity value. This function will satisfy equation of heat conductivity type equation, i.e., will play the role of quasi-temperature [9]. Figure 2.6shows diagrams of the function U x/ U 0at various values of the recovery factor R . Fading of the velocity of reservoir particles has exponential nature, which agrees with the above mentioned experimental results.
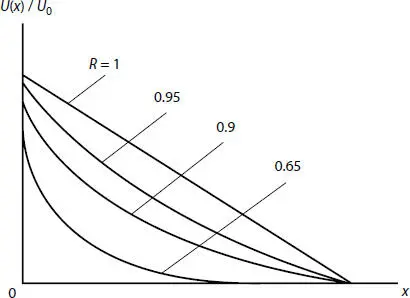
Figure 2.6 Velocity distribution in unconsolidated reservoir at transverse vibrations of its confining surface.
Certain specificity is typical of the vibration penetration dynamics in the cement grouts. The cement grouts are a multi-component medium composed of large and small filling aggregate, cohesive material, and water especially selected by the composition. In the process of mixture preparation, air unavoidably is getting into it. The amount of air in the mixture is relatively small (and is changing in the preparation process). Physicomechanical properties of the mixture and of the solidified cement substantially depend on its contents. As result, there is a rather complex rheological property of the cement mixture. Most important among them are resistance of a dry friction type and also the viscous friction and elasticity (the elasticity is mostly defined by the presence of air component). The vibration causes transformation of the mixture rheological parameters and properties, in particular, its pseudo-fluidization, which provides for the efficient compaction necessary for obtaining a cement with high strength parameters. For this reason, the cement mixture is modeled in theoretical studies as a continuous medium with elastic, plastic, and viscous properties.
2.4 Excitation of Vibration in Oil Reservoirs
Vibration excitation in oil reservoirs is best studied in cases of power load application directly to the land surface. It is implemented for a directional vibroseismic action on shallow oil accumulations and for a solution of seismic exploration tasks. Of greatest interest are issues of coordinating the sources with the medium from a point of view of the best transformation of the source power in the power of irradiated waves. Reviewed have been the models of spherical sources and sources distributed over the surface of elastic half-space [25]. A solution of the problem of creating efficient method of forming highly directional radiation suggests that the use of acoustic antenna theory constructed for ideal uniform acoustic medium in a case of stratified media results in significant errors. Taking into account vertical nonuniformity of the medium plays an important role for obtaining acceptable practical results. Distribution studies of energy supply arriving in multilayer elastic half-space from a harmonic surface power loading established that, in the multilayer half-space, may exist the frequency range wherein emerge reflected waves with the opposite direction of phase and group velocities.
An analysis of energy flow lines, which may be strongly involuted up to generating the areas where energy is circulating on closed trajectories, indicated the following. In the vicinity of resonance frequencies, the power flow of these internal circular flows may substantially exceed the flow coming from the source. This indicates a possibility of a vibration source energy accumulation with an unlimited amplitude increase in certain areas of semi-infinite laminated space. In these studies, the actual rocks have been modeled by an elastic medium. The solutions of dynamic problems for elastoporous media are known where, applying the Frenkel-Bio equations was conducted an analysis of the wave field excitation by a load varying in time according to the harmonic law. At that, the excited field energy distribution by the wave type has been estimated.
Similar tasks related to the half-space force excitement had a practical value for selecting efficient vibroseismic action regimes on shallow oil reservoirs using powerful surficial vibration sources developing force up to 10 6H.
The energy transfer processes from well to a reservoir are associated with substantial difficulties. These difficulties are associated with well geometry and paucity of a well as an irradiator compared with the excited wave length. If a source is creating vibration in the well fluid, then the field generated in the surrounding reservoir is equivalent to the field of an infinitely long cylinder on the surface of which one of possible is excited vibration modes. In this case, a solution of the wave equation is
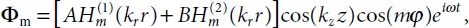
where 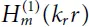 and
and 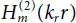 are Hankel functions of the first and second kind, m = k y R c; R cis the well radius; k r, k y, and k zare wave numbers.
are Hankel functions of the first and second kind, m = k y R c; R cis the well radius; k r, k y, and k zare wave numbers.
The first term in this equation corresponds to a wave converging to the cylinder axis, and the second term corresponds to the wave expanding from the cylinder. For the expanding running waves, the k rnumber must be a real value, i.e., the condition  must be observed. If k z˃ k r, then k ris a purely imaginary value, and in such a case, the field sharply exponentially declining with distancing from the cylinder surface. No irradiation occurs in such a case. The length of a flexural wave in the axial direction turns out smaller than a sound wave in the encircling medium regardless of another wave number k y= m/R e, which corresponds to the circular system of nodal lines. If we introduce the angle θ = arcsin ( ξ/k ), k = ωR e /c as the incidence angle or reflection angle of cylindrical wave, normal or modulated by front, then at incidence angles smaller than θ 1= arcsin( c/ c p), the energy enters the reservoir, and at the angle larger than θ 1, it returns in the well for forming head-waves in the liquid. Within the angle range between a critical value θ 1to the second critical value θ 2= arcsin( c/c s), the energy flow into the medium is caused only by irradiation of the shear waves. At high frequencies, such that
must be observed. If k z˃ k r, then k ris a purely imaginary value, and in such a case, the field sharply exponentially declining with distancing from the cylinder surface. No irradiation occurs in such a case. The length of a flexural wave in the axial direction turns out smaller than a sound wave in the encircling medium regardless of another wave number k y= m/R e, which corresponds to the circular system of nodal lines. If we introduce the angle θ = arcsin ( ξ/k ), k = ωR e /c as the incidence angle or reflection angle of cylindrical wave, normal or modulated by front, then at incidence angles smaller than θ 1= arcsin( c/ c p), the energy enters the reservoir, and at the angle larger than θ 1, it returns in the well for forming head-waves in the liquid. Within the angle range between a critical value θ 1to the second critical value θ 2= arcsin( c/c s), the energy flow into the medium is caused only by irradiation of the shear waves. At high frequencies, such that  we have cos θ ≈ 1, and the waves irradiated by the cylinder spread perpendicular to its surface. With the k decline, the θ angle is increasing, and at k = k z, the wave is spreading only tangentially to the cylinder’s surface. As soon as the axial flexural wave length becomes shorter than the sound wave length in the enclosing medium, appropriately k becomes smaller than k z, and the cylinder-well is not radiating in the enclosing medium at all. Irradiation in a case
we have cos θ ≈ 1, and the waves irradiated by the cylinder spread perpendicular to its surface. With the k decline, the θ angle is increasing, and at k = k z, the wave is spreading only tangentially to the cylinder’s surface. As soon as the axial flexural wave length becomes shorter than the sound wave length in the enclosing medium, appropriately k becomes smaller than k z, and the cylinder-well is not radiating in the enclosing medium at all. Irradiation in a case 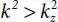 is studied in great detail, the results are practically applied in geophysical acoustic studies in wells and at high-frequency thermoacoustic action on the reservoir’s bottomhole zone.
is studied in great detail, the results are practically applied in geophysical acoustic studies in wells and at high-frequency thermoacoustic action on the reservoir’s bottomhole zone.
Читать дальше



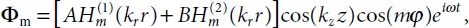
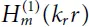 and
and 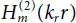 are Hankel functions of the first and second kind, m = k y R c; R cis the well radius; k r, k y, and k zare wave numbers.
are Hankel functions of the first and second kind, m = k y R c; R cis the well radius; k r, k y, and k zare wave numbers. must be observed. If k z˃ k r, then k ris a purely imaginary value, and in such a case, the field sharply exponentially declining with distancing from the cylinder surface. No irradiation occurs in such a case. The length of a flexural wave in the axial direction turns out smaller than a sound wave in the encircling medium regardless of another wave number k y= m/R e, which corresponds to the circular system of nodal lines. If we introduce the angle θ = arcsin ( ξ/k ), k = ωR e /c as the incidence angle or reflection angle of cylindrical wave, normal or modulated by front, then at incidence angles smaller than θ 1= arcsin( c/ c p), the energy enters the reservoir, and at the angle larger than θ 1, it returns in the well for forming head-waves in the liquid. Within the angle range between a critical value θ 1to the second critical value θ 2= arcsin( c/c s), the energy flow into the medium is caused only by irradiation of the shear waves. At high frequencies, such that
must be observed. If k z˃ k r, then k ris a purely imaginary value, and in such a case, the field sharply exponentially declining with distancing from the cylinder surface. No irradiation occurs in such a case. The length of a flexural wave in the axial direction turns out smaller than a sound wave in the encircling medium regardless of another wave number k y= m/R e, which corresponds to the circular system of nodal lines. If we introduce the angle θ = arcsin ( ξ/k ), k = ωR e /c as the incidence angle or reflection angle of cylindrical wave, normal or modulated by front, then at incidence angles smaller than θ 1= arcsin( c/ c p), the energy enters the reservoir, and at the angle larger than θ 1, it returns in the well for forming head-waves in the liquid. Within the angle range between a critical value θ 1to the second critical value θ 2= arcsin( c/c s), the energy flow into the medium is caused only by irradiation of the shear waves. At high frequencies, such that  we have cos θ ≈ 1, and the waves irradiated by the cylinder spread perpendicular to its surface. With the k decline, the θ angle is increasing, and at k = k z, the wave is spreading only tangentially to the cylinder’s surface. As soon as the axial flexural wave length becomes shorter than the sound wave length in the enclosing medium, appropriately k becomes smaller than k z, and the cylinder-well is not radiating in the enclosing medium at all. Irradiation in a case
we have cos θ ≈ 1, and the waves irradiated by the cylinder spread perpendicular to its surface. With the k decline, the θ angle is increasing, and at k = k z, the wave is spreading only tangentially to the cylinder’s surface. As soon as the axial flexural wave length becomes shorter than the sound wave length in the enclosing medium, appropriately k becomes smaller than k z, and the cylinder-well is not radiating in the enclosing medium at all. Irradiation in a case 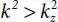 is studied in great detail, the results are practically applied in geophysical acoustic studies in wells and at high-frequency thermoacoustic action on the reservoir’s bottomhole zone.
is studied in great detail, the results are practically applied in geophysical acoustic studies in wells and at high-frequency thermoacoustic action on the reservoir’s bottomhole zone.










