Alexander Akulov - Manual of comparative linguistics
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Alexander Akulov - Manual of comparative linguistics» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. ISBN: , Жанр: Языкознание, на русском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Manual of comparative linguistics
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:9785447441906
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Manual of comparative linguistics: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Manual of comparative linguistics»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Manual of comparative linguistics — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Manual of comparative linguistics», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
As far as any language actually has some ability to make prefixation so there is no strict border between languages with prefixation and languages without prefixation and we should give up ideas of strict subdivision of all existing languages into two sets that have no intersection.
Hence thereupon, linear model of word forms have the following structures:
(P) + (R) + r + (s) – linear model of word form of American type;
(p) + (r) + r + (S) – linear model of word form of Altaic type.
Capital letters are markers of positions that are used more than positions marked by small letters.
Thereby, there is no principal structural difference between languages of American type and Altaic type, difference is in degree of manifestation of certain parameters and so, in order to our conclusion will not be speculative, we should speak about degree of prefixation producing ability / prefixation ability degree / prefixation ability index, i.e.: of certain measure of prefixation.
I suppose that each language has its own ability to produce prefixation and that this ability doesn’t change seriously during all stages of its history.
Also I suppose that prefixation ability demonstrates itself in any circumstances, i.e.: it is manifested by any means: by means of original morphemes existing in a certain language or by borrowed morphemes.
If a language has certain prefixation ability it is shown anyway. That’s why I don’t make difference between original and borrowed affixes.
Also for current consideration is not principal whether this or that affix is derivative or relative: if we take into account relative affixes only, then, for instance, Japanese is a language without prefixes.
That’s why we should define prefixes not by its derivative or by its relative role but by its positions inside word form, prefix is any morpheme that meets the following requirements:
1) it can be placed only left from nuclear position;
2) it never can be placed upon nuclear position;
3) between this morpheme and nuclear can’t be placed any meaningful morpheme with its clitics (i.e.: between nuclear root and prefix can’t be placed a meaningful morpheme with its auxiliary morphemes).
I am specially to note that there are no so called semi-prefixes. If a morpheme can be placed in nuclear position it is meaningful morpheme and any combinations with it should be considered as compounds.
Thus can be resumed the following:
1) Each language has its own ability to produce prefixation and this ability doesn’t change seriously during all stages of its history.
2) Prefixation ability is manifested by any means: by means of original morphemes existing in a certain language or by borrowed morphemes. That’s why the method doesn’t suppose distinction between original and loaned affixes.
3) Genetically related languages are supposed to have rather close values of Prefixation Ability Index.
2.1.3. PAI calculation algorithm
How Prefixation Ability Index (here and further in this text abbreviation PAI is used) can be measured?
Value of PAI is portion of prefixes among affixes of a language.
Hence, in order to estimate portion/percentage of prefixes of a certain language we should do the following:
1) Count total number of prefixes;
2) Count total number of affixes;
3) Calculate the ratio of total number of prefixes to the total number of affixes.
Why is it important to count total number of prefixes and then calculate the ratio to the total number of affixes but not to estimate PAI by frequency of prefix forms in a random text?
A certain language can have quite high value of PAI but in a particular text word forms with prefixes can be of low frequency. Our task is to estimate portion of prefixes in grammar but not portion of prefix forms in a random text. Prefixes/World index estimated by Greenberg was exactly that estimation of prefix forms frequency in a text (Greenberg 1960).
Of course, that index also can give some general notion of prefixation ability of a language, though it is extremely rough and inaccurate since in a randomly chosen text can be very little amount of words with prefixes: the longer text is the more precision is the conclusion but anyway error of such estimation still remains very high; while when we count all exiting affixes of a certain language potential error is extremely low and even if we occasionally forget some affixes it doesn’t influence seriously on our results.
Moreover I am to note that despite Greenberg made great work on the field of typology he didn’t actually use those results in his research; he was an adept of megalocomparison and made his conclusions basing on “mass comparison” of lexis but not on structural correlations; his interest in typology was a “glass beads game” and was separated from his actual field of studies.
To those who think, that it’s impossible to estimate number of morphemes since living language always changes, I am to tell that living language doesn’t invent new morphemes every day, especially auxiliary morphemes. The fact that learning a language we can use descriptions of its grammar written some decades ago is the best proof that grammar is a very conservative level of any language.
Hence, we can estimate total number of affixes of a living language as far as we can get its description where all stable forms are represented. And there is no need to care of what can be in a certain language in future, i.e.: we consider current stage of living language and don’t care of possible future stages since they simply don’t exist yet.
As for possibility of count, I am to tell that even set of words is countable set while set of morphemes and especially auxiliary morphemes is not just countable set but also is finite set.
2.1.4. PAI method testing: from a hypothesis toward a theory
In order to test PAI hypothesis I paid attention to some languages of firmly assembled stocks: Austronesian, Indo-European and Afroasiatic.
2.1.4.1. PAI of languages of Austronesian stock
Polynesian group
Eastern Polynesian Subgroup
Hawaiian 0.82 (calculated after Krupa 1979)
Maori 0.88 (calculated fater Krupa 1967)
Tahitian 0.66 (calculated after Arakin 1981)
Samoan-Tokelauan subgroup
Samoan 0.5 (calculated after Arakin 1973)
Tongic subgroup
Niuean 0.8 (calculated after Polinskaya 1995)
Tongan 0.78 (calculated after Fell 1918)
Philippine group
South Mindanao subgroup
T’boli 0.72 (calculated after Porter 1977)
Northern Luzon subgroup
Pangasinan 0.6 (calculated after Rayner 1923)
Malayo-Sumbawan group
Malay subgroup
Indonesian 0.53 (calculated after Ogloblin 2008)
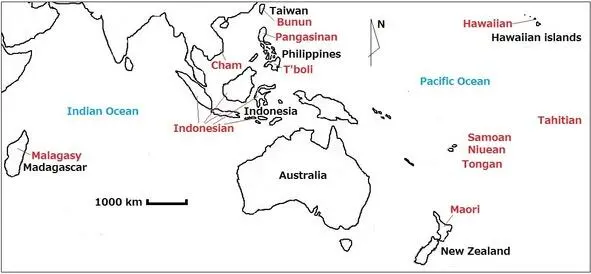
Pic. 2. Map representing location of Austronesian languages mentioned in current chapter: languages are marked by red, place names are maked by black.
Chamic subgroup
Cham 0.6 (calculated after Aymonier 1889; Alieva, Bùi 1999)
Formosan group
Bunun 0.8 (calculated after De Busser 2009)
Eastern Barito group
Malagasy 0.74 (calculated after Arakin 1963)
2.1.4.2. PAI of languages Indo-European stock
German group
Dutch 0.49 (calculated after Donaldson 1997)
German 0.51 (calculated after Donaldson 2007)
English 0.61 (calculated after Barhkhudarov et al. 2000)
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Manual of comparative linguistics»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Manual of comparative linguistics» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Manual of comparative linguistics» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.

![Andrew Radford - Linguistics An Introduction [Second Edition]](/books/397851/andrew-radford-linguistics-an-introduction-second-thumb.webp)










