While such countries may seem wild to us, these are no backwaters, no obscure wastelands. In fact the bridge between east and west is the very crossroads of civilisation. Far from being on the fringe of global affairs, these countries lie at its very centre—as they have done since the beginning of history. It was here that Civilisation was born, and where many believed Mankind had been created—in the Garden of Eden, “planted by the Lord God” with “every tree that is pleasant to the sight and good for food,” which was widely thought to be located in the rich fields between the Tigris and Euphrates.5
It was in this bridge between east and west that great metropolises were established nearly 5,000 years ago, where the cities of Harappa and Mohenjo-daro in the Indus valley were wonders of the ancient world, with populations numbering in the tens of thousands and streets connecting into a sophisticated sewage system that would not be rivalled in Europe for thousands of years.6 Other great centres of civilisation such as Babylon, Nineveh, Uruk and Akkad in Mesopotamia were famed for their grandeur and architectural innovation. One Chinese geographer, meanwhile, writing more than two millennia ago, noted that the inhabitants of Bactria, centred on the Oxus river and now located in northern Afghanistan, were legendary negotiators and traders; its capital city was home to a market where a huge range of products were bought and sold, carried from far and wide.7
This region is where the world’s great religions burst into life, where Judaism, Christianity, Islam, Buddhism and Hinduism jostled with each other. It is the cauldron where language groups competed, where Indo-European, Semitic and Sino-Tibetan tongues wagged alongside those speaking Altaic, Turkic and Caucasian. This is where great empires rose and fell, where the after-effects of clashes between cultures and rivals were felt thousands of miles away. Standing here opened up new ways to view the past and showed a world that was profoundly interconnected, where what happened on one continent had an impact on another, where the after-shocks of what happened on the steppes of Central Asia could be felt in North Africa, where events in Baghdad resonated in Scandinavia, where discoveries in the Americas altered the prices of goods in China and led to a surge in demand in the horse markets of northern India.
These tremors were carried along a network that fans out in every direction, routes along which pilgrims and warriors, nomads and merchants have travelled, goods and produce have been bought and sold, and ideas exchanged, adapted and refined. They have carried not only prosperity, but also death and violence, disease and disaster. In the late nineteenth century, this sprawling web of connections was given a name by an eminent German geologist, Ferdinand von Richthofen (uncle of the First World War flying ace the “Red Baron”) that has stuck ever since: “Seidenstraßen”—the Silk Roads.8
These pathways serve as the world’s central nervous system, connecting peoples and places together, but lying beneath the skin, invisible to the naked eye. Just as anatomy explains how the body functions, understanding these connections allows us to understand how the world works. And yet, despite the importance of this part of the world, it has been forgotten by mainstream history. In part, this is because of what has been called “orientalism”—the strident and overwhelmingly negative view of the east as undeveloped and inferior to the west, and therefore unworthy of serious study.9 But it also stems from the fact that the narrative of the past has become so dominant and well established that there is no place for a region that has long been seen as peripheral to the story of the rise of Europe and of western society.
Today, Jalalabad and Herat in Afghanistan, Fallujah and Mosul in Iraq or Homs and Aleppo in Syria seem synonymous with religious fundamentalism and sectarian violence. The present has washed away the past: gone are the days when the name of Kabul conjured up images of the gardens planted and tended by the great Bābur, founder of the Mughal Empire in India. The Bagh-i-Wafa (“Garden of Fidelity”) included a pool surrounded by orange and pomegranate trees and a clover meadow—of which Bābur was extremely proud: “This is the best part of the garden, a most beautiful sight when the oranges take colour. Truly that garden is admirably situated!”10
In the same way, modern impressions about Iran have obscured the glories of its more distant history when its Persian predecessor was a byword for good taste in everything, from the fruit served at dinner, to the stunning miniature portraits produced by its legendary artists, to the paper that scholars wrote on. A beautifully considered work written by Simi Nīshāpūrī, a librarian from Mashad in eastern Iran around 1400, records in careful detail the advice of a book lover who shared his passion. Anyone thinking of writing, he counsels solemnly, should be advised that the best paper for calligraphy is produced in Damascus, Baghdad or Samarkand. Paper from elsewhere “is generally rough, blotches and is impermanent.” Bear in mind, he cautions, that it is worth giving paper a slight tint before committing ink to it, “because white is hard on the eyes and the master calligraphic specimens that have been observed have all been on tinted paper.”11
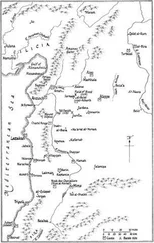
Places whose names are all but forgotten once dominated, such as Merv, described by one tenth-century geographer as a “delightful, fine, elegant, brilliant, extensive and pleasant city,” and “the mother of the world”; or Rayy, not far from modern Teheran, which to another writer around the same time was so glorious as to be considered “the bridegroom of the earth” and the world’s “most beautiful creation.”12 Dotted across the spine of Asia, these cities were strung like pearls, linking the Pacific to the Mediterranean.
Urban centres spurred each other on, with rivalry between rulers and elites prompting ever more ambitious architecture and spectacular monuments. Libraries, places of worship, churches and observatories of immense scale and cultural influence dotted the region, connecting Constantinople to Damascus, Isfahan, Samarkand, Kabul and Kashgar. Cities such as these became home to brilliant scholars who advanced the frontiers of their subjects. The names of only a small handful are familiar today—men like Ibn Sīnā, better known as Avicenna, al-Bīrūnī and al-Khwārizmi—giants in the fields of astronomy and medicine; but there were many more besides. For centuries before the early modern era, the intellectual centres of excellence of the world, the Oxfords and Cambridges, the Harvards and Yales, were not located in Europe or the west, but in Baghdad and Balkh, Bukhara and Samarkand.
There was good reason why the cultures, cities and peoples who lived along the Silk Roads developed and advanced: as they traded and exchanged ideas, they learnt and borrowed from each other, stimulating further advances in philosophy, the sciences, language and religion. Progress was essential, as one of the rulers of the kingdom of Zhao in north-eastern China at one extremity of Asia more than 2,000 years ago knew all too well. “A talent for following the ways of yesterday,” declared King Wu-ling in 307 BC, “is not sufficient to improve the world of today.”13 Leaders in the past understood how important it was to keep up with the times.
The mantle of progress shifted, however, in the early modern period as a result of two great maritime expeditions that took place at the end of the fifteenth century. In the course of six years in the 1490s, the foundations were laid for a major disruption to the rhythm of long-established systems of exchange. First Christopher Columbus crossed the Atlantic, paving the way for two great land masses that were hitherto untouched to connect to Europe and beyond; then, just a few years later, Vasco da Gama successfully navigated the southern tip of Africa, sailing on to India, opening new sea routes in the process. The discoveries changed patterns of interaction and trade, and effected a remarkable change in the world’s political and economic centre of gravity. Suddenly, western Europe was transformed from its position as a regional backwater into the fulcrum of a sprawling communication, transportation and trading system: at a stroke, it became the new mid-point between east and west.
Читать дальше