Even though liberal humanism sanctifies humans, it does not deny the existence of God, and is, in fact, founded on monotheist beliefs. The liberal belief in the free and sacred nature of each individual is a direct legacy of the traditional Christian belief in free and eternal individual souls. Without recourse to eternal souls and a Creator God, it becomes embarrassingly difficult for liberals to explain what is so special about individual Sapiens.
Another important sect is socialist humanism. Socialists believe that ‘humanity’ is collective rather than individualistic. They hold as sacred not the inner voice of each individual, but the species Homo sapiens as a whole. Whereas liberal humanism seeks as much freedom as possible for individual humans, socialist humanism seeks equality between all humans. According to socialists, inequality is the worst blasphemy against the sanctity of humanity, because it privileges peripheral qualities of humans over their universal essence. For example, when the rich are privileged over the poor, it means that we value money more than the universal essence of all humans, which is the same for rich and poor alike.
Like liberal humanism, socialist humanism is built on monotheist foundations. The idea that all humans are equal is a revamped version of the monotheist conviction that all souls are equal before God. The only humanist sect that has actually broken loose from traditional monotheism is evolutionary humanism, whose most famous representatives are the Nazis. What distinguished the Nazis from other humanist sects was a different definition of ‘humanity’, one deeply influenced by the theory of evolution. In contrast to other humanists, the Nazis believed that humankind is not something universal and eternal, but rather a mutable species that can evolve or degenerate. Man can evolve into superman, or degenerate into a subhuman.
The main ambition of the Nazis was to protect humankind from degeneration and encourage its progressive evolution. This is why the Nazis said that the Aryan race, the most advanced form of humanity, had to be protected and fostered, while degenerate kinds of Homo sapiens like Jews, Roma, homosexuals and the mentally ill had to be quarantined and even exterminated. The Nazis explained that Homo sapiens itself appeared when one ‘superior’ population of ancient humans evolved, whereas ‘inferior’ populations such as the Neanderthals became extinct. These different populations were at first no more than different races, but developed independently along their own evolutionary paths. This might well happen again. According to the Nazis, Homo sapiens had already divided into several distinct races, each with its own unique qualities. One of these races, the Aryan race, had the finest qualities – rationalism, beauty, integrity, diligence. The Aryan race therefore had the potential to turn man into superman. Other races, such as Jews and blacks, were today’s Neanderthals, possessing inferior qualities. If allowed to breed, and in particular to intermarry with Aryans, they would adulterate all human populations and doom Homo sapiens to extinction.
Biologists have since debunked Nazi racial theory. In particular, genetic research conducted after 1945 has demonstrated that the differences between the various human lineages are far smaller than the Nazis postulated. But these conclusions are relatively new. Given the state of scientific knowledge in 1933, Nazi beliefs were hardly outside the pale. The existence of different human races, the superiority of the white race, and the need to protect and cultivate this superior race were widely held beliefs among most Western elites. Scholars in the most prestigious Western universities, using the orthodox scientific methods of the day, published studies that allegedly proved that members of the white race were more intelligent, more ethical and more skilled than Africans or Indians. Politicians in Washington, London and Canberra took it for granted that it was their job to prevent the adulteration and degeneration of the white race, by, for example, restricting immigration from China or even Italy to ‘Aryan’ countries such as the USA and Australia.
Humanist Religions – Religions that Worship Humanity
Liberal humanism
Socialist humanism
Evolutionary humanism
Homo sapiens
has a unique and sacred nature that is fundamentally different from the nature of all other beings and phenomena. The supreme good is the good of humanity.
‘Humanity’ is individualistic and resides within each individual
Homo sapiens
.
‘Humanity’ is collective and resides within the species
Homo sapiens
as a whole.
‘Humanity’ is a mutable species. Humans might degenerate into subhumans or evolve into superhumans.
The supreme commandment is to protect the inner core and freedom of each individual
Homo sapiens
.
The supreme commandment is to protect equality within the species
Homo sapiens
.
The supreme commandment is to protect humankind from degenerating into subhumans, and to encourage its evolution into superhumans.
These positions did not change simply because new scientific research was published. Sociological and political developments were far more powerful engines of change. In this sense, Hitler dug not just his own grave but that of racism in general. When he launched World War Two, he compelled his enemies to make clear distinctions between ‘us’ and ‘them’. Afterwards, precisely because Nazi ideology was so racist, racism became discredited in the West. But the change took time. White supremacy remained a mainstream ideology in American politics at least until the 1960s. The White Australia policy which restricted immigration of non-white people to Australia remained in force until 1973. Aboriginal Australians did not receive equal political rights until the 1960s, and most were prevented from voting in elections because they were deemed unfit to function as citizens.

30. A Nazi propaganda poster showing on the right a ‘racially pure Aryan’ and on the left a ‘cross-breed’. Nazi admiration for the human body is evident, as is their fear that the lower races might pollute humanity and cause its degeneration.
The Nazis did not loathe humanity. They fought liberal humanism, human rights and Communism precisely because they admired humanity and believed in the great potential of the human species. But following the logic of Darwinian evolution, they argued that natural selection must be allowed to weed out unfit individuals and leave only the fittest to survive and reproduce. By succouring the weak, liberalism and Communism not only allowed unfit individuals to survive, they actually gave them the opportunity to reproduce, thereby undermining natural selection. In such a world, the fittest humans would inevitably drown in a sea of unfit degenerates. Humankind would become less and less fit with each passing generation – which could lead to its extinction.
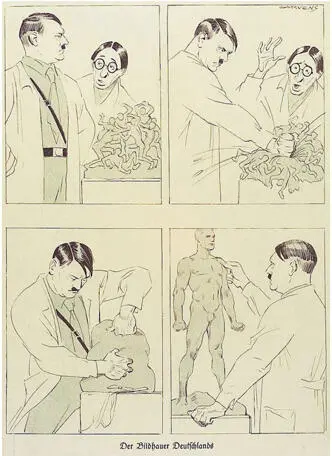
31. A Nazi cartoon of 1933. Hitler is presented as a sculptor who creates the superman. A bespectacled liberal intellectual is appalled by the violence needed to create the superman. (Note also the erotic glorification of the human body.)
A 1942 German biology textbook explains in the chapter ‘The Laws of Nature and Mankind’ that the supreme law of nature is that all beings are locked in a remorseless struggle for survival. After describing how plants struggle for territory, how beetles struggle to find mates and so forth, the textbook concludes that:
Читать дальше





![Юваль Ной Харари - Sapiens. Краткая история человечества [litres]](/books/34310/yuval-noj-harari-sapiens-kratkaya-istoriya-cheloveche-thumb.webp)





![Юваль Ной Харари - 21 урок для XXI века [Версия с комментированными отличиями перевода]](/books/412481/yuval-noj-harari-21-urok-dlya-xxi-veka-versiya-s-ko-thumb.webp)


