Herbert Wells - A Short History of the World
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Herbert Wells - A Short History of the World» весь текст электронной книги совершенно бесплатно (целиком полную версию без сокращений). В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Год выпуска: 2011, Жанр: История, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:A Short History of the World
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:2011
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
A Short History of the World: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «A Short History of the World»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
A Short History of the World — читать онлайн бесплатно полную книгу (весь текст) целиком
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «A Short History of the World», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
KING ASOKA
FOR some generations after the death of Gautama, these high and noble Buddhist teachings, this first plain teaching that the highest good for man is the subjugation of self, made comparatively little headway in the world. Then they conquered the imagination of one of the greatest monarchs the world has ever seen.
We have already mentioned how Alexander the Great came down into India and fought with Porus upon the Indus. It is related by the Greek historians that a certain Chandragupta Maurya came into Alexander’s camp and tried to persuade him to go on to the Ganges and conquer all India. Alexander could not do this because of the refusal of his Macedonians to go further into what was for them an unknown world, and later on (303 B.C.) Chandragupta was able to secure the help or various hill tribes and realize his dream without Greek help. He built up an empire in North India and was presently (303 B.C.) able to attack Seleucus I in the Punjab and drive the last vestige of Greek power out of India. His son extended this new empire. His grandson, Asoka, the monarch of whom we now have to tell, found himself in 264 B.C. ruling from Afghanistan to Madras.
Asoka was at first disposed to follow the example of his father and grandfather and complete the conquest of the Indian peninsula. He invaded Kalinga (255 B.C.), a country on the east coast of Madras, he was successful in his military operations and—alone among conquerors—he was so disgusted by the cruelty and horror of war that he renounced it. He would have no more of it. He adopted the peaceful doctrines of Buddhism and declared that henceforth his conquests should be the conquests of religion.
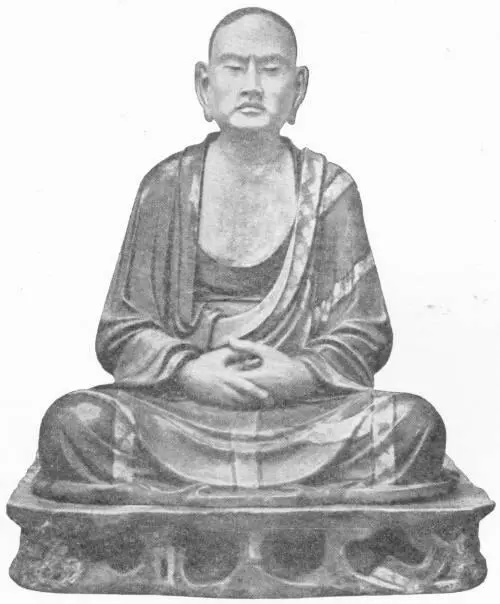

A LOHAN OR BUDDHIST APOSTLE (Tang Dynasty)
(From the statue in the British Museum)
His reign for eight-and-twenty years was one of the brightest interludes in the troubled history of mankind. He organized a great digging of wells in India and the planting of trees for shade. He founded hospitals and public gardens and gardens for the growing of medicinal herbs. He created a ministry for the care of the aborigines and subject races of India. He made provision for the education of women. He made vast benefactions to the Buddhist teaching orders, and tried to stimulate them to a better and more energetic criticism of their own accumulated literature. For corruptions and superstitious accretions had accumulated very speedily upon the pure and simple teaching of the great Indian master. Missionaries went from Asoka to Kashmir, to Persia, to Ceylon and Alexandria.
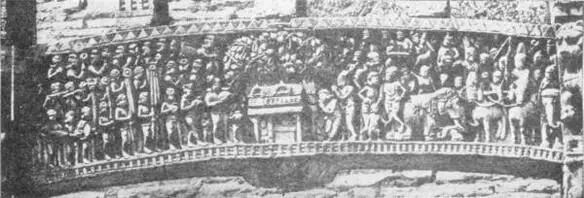
TRANSOME SHOWING THE COURT OF ASOKA
India Mus.

ASOKA PANEL FROM BHARHUT
India Mus.
Such was Asoka, greatest of kings. He was far in advance of his age. He left no prince and no organization of men to carry on his work, and within a century of his death the great days of his reign had become a glorious memory in a shattered and decaying India. The priestly caste of the Brahmins, the highest and most privileged caste in the Indian social body, has always been opposed to the frank and open teaching of Buddha. Gradually they undermined the Buddhist influence in the land. The old monstrous gods, the innumerable cults of Hinduism, resumed their sway. Caste became more rigorous and complicated. For long centuries Buddhism and Brahminism flourished side by side, and then slowly Buddhism decayed and Brahminism in a multitude of forms replaced it. But beyond the confines of India and the realms of caste Buddhism spread—until it had won China and Siam and Burma and Japan, countries in which it is predominant to this day.
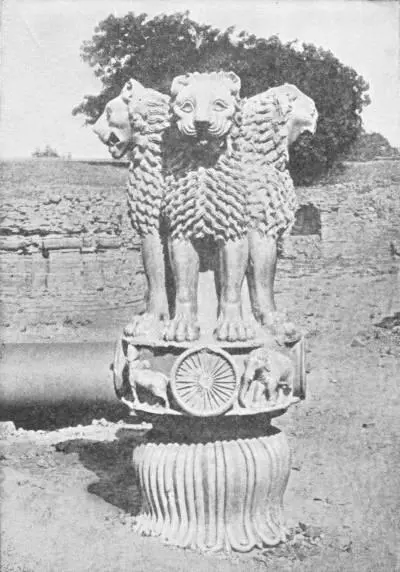

THE PILLAR OF LIONS
Capital of the Pillar (column lying on side) erected in Deer Park in the time of Asoka, where Buddha preached his first sermon
(From a print in the India Museum)
XXX
CONFUCIUS AND LAO TSE
WE have still to tell of two other great men, Confucius and Lao Tse, who lived in that wonderful century which began the adolescence of mankind, the sixth century B.C. In this history thus far we have told very little of the early story of China. At present that early history is still very obscure, and we look to Chinese explorers and archæolologists in the new China that is now arising to work out their past as thoroughly as the European past has been worked out during the last century. Very long ago the first primitive Chinese civilizations arose in the great river valleys out of the primordial heliolithic culture. They had, like Egypt and Sumeria, the general characteristics of that culture, and they centred upon temples in which priests and priest kings offered the seasonal blood sacrifices. The life in those cities must have been very like the Egyptian and Sumerian life of six or seven thousand years ago and very like the Maya life of Central America a thousand years ago.
If there were human sacrifices they had long given way to animal sacrifices before the dawn of history. And a form of picture writing was growing up long before a thousand years B.C.
And just as the primitive civilizations of Europe and western Asia were in conflict with the nomads of the desert and the nomads of the north, so the primitive Chinese civilizations had a great cloud of nomadic peoples on their northern borders. There was a number of tribes akin in language and ways of living, who are spoken of in history in succession as the Huns, the Mongols, the Turks and Tartars. They changed and divided and combined and re-combined, just as the Nordic peoples in north Europe and central Asia changed and varied in name rather than in nature. These Mongolian nomads had horses earlier than the Nordic peoples, and it may be that in the region of the Altai Mountains they made an independent discovery of iron somewhen after 1000 B.C. And just as in the western case so ever and again these eastern nomads would achieve a sort of political unity, and become the conquerors and masters and revivers of this or that settled and civilized region.
It is quite possible that the earliest civilization of China was not Mongolian at all any more than the earliest civilization of Europe and western Asia was Nordic or Semitic. It is quite possible that the earliest civilization of China was a brunette civilization and of a piece with the earliest Egyptian, Sumerian and Dravidian civilizations, and that when the first recorded history of China began there had already been conquests and intermixture. At any rate we find that by 1750 B.C. China was already a vast system of little kingdoms and city states, all acknowledging a loose allegiance and paying more or less regularly, more or less definite feudal dues to one great priest emperor, the “Son of Heaven.” The “Shang” dynasty came to an end in 1125 B.C. A “Chow” dynasty succeeded “Shang,” and maintained China in a relaxing unity until the days of Asoka in India and of the Ptolemies in Egypt. Gradually China went to pieces during that long “Chow” period. Hunnish peoples came down and set up principalities; local rulers discontinued their tribute and became independent. There was in the sixth century B.C., says one Chinese authority, five or six thousand practically independent states in China. It was what the Chinese call in their records an “Age of Confusion.”
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «A Short History of the World»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «A Short History of the World» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «A Short History of the World» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.








