Herbert Wells - A Short History of the World
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Herbert Wells - A Short History of the World» весь текст электронной книги совершенно бесплатно (целиком полную версию без сокращений). В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Год выпуска: 2011, Жанр: История, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:A Short History of the World
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:2011
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
A Short History of the World: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «A Short History of the World»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
A Short History of the World — читать онлайн бесплатно полную книгу (весь текст) целиком
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «A Short History of the World», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
It is easy to see how important the man of knowledge and experience, the man who knew about the blood sacrifice and the stars, became in this early Neolithic world.
The fear of uncleanness and pollution, and the methods of cleansing that were advisable, constituted another source of power for the knowledgeable men and women. For there have always been witches as well as wizards, and priestesses as well as priests. The early priest was really not so much a religious man as a man of applied science. His science was generally empirical and often bad; he kept it secret from the generality of men very jealously; but that does not alter the fact that his primary function was knowledge and that his primary use was a practical use.

SPECIMEN OF NEOLITHIC POTTERY
Dug up at Mortlake from the Thames Bed
Brit. Mus.
Twelve or fifteen thousand years ago, in all the warm and fairly well-watered parts of the Old World these Neolithic human communities, with their class and tradition of priests and priestesses and their cultivated fields and their development of villages and little walled cities, were spreading. Age by age a drift and exchange of ideas went on between these communities. Eliot Smith and Rivers have used the term “Heliolithic culture” for the culture of these first agricultural peoples. “Heliolithic” (Sun and Stone) is not perhaps the best possible word to use for this, but until scientific men give us a better one we shall have to use it. Originating somewhere in the Mediterranean and western Asiatic area, it spread age by age eastward and from island to island across the Pacific until it may even have reached America and mingled with the more primitive ways of living of the Mongoloid immigrants coming down from the North.
Wherever the brownish people with the Heliolithic culture went they took with them all or most of a certain group of curious ideas and practices. Some of them are such queer ideas that they call for the explanation of the mental expert. They made pyramids and great mounds, and set up great circles of big stones, perhaps to facilitate the astronomical observation of the priests; they made mummies of some or all of their dead; they tattooed and circumcized; they had the old custom, known as the couvade , of sending the father to bed and rest when a child was born, and they had as a luck symbol the well-known Swastika.
If we were to make a map of the world with dots to show how far these group practices have left their traces, we should make a belt along the temperate and sub-tropical coasts of the world from Stonehenge and Spain across the world to Mexico and Peru. But Africa below the equator, north central Europe, and north Asia would show none of these dottings; there lived races who were developing along practically independent lines.
[1] The term Palæolithic we may note is also used to cover the Neanderthaler and even the Eolithic implements. The pre-human age is called the “Older Palæolithic;” the age of true men using unpolished stones in the “Newer Palæolithic.”
XIV
PRIMITIVE NEOLITHIC CIVILIZATIONS
ABOUT 10,000 B.C. the geography of the world was very similar in its general outline to that of the world to-day. It is probable that by that time the great barrier across the Straits of Gibraltar that had hitherto banked back the ocean waters from the Mediterranean valley had been eaten through, and that the Mediterranean was a sea following much the same coastlines as it does now. The Caspian Sea was probably still far more extensive than it is at present, and it may have been continuous with the Black Sea to the north of the Caucasus Mountains. About this great Central Asian sea lands that are now steppes and deserts were fertile and habitable. Generally it was a moister and more fertile world. European Russia was much more a land of swamp and lake than it is now, and there may still have been a land connexion between Asia and America at Behring Straits.
It would have been already possible at that time to have distinguished the main racial divisions of mankind as we know them to-day. Across the warm temperate regions of this rather warmer and better-wooded world, and along the coasts, stretched the brownish peoples of the Heliolithic culture, the ancestors of the bulk of the living inhabitants of the Mediterranean world, of the Berbers, the Egyptians and of much of the population of South and Eastern Asia. This great race had of course a number of varieties. The Iberian or Mediterranean or “dark-white” race of the Atlantic and Mediterranean coast, the “Hamitic” peoples which include the Berbers and Egyptians, the Dravidians; the darker people of India, a multitude of East Indian people, many Polynesian races and the Maoris are all divisions of various value of this great main mass of humanity. Its western varieties are whiter than its eastern.
In the forests of central and northern Europe a more blonde variety of men with blue eyes was becoming distinguishable, branching off from the main mass of brownish people, a variety which many people now speak of as the Nordic race. In the more open regions of northeastern Asia was another differentiation of this brownish humanity in the direction of a type with more oblique eyes, high cheek-bones, a yellowish skin, and very straight black hair, the Mongolian peoples. In South Africa, Australia, in many tropical islands in the south of Asia were remains of the early negroid peoples. The central parts of Africa were already a region of racial intermixture. Nearly all the coloured races of Africa to-day seem to be blends of the brownish peoples of the north with a negroid substratum.
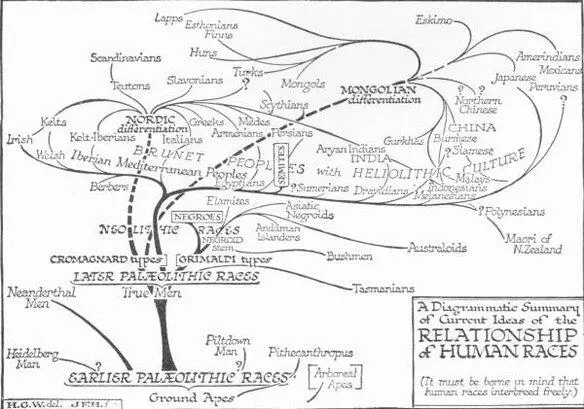
We have to remember that human races can all interbreed freely and that they separate, mingle and reunite as clouds do. Human races do not branch out like trees with branches that never come together again. It is a thing we need to bear constantly in mind, this remingling of races at any opportunity. It will save us from many cruel delusions and prejudices if we do so. People will use such a word as race in the loosest manner, and base the most preposterous generalizations upon it. They will speak of a “British” race or of a “European” race. But nearly all the European nations are confused mixtures of brownish, dark-white, white and Mongolian elements.

A MAYA STELE
Showing a worshipper and a Serpent God. Note the grotesque faces in the writing
Brit. Mus.
It was at the Neolithic phase of human development that peoples of the Mongolian breed first made their way into America. Apparently they came by way of Behring Straits and spread southward. They found caribou, the American reindeer, in the north and great herds of bison in the south. When they reached South America there were still living the Glyptodon, a gigantic armadillo, and the Megatherium, a monstrous clumsy sloth as high as an elephant. They probably exterminated the latter beast, which was as helpless as it was big.
The greater portion of these American tribes never rose above a hunting nomadic Neolithic life. They never discovered the use of iron, and their chief metal possessions were native gold and copper. But in Mexico, Yucatan and Peru conditions existed favourable to settled cultivation, and here about 1000 B.C. or so arose very interesting civilizations of a parallel but different type from the old-world civilization. Like the much earlier primitive civilizations of the old world these communities displayed a great development of human sacrifice about the processes of seed time and harvest; but while in the old world, as we shall see, these primary ideas were ultimately mitigated, complicated and overlaid by others, in America they developed and were elaborated, to a very high degree of intensity. These American civilized countries were essentially priest-ruled countries; their war chiefs and rulers were under a rigorous rule of law and omen.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «A Short History of the World»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «A Short History of the World» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «A Short History of the World» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.








