Implementing Callbacks Using Delegates
One of the useful things you can do with delegates is to implement callbacks. Callbacks are methods that you pass into a function that will be called when the function finishes execution. For example, you have a function that performs a series of mathematical operations. When you call the function, you also pass it a callback method so that when the function is done with its calculation, the callback method is called to notify you of the calculation result.
Following is an example of how to implement callbacks using delegates:
class Program {
delegate void callbackDelegate(string Message);
static void Main(string[] args) {
callbackDelegate result = ResultCallback;
AddTwoNumbers(5, 3, result);
Console.ReadLine();
}
static private void AddTwoNumbers(
int num1, int num2, callbackDelegate callback) {
int result = num1 + num2;
callback("The result is: " + result.ToString());
}
static private void ResultCallback(string Message) {
Console.WriteLine(Message);
}
}
First, you declare two methods:
□ AddTwoNumbers()— Takes in two integer arguments and a delegate of type callbackDelegate
□ ResultCallback()— Takes in a string argument and displays the string in the console window
Then you declare a delegate type:
delegate void callbackDelegate(string Message);
Before you call the AddTwoNumbers()function, you create a delegate of type callbackDelegateand assign it to point to the ResultCallback()method. The AddTwoNumbers()function is then called with two integer arguments and the resultcallback delegate:
callbackDelegate result = ResultCallback;
AddTwoNumbers(5, 3, result);
In the AddTwoNumbers()function, when the calculation is done, you invoke the callbackdelegate and pass to it a string:
static private void AddTwoNumbers(
int num1, int num2, callbackDelegate callback) {
int result = num1 + num2;
callback("The result is: " + result.ToString());
}
The callbackdelegate calls the ResultCallback()function, which prints the result to the console. The output is:
The result is: 8
Callbacks are most useful if they are asynchronous. The callback illustrated in the previous example is synchronous , that is, the functions are called sequentially. If the AddTwoNumbers()function takes a long time to execute, all the statements after it will block. Figure 7-1 shows the flow of execution when the callback is synchronous.

Figure 7-1
A better way to organize the program is to call the AddTwoNumbers()method asynchronously, as shown in Figure 7-2. Calling a function asynchronously allows the main program to continue executing without waiting for the function to return.
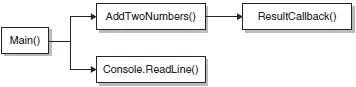
Figure 7-2
In this asynchronous model, when the AddTwoNumbers()function is called, the statement(s) after it can continue to execute. When the function finishes execution, it calls the ResultCallback()function.
Here's the rewrite of the previous program, using an asynchronous callback:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging;
namespace Delegates {
class Program {
//---delegate to the AddTwoNumbers() method---
delegate int MethodDelegate(int num1, int num2);
static void Main(string[] args) {
//---assign the delegate to point to AddTwoNumbers()---
MethodDelegate del = AddTwoNumbers;
//---creates a AsyncCallback delegate---
AsyncCallback callback = new AsyncCallback(ResultCallback);
//---invoke the method asychronously---
Console.WriteLine("Invoking the method asynchronously...");
IAsyncResult result = del.BeginInvoke(5, 3, callback, null);
Console.WriteLine("Continuing with the execution...");
Console.ReadLine();
}
//---method to add two numbers---
static private int AddTwoNumbers(int num1, int num2) {
//---simulate long execution---
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(5000);
return num1 + num2;
}
static private void ResultCallback(IAsyncResult ar) {
MethodDelegate del =
(MethodDelegate)((AsyncResult)ar).AsyncDelegate;
//---get the result---
int result = del.EndInvoke(ar);
Console.WriteLine("Result of addition is: " + result);
}
}
}
First, you define a delegate type so that you can point to the AddTwoNumbers()method:
delegate int MethodDelegate(int num1, int num2);
Then create a delegate, and assign it to point to the AddTwoNumbers()method:
//---assign the delegate to point to AddTwoNumbers()---
MethodDelegate del = AddTwoNumbers;
Next, define a delegate of type AsyncCallback:
//---creates a AsyncCallback delegate---
AsyncCallback callback = new AsyncCallback(ResultCallback);
The AsyncCallbackis a delegate that references a method to be called when an asynchronous operation completes. Here, you set it to point to ResultCallback(which you will define later).
To call the AddTwoNumbers()methods asynchronously, you use the BeginInvoke()method of the deldelegate, passing it two integer values (needed by the AddTwoNumbers()method), as well as a delegate to call back when the method finishes executing:
//---invoke the method asynchronously---
Console.WriteLine("Invoking the method asynchronously...");
IAsyncResult result = del.BeginInvoke(5, 3, callback, null);
Console.WriteLine("Continuing with the execution...");
The BeginInvoke()method calls the delegate asynchronously, and the next statement continues execution after the async delegate is called. This method returns a variable of type IAsyncResultto represent the status of an asynchronous operation.
To obtain the result of the calculation, you define the ResultCallback()method, which takes in an argument of type IAsyncResult:
static private void ResultCallback(IAsyncResult ar) {
Читать дальше














