Oskar Andreasson - Iptables Tutorial 1.2.2
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Oskar Andreasson - Iptables Tutorial 1.2.2» весь текст электронной книги совершенно бесплатно (целиком полную версию без сокращений). В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: Интернет, на русском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Iptables Tutorial 1.2.2
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Iptables Tutorial 1.2.2: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Iptables Tutorial 1.2.2»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Iptables Tutorial 1.2.2 — читать онлайн бесплатно полную книгу (весь текст) целиком
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Iptables Tutorial 1.2.2», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:

The IPv4 parameter is used to send an IPv4 address in the INIT chunk. The IPv4 address can be used to send data through the association. Multiple IPv4 and IPv6 addresses can be specified for a single SCTP association.
Parameter Type - bit 0-15. This is always set to 5 for IPv4 address parameters.
Length - bit 16-31. This is always set to 8 for IPv4 address parameters.
IPv4 Address - bit 32-63. This is an IPv4 address of the sending endpoint.
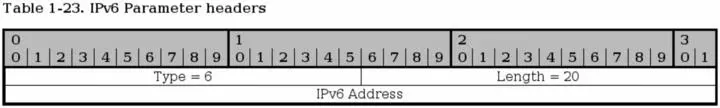
This parameter is used to send IPv6 addresses in the INIT chunk. This address can then be used to contact the sending endpoint with this association.
Type - bit 0-15. Always set to 6 for the IPv6 parameters.
Length bit 16-31. Always set to 20 for IPv6 parameters.
IPv6 address- bit 32-159. This is an IPv6 address of the sending endpoint that can be used to connect to by the receiving endpoint.
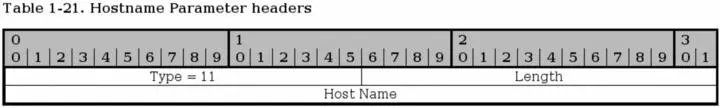
The Hostname parameter is used to send a single hostname as an address. Thea receiving host must then look up the hostname and use any and/or all of the addresses it receives from there. If a hostname parameter is sent, no other IPv4, IPv6 or Hostname parameters may be sent.
Type- bit 0-15. This is always set to 11 for Hostname Parameters.
Length- bit 16-31. The length of the whole parameter, including type, length and hostname field. The Hostname field is variable length. The length is counted in bytes.
Hostname- bit 32-n. A variable length parameter containing a hostname. The hostname is resolved by the receiving end to get the addresses that can be used to contact the sending endpoint.
SCTP INIT ACK chunk
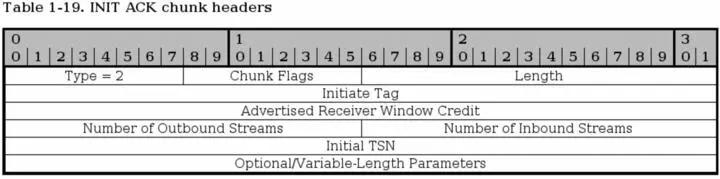
The INIT ACK chunk is sent in response to a INIT chunk and contains basically the same headers, but with values from the recipient of the original INIT chunk. In addition, it has two extra variable length parameters, the State Cookie and the Unrecognized Parameter parameters.
Type - bit 0-7. This header is always set to 2 for INIT ACK chunks.
Chunk flags - bit 8-15. Not used today. Might be applicable for change. See SCTP Common and generic headers for more information.
Chunk Length - bit 16-31. The chunk length is the length of the whole packet, including everything in the headers, and the optional parameters.
Initiate Tag - bit 32-63. The receiver of the Initiate Tag of the INIT ACK chunk must save this value and copy it into the Verification Tag field of every packet that it sends to the sender of the INIT ACK chunk. The Initiate Tag must not be 0, and if it is, the receiver of the INIT ACK chunk must close the connection with an ABORT.
Advertised Receiver Window Credit (a_rwnd) - bit 64-95. The dedicated buffers that the sender of this chunk has located for traffic, counted in bytes. The dedicated buffers should never be lowered to below this value.
Number of Outbound Streams - bit 96-111. How many outbound streams that the sending host wishes to create. Must not be 0, or the receiver of the INIT ACK should ABORT the association. There is no negotiation of the minimum number of outbound or inbound streams, it is simply set to the lowest that either host has set in the header.
Number of Inbound Streams - bit 112-127. How many inbound streams that the sending endpoint is willing to accept. Must not be 0, or the receiver of the INIT ACK should ABORT the association. There is no negotiation of the minimum number of outbound or inbound streams, it is simply set to the lowest that either host has set in the header.
Initial TSN - bit 128-159. This is set to the Initial Transmission Sequence Number (I-TSN) which will be used by the sending party in the association to start with.
After this point, the INIT ACK chunk continues with optional variable-length parameters. The parameters are exactly the same as for the INIT chunk, with the exception of the addition of the State Cookie and the Unrecognized Parameters parameter, and the deletion of the Supported Address Types parameter. The list in other words look like this:
Table 2-4. INIT ACK Variable Parameters
| Parameter Name | Status | Type Value |
|---|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | Optional | 5 |
| IPv6 Address | Optional | 6 |
| State Cookie | Mandatory | 7 |
| Unrecognized Parameters | Optional | 8 |
| Cookie Preservative | Optional | 9 |
| Host Name Address | Optional | 11 |
| Reserved for ECN Capable | Optional | 32768 |
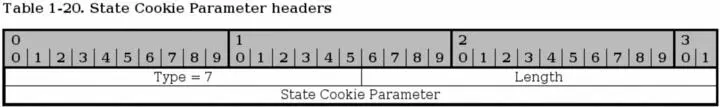
The State Cookie is used in INIT ACK to send a cookie to the other host, and until the receiving host has replied with a COOKIE ECHO chunk, the association is not guaranteed. This is to prevent basically the same as a SYN attack in TCP protocol.
Type - bit 0-15. Always set to 7 for all State Cookie parameters.
Length - bit 16-31. The size of the whole parameter, including the type, length and State Cookie field in bytes.
State Cookie - bit 31-n. This parameter contains a cookie of variable length. For a description on how this cookie is created, see the RFC 2960 - Stream Control Transmission Protocol document.
SCTP SACK chunk
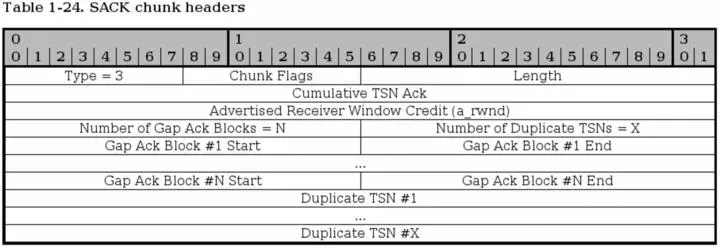
The SACK chunk is used to tell the sender of DATA chunks which chunks has been received and where there has been a gap in the stream, based on the received TSN's. Basically, the SACK chunk acknowledges that it has received data up to a certain point (the Cumulative TSN Ack parameter), and then adds Gap Ack Blocks for all of the data that it has received after the Cumulative TSN Ack point. A SACK chunk must not be sent more than once for every DATA chunk that is received.
Type - bit 0-7. This header is always set to 3 for SACK chunks.
Chunk flags - bit 8-15. Not used today. Might be applicable for change. See SCTP Common and generic headers for more information.
Chunk Length - bit 16-31. The chunk length is the length of the whole chunk, including everything in the headers and all the parameters.
Cumulative TSN Ack - bit 32-63. This is the Cumulative TSN Ack parameter, which is used to acknowledge data. The DATA chunk receiver will use this field to tell the sending host that it has received all data up to this point of the association. After this point, all data that has not been specifically acknowledged by the Gap Ack Blocks will, basically, be considered unaccounted for.
Advertised Receiver Window Credit (a_rwnd) - bit 64-95. The a_rwnd field is basically the same as the a_rwnd in the INIT and INIT ACK chunks, but can be used to raise or lower the a_rwnd value. Please read more in the RFC 2960 - Stream Control Transmission Protocol document about this.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Iptables Tutorial 1.2.2»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Iptables Tutorial 1.2.2» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Iptables Tutorial 1.2.2» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.








