Inability to drive car in a drift often leads to accidents. Rear-wheel-drive car with usual differential (zero or low friction) is quite difficult to drive in a drift. Take for testing a rear-wheel-drive car with zero-friction differential (factory) on the rear axle. Let us look at what may be causes of occurrence and ways to provoke rear axle drift.
1. Braking by handbrake. It is the simplest and most understandable cause.
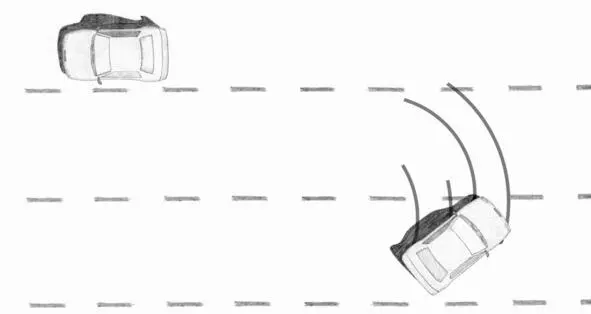
2. Aggressive throttling on a rear-wheel-drive car. Please note – with a standard differential the first starts to skid wheel from the inside of corner (the unloaded wheel).
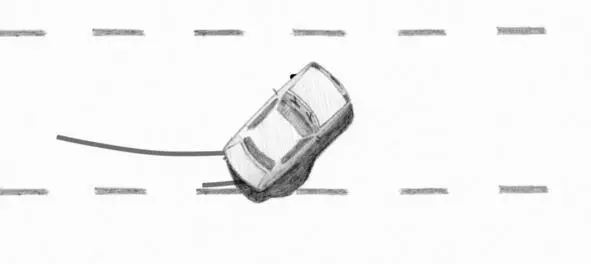
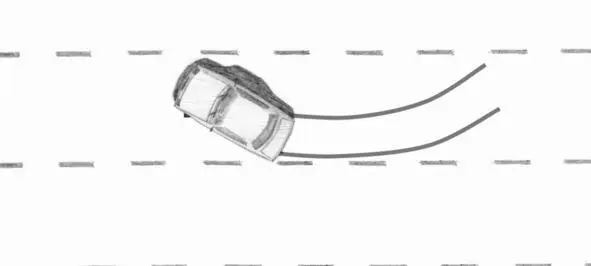
3. Speeding of engine and depressing the clutch on a rear-wheel-drive car. If you push the clutch, gain engine speed and, without releasing the throttle, release the clutch, the rear wheels will skid.
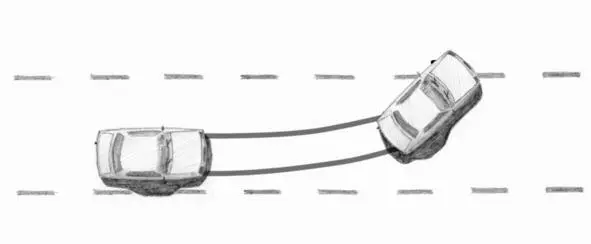
We revved up the engine and casted off the clutch pedal. The both rear wheels began to skip, the rear axle began to drift.
4. Engine braking on a rear-wheel-drive car. When the throttle pedal is released, firstly, the front axle is loaded and the rear – is unloaded.
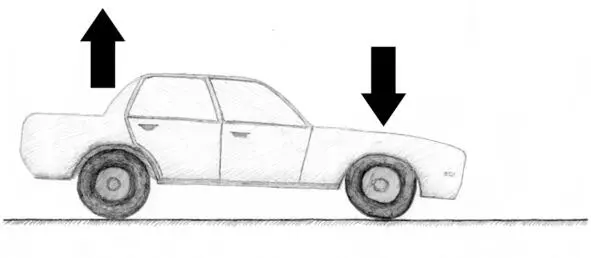
Because of this grip of the front tyres with the road increases, the rear – decreases. Secondly, there is a braking effort on the rear wheels caused by engine braking. These facts lead to increase of steerability and can cause drift when maneuvering on a rear-wheel-drive car, especially on a high steerability car. Soft braking with engine braking together can have the same effect. In addition, roughs on the road unload the rear axle awhile, which combined with engine braking increases risk of sliding on a rear-wheel-drive.
5. Downshift without throttle blip on a rear-wheel-drive car with a manual gearbox. After lowering the gear and releasing the clutch pedal the engine is forced to gain speed in a short time distance, which can be indicated by a jump of the tachometer needle. On rear-wheel-drive, this is equal to action of the handbrake.
6. Braking with a strong shift of brake balance to the rear axle. When balance of the braking system is shifted to the rear axle, steerability may increases during braking. It may happen that the rear wheels will be first to brake.
7. Rocking the center of mass. Rocking can cause drift when passing an S-like corner.

When direction of movement changes, the energy stored in the compressed suspension, is freed and pushes car in opposite direction, which can lead to drift.
8. Together pressing the throttle and brake pedals on a front-wheel-drive car. Moving along the ring on a front-wheel-drive car, let us press the throttle and brake pedals at one time.

There was drift of the rear axle, the car rushed inside the ring. That is, the pressed throttle and brake pedals on a front-wheel-drive car create oversteer. Since we pressed on the throttle when braking, there was traction from the engine on the front axle. The rear axle brakes more intensively than the front, not exclude the rear wheels may be locked. Braking by the rear wheels creates oversteer, which is similar to braking by the handbrake. To describe operation of the front axle we take into account the several factors:
• due to the roll in the corner the left wheels were loaded with mass of the car, and the right wheels were unloaded;
• the front wheels are affected by the engine torque and braking effort;
• the engine torque is divided between the front wheels by the differential.
On the front axle of the car a zero-friction differential is installed, which transmits half of the engine’s torque to the each wheel. To explain the test results, we assume that the engine torque is enough to maintain traction on the front wheels when the brake pedal is pressed full way down.
For demonstrativeness of illustrations we introduce the concept of equivalent force. Equivalent force is the force that must be applied to the top of wheel to obtain the torque on wheel (this may be engine torque or torque generated by a braking system).
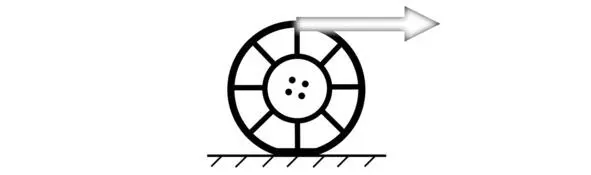
The figure shows the force was applied to the top of the wheel and compels the wheel to rotate faster clockwise.
Let us draw equivalent forces that occurred when one time press the throttle and brake pedals in the previous test.
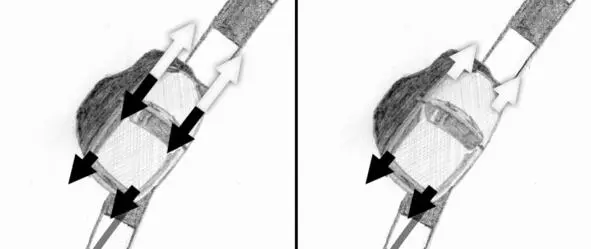
At the left figure black arrows indicate equivalent forces created by braking system, white arrows – equal equivalent forces corresponding to torque produced by the engine and is divided between the wheels by differential. The right figure shows the resulting equivalent forces on each front wheel, which corresponds to the resulting torque (difference between engine torque and brake system torque). We did not press the brake pedal to the end, the braking effort on rear loaded wheel was not enough to lock it.
If braking effort is high enough, the rear wheels may become locked. Let us imagine a case when the rear wheels are locked. Note the locked wheels with crosses.
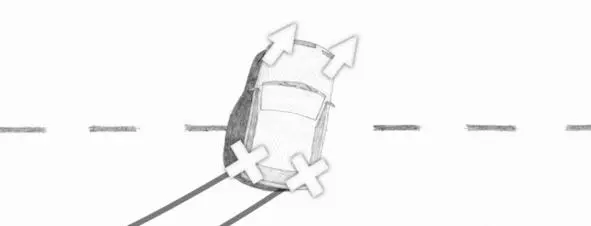
Direction of the equivalent forces corresponds to direction of movement of the front wheels. Front unloaded wheel has worse grip on the road than the loaded one, and there is a chance that it starts to slip. If the unloaded wheel starts to skid, the main part of the engine’s power will be transferred to it.
Although pressing the throttle and brake pedals creates oversteer on a front-wheel-drive car, steerability may be reduced by engine’s torque. If the rear wheels are locked, but the engine has an enough high torque, car will not turn around in a drift due to high traction on the front wheels. At the same time, if braking effort on the front wheels is fully compensated by the engine torque, maximum steerability will be achieved.
Increased friction of differential allows you to transfer more torque to loaded front wheel and thus more efficiently implement engine power. Let us represent equivalent forces, when a limited slip differential is set on the front axle.
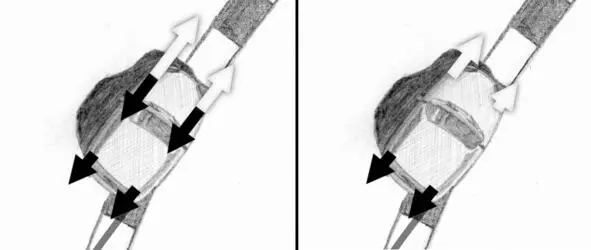
The left figure shows equivalent forces generated by braking (black arrows) and engine torque (white arrows). Figure on the right shows resulting equivalent forces on the front wheels after subtracting the braking effort from engine torque. A greater amount of torque on loaded front wheel means that more engine power will be transferred to the wheel compared to situation, when a zero-friction differential was installed.
Читать дальше























