Chapter 2. Tiflis mail of the ХIХ century
Postal Service of the Caucasus in the second half of the nineteenth century
After the accession of Georgia to Russia in the first place it was scheduled to continue the construction of post tract from Mozdok to Tiflis with the length of 258 versts with the construction of ten stations to serve the postal rush on it and one post office in Tiflis. But those plans were hold back by the scarcity of funds allocated.
In 1830, to simplify and accelerate the movement of office correspondence, the Post Agency reorganized the Russian post offices. By the nominative Decree of Tsar Nicholas I to the Senate “On the new structure of the mail system” from October 22, 1830, the division of the territory of Russia into 11 postal districts was provided. (See. Table 1).
Five provincial post offices were canceled, and provincial, regional, border and foreign post offices had to report directly to the Postal Department. Georgia postal institutions were included in the postal district VIII.
The city of Stavropol was determined to be the seat of Postal Inspector of the district; one of his assistants had to reside in Tiflis to supervise the post offices of the Transcaucasian region. Tiflis post office was elevated to the rank of regional office with a staff of 12 people (4 sorters were added). The new “Regulation on the system of the postal unit” was put into operation since January 1, 1831.
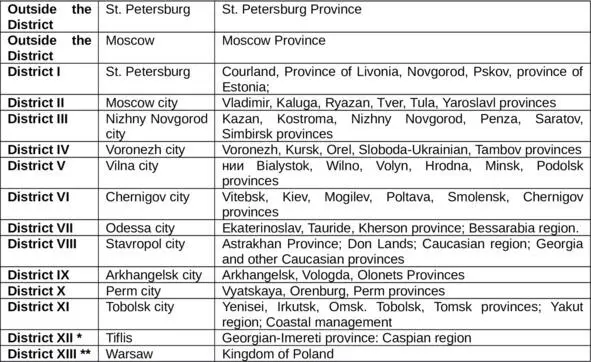
Table 1. DIVISION of Russian territory into the postal districts in the first half of the nineteenth century. * Since 1940. **XIII postal district was formed in 1851 by a nominal decree of the Senate on March 4, 1851 (COR-2, SP6, 1852, t. XXVI, Department 1st, number 2500).
Further reorganization of Tiflis post office is associated with the general changes made by the tsarist government in 1840 for civilian control of the Transcaucasian region. According to the nominative decree to the Senate on April 10, 1840, the provinces lying between the Black and Caspian seas were to form Georgian-Imereti province and the Caspian region. Tiflis was determined to be the main city of Georgia-Imereti, and Shamakhi of the Caspian region. This decree came into force since January 1841. It is mentioned in the first chapter of this book.
By that time, the post offices had been established:
the regional one in Tiflis;
the county ones of the first class – in Baku, Erivan, Nakhichevan, Kutaisi and Redoubt-Calais;
second class – in Gori, Dushet, Ananuri, Telavi, Sngnahe, Yelizavetpol, Cuba, Derbent and Vladikavkaz.

Yamskaya rush. Postage stamp.
County post offices were to report to the regional office of Tiflis. Further, with the abolition of earlier existing establishments in Georgia and the development of administrative management in the conquered areas of the region (which coincided with the intensification of military operations in the Black Sea and on the Caucasus line) – it is natural that the role and the importance of postal services in the South Caucasus should strengthen.
By the middle of forties there were operating the following types of postal service in Georgia and Tiflis:
1) Extra-mail , with which the correspondence was sent to the center on a regular basis, twice a week, according to a strictly determined route (St. Petersburg, Moscow, Novgorod, Tver, Tula, Voronezh provinces, the Land of the Don Cossack Host, Nizhny Novgorod, Odessa and Warsaw Provinces)
2) Heavy-mail – also to the center twice a week, with the division of correspondence to other places of the empire.
3) Easy-mail – to the postal places of the Caucasus and adjacent provinces.
4) Fly-mail – to border garrisons.
5) Relay mail – abroad, Vladikavkaz, according to a special work sheet with the payment of money for postal services.
There didn’t exist any telegraph lines at that time. The first telegraph line was opened in the Caucasus between Tiflis and Poti in 1860.
The formation of new province and region in the Transcaucasian region made Postal Department change the division of Russian into postal districts. In December 1840 taking into account the peculiarities of the region, it was decided to establish a new postal district for Georgian-Imereti province and for the Caspian region. [14] All post offices of Georgian-Imereti province and the Caspian region were transferred to the newly formed Mail District XII. Tiflis was identified to be the residence of the Postal inspector of a new district, and for his assistant – Shamakhi. The Cossacks were exempted from their obligation to accompany the mail in the Caucasus. They were replaced by postmen. The responsibilities of Tiflis post office had increased. With the addition of 10 postmen to accompany the mail its staff became 22 people. Tiflis regional post office in 1841 became known as provincial one. However, the order implemented in 1840 for civilian management of the Transcaucasian region, turned out to be in many ways uncomfortable.
In 1842, when inspecting the region, it was found out that due to its remoteness and the specific local conditions, the Ministry failed to establish there a proper supervision over the introduction of a new civil management. In addition, the intervention of the Ministries in the affairs of the Transcaucasian region often weakened the authority of the local manager. The Special Committee of the Caucasus established by the decree to the Senate of April 24, 1840, was only interested in the general direction of civil affairs in the region and failed to exercise proper supervision over the activities of new institutions in the Caucasus. According to the Minister of War Knyazh A.I.Chernyshev responsible for the general management of the affairs of the Transcaucasian region, to address the difficulties encountered, it was necessary to establish a special institution in St. Petersburg, which could keep all cases on civil management in Transcaucasia, having withdrawn them from Ministry, “until all the sections will get the complete control”, that was what he wrote to the Emperor Nicholas I on August 19, 1842. [15]
A temporary department was organized according to the Decree to the Senate on August 30, 1842. At the same time Caucasian Committee was also completely reorganized. In connection with this the reorganization of the main department of the Transcaucasian region located in Tbilisi also took place. On November 12, 1842, Tsar Nicholas I approved “Mandate to the General Directorate of the Transcaucasian region”, which determined the main goal: to rapidly establish “strong civil accomplishment” in the South Caucasus This “Mandate” raised the authorities of the Chief Commander of the region up to ministerial authority, acting in place. The Ministry could apply to the institutions reporting to them which were located in the South Caucasus only through the Chief Commander. Chief Directorate of the Council composition was limited to five members: three soldiers and two civilians. Military members of the Council in addition to their common duties were obliged to supervise departmental agencies which were out of local supervision: one was made responsible for training, the other supervised the customs and the third one took care of mail. In this regard, the positions of corresponding supervisors were abolished, including the position of postal Inspector of XII postal district.
Читать дальше














