• 5th Shock/28th, 44th and 51st Armies
○ 4x Tank Brigades (140; 6 G, 32 G, 33 G)
○ 1x Tank Regiments (22 G)
• Under Front Control:
○ 4th Guards Mechanized Corps (General-major Trofim I. Tanaschishin) {7}
North Caucasus Front (General-leytenant Ivan E. Petrov)
• 2x Tank Brigades (63; 5 G)
• 5x Tank Regiments (85, 244, 257, 258; 6 G)
• 2x OTB (75, 132)
• 2x SAP (1448, 1449)
Stavka Reserve (RVGK)/Steppe Front (General Ivan S. Konev)
• 4th Guards Army (General-leytenant Grigoriy I. Kulik)
○ 3rd Guards Tank Corps (General-major I.A. Vovchenko)
• 5th Guards Army (General-leytenant Aleksei S. Zhadov)
○ 10th Tank Corps (General-leytenant V.G. Burkov)
• 5th Guards Tank Army (General-leytenant Pavel A. Rotmistrov)
○ 5th Guards Mechanized Corps (General-major Boris M. Skvortsov)
○ 29th Tank Corps (General-major I. F. Kirichenko)
○ 53rd Guards Tank Regiment
○ 1549 SAP
• Other forces in Steppe Military District:
○ 4th Guards Tank Corps (General-leytenant Pavel P. Poluboiarov)
○ 3rd Guards Mechanized Corps (General-major Viktor T. Obukhov)
○ 1st Mechanized Corps (General-leytenant Mikhail D. Solomatin)
○ 2nd Mechanized Corps (General-leytenant Ivan P. Korchagin)
○ 93rd Tank Brigade
○ 34th, 35th and 39th Tank Regiments
Stavka Reserve (RVGK)/Separate Armies
• 3rd Guards Tank Army (General-leytenant Pavel S. Rybalko)
○ 12th Tank Corps (General-major Mitrofan I. Zin’kovich) {8}
○ 15th Tank Corps (General-major Filipp N. Rudkin)
○ 91st Tank Brigade
• 5th Mechanized Corps (General-major Mikhail V. Volkov)
• 18th Tank Corps (General-major Boris S. Bakharov)
• 25th Tank Corps (General-major Fedor G. Anikushkin)
• Tank Regimens (126, 127, 225)
• SAP (1547, 1548)
Moscow Military District
• 6th Guards Mechanized Corps (General-major Aleksandr I. Akimov)
• 11th Tank Corps (General-major Nikolai N. Radkevich)
• 20th Tank Corps (General-leytenant Ivan G. Lazarev)
• 30th Tank Corps (General-leytenant Georgy S. Rodin)
• 6x Tank Brigades (88, 92, 118, 144; 31 G, 34 G)
Volga Military District
• 9th Mechanized Corps (General-major Konstantin A. Malygin)
• 8x Tank Brigades (41 G; 2, 10, 14, 15, 116, 207, 254)
• 5x Tank Regiments (51, 61, 104, 154, 250)
• 6x OTB (126, 249, 258, 563, 564, 608)
Reinforcements:
• August 1943
○ 7th Mechanized Corps (General-major Ivan V. Dubovoi)
○ 8th Mechanized Corps (General-major Abram M. Khasin)
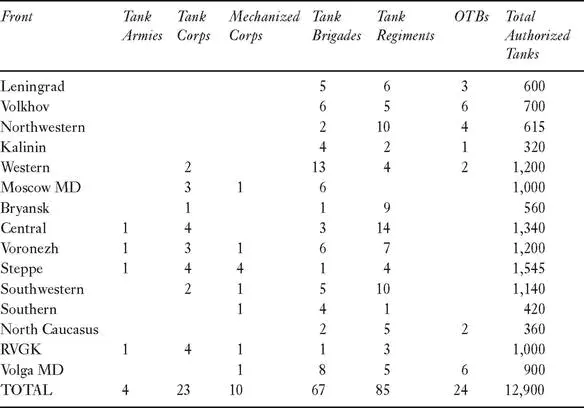
Appendix III
Tanks on the Eastern Front, 1943–44
Appendix IV
Tank Production, 1943
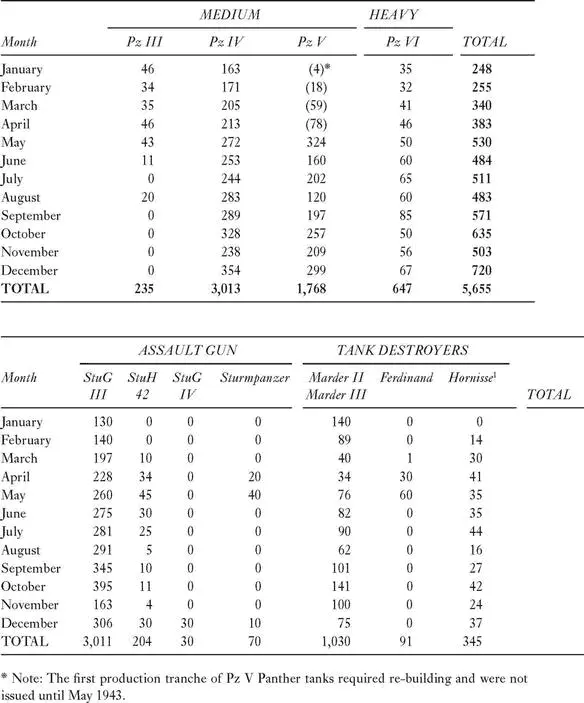
1Name changed to Nashorn in January 1944.
Key Industrial Decisions, 1943
• Hitler is impressed with the 128-mm gun and orders it mounted on either a Panther or Tiger as a tank destroyer.
• May 1943, Hitler approves the Maus super-heavy tank (188 tons) for production, which will divert resources from Krupp and Alkett for the next two years.
• August 1943, Pz III production terminated and facilities shift to Sturmgeschütz production.
• December 1943, Hitler approves Jagdpanzer IV for production against Guderian’s objections. Krupp-Grusonwerk AG plant ceases Pz IV production in favor of Jagdpanzer IV.
Primary AFV Manufacturing Centers:
• Braunschweig ( Muehlenbau und Industrie AG (MIAG), Pz III, StuG-III
• Nurnberg ( Maschinenfabrik Augsburg Nurnberg AG or MAN), Pz III, Pz V
• Berlin-Marienfelde (Daimler-Benz AG); Pz III, Pz V
• St. Valentin, Nibelungenwerke , Pz IV
• Plauen (Vogtlaendische Maschinenfabrik AG or VOMAG), Pz IV
• Magdeburg (Krupp-Grusonwerk AG), Pz IV
• Hannover ( Maschinenfabrik Niedersachen Hannover, GmbH), Pz V
• Kassel (Henschel & Sohn AG), Pz V, Pz VI
• Berlin-Borsigwalde (Alkett or Altmärkische Kettenwerk GmbH), StuG-III, StuH 42, Marder II
• Breslau (Fahrzeug und Motorenbau , GmbH (FAMO), Marder
• Duisburg, (Deutsche-Eisenwerke AG or DEW), Hornisse/Nashorn
Tank Engines:
• Friedrichshafen ( Maybach Motorenbau GmbH): Maybach HL 120 TRM; Maybach HL 230 P30 V12;
• Berlin ( Norddeutsche Motorenbau); Maybach HL 120 TRM
• Berlin-Niederschönewide (assembly plant)
• Berlin (Daimler-Benz AG); Maybach HL 230 P30 V12
• Zwickau (Auto Union AG): Maybach HL 230 P30 V12
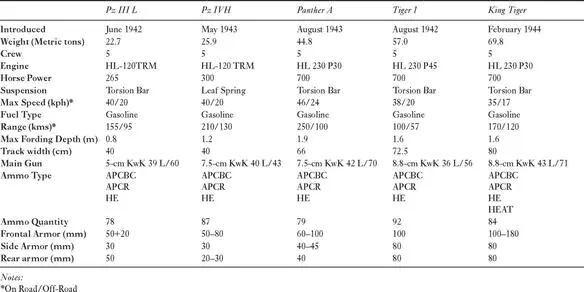
New tank models (3):
• April 1943, Pz IV Ausf H with new KwK 40 L/48 gun, improved frontal armor protection up to 80-mm but increased weight by 2.5 ton
• July 1943, Pz V Ausf D with long 7.5-cm KwK 42 L/70 introduced
• August 1943, Pz V Ausf A introduced
New assault gun models (3):
• March 1943, StuH 42 assault gun with 10.5-cm StuH 42 L / 28 howitzer starts mass production. Ten pre-production models were built in November 1942 and sent to Leningrad.
• April 1943, Sturmpanzer introduce with 15-cm StuH 43 L/12 howitzer on Pz IV hull, built by Deutsche Eisenwerke A.G.
• December 1943, StuG IV introduced
New tank destroyer models (2):
• February 1943, Nashhorn tank destroyer equipped with 8.8-cm Pak 43 L/71 on Pz IV chassis. Built by DEW (Deutsche-Eisenwerke AG) in Duisburg
• April 1943, Ferdinand tank destroyer introduced with 8.8-cm KwK 43 L/71 gun, built at Nibelungenwerke
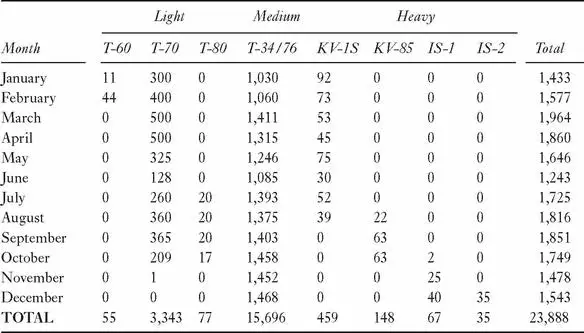
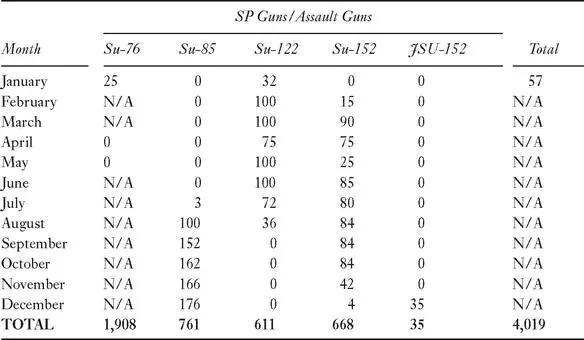
Key Industrial Decisions, 1943
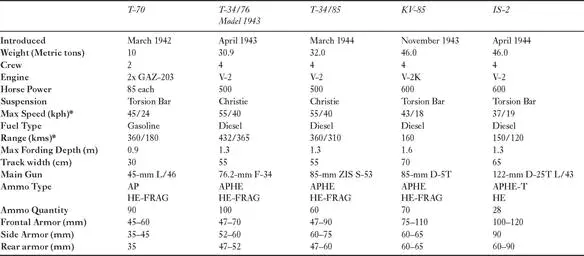
• 21 March 1943, Production of the Su-76 is stopped by GKO after only 170 built due to engine and transmission failures. The improved version, Su-76M, re-enters production in late May or June 1943
• August 1943, Phase-out of KV-1 heavy tank, shift to heavy assault guns and new IS-series heavy tanks
• October 1943, all light tank production programs are cancelled
Primary AFV Manufacturing Centers:
• Sverdlovsk/Plant 37, T-60, Su-76
• Gorky/GAZ Plant, T-70, Su-76
• Nizhniy Tagil/Stalin Ural Tank Factory183, T-34/76
• Chelyabinsk (ChTZ), T-34/76, KV-1, KV-85, IS-1/2, SU-152
• Gorky/Krasnoye Sormovo Plant No. 112, T-34/76
• Omsk/Lenin Plant 174, T-34/76
• Sverdlovsk/UZTM Uralmash , T-34/76, Su-85, Su-122
• Kirov/Plant 38, Su-76
• Mytishchi/Plant 40; Su-76
Tank Engines:
• V-2 Diesel engine (Zavod 75)
Читать дальше












![John Stieber - Against the Odds - Survival on the Russian Front 1944-1945 [2nd Edition]](/books/405234/john-stieber-against-the-odds-survival-on-the-russian-front-1944-1945-2nd-edition-thumb.webp)



