Daniel Defoe - History of the Plague in London
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Daniel Defoe - History of the Plague in London» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_antique, foreign_prose, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:History of the Plague in London
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
History of the Plague in London: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «History of the Plague in London»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
History of the Plague in London — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «History of the Plague in London», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Those who wish to know more about the plague than Defoe tells them should consult Besant's "London," pp. 376-394 (New York, Harpers). Besant refers to two pamphlets, "The Wonderful Year" and "Vox Civitatis," which he thinks Defoe must have used in writing his book.
HISTORY
OF
THE PLAGUE IN LONDON
It was about the beginning of September, 1664, that I, among the rest of my neighbors, heard in ordinary discourse that the plague was returned again in Holland; for it had been very violent there, and particularly at Amsterdam and Rotterdam, in the year 1663, whither, they say, it was brought (some said from Italy, others from the Levant) among some goods which were brought home by their Turkey fleet; others said it was brought from Candia; others, from Cyprus. It mattered not from whence it came; but all agreed it was come into Holland again. 4 4 It was popularly believed in London that the plague came from Holland; but the sanitary (or rather unsanitary) conditions of London itself were quite sufficient to account for the plague's originating there. Andrew D. White tells us, that it is difficult to decide to-day between Constantinople and New York as candidates for the distinction of being the dirtiest city in the world.
We had no such thing as printed newspapers in those days, to spread rumors and reports of things, and to improve them by the invention of men, as I have lived to see practiced since. But such things as those were gathered from the letters of merchants and others who corresponded abroad, and from them was handed about by word of mouth only; so that things did not spread instantly over the whole nation, as they do now. But it seems that the government had a true account of it, and several counsels 5 5 Incorrectly used for "councils."
were held about ways to prevent its coming over; but all was kept very private. Hence it was that this rumor died off again; and people began to forget it, as a thing we were very little concerned in and that we hoped was not true, till the latter end of November or the beginning of December, 1664, when two men, said to be Frenchmen, died of the plague in Longacre, or rather at the upper end of Drury Lane. 6 6 In April, 1663, the first Drury Lane Theater had been opened. The present Drury Lane Theater (the fourth) stands on the same site.
The family they were in endeavored to conceal it as much as possible; but, as it had gotten some vent in the discourse of the neighborhood, the secretaries of state 7 7 The King's ministers. At this time they held office during the pleasure of the Crown, not, as now, during the pleasure of a parliamentary majority.
got knowledge of it. And concerning themselves to inquire about it, in order to be certain of the truth, two physicians and a surgeon were ordered to go to the house, and make inspection. This they did, and finding evident tokens 8 8 Gangrene spots (see text, pp. 197, 198).
of the sickness upon both the bodies that were dead, they gave their opinions publicly that they died of the plague. Whereupon it was given in to the parish clerk, 9 9 The local government of London at this time was chiefly in the hands of the vestries of the different parishes. It is only of recent years that the power of these vestries has been seriously curtailed, and transferred to district councils.
and he also returned them 10 10 The report.
to the hall; and it was printed in the weekly bill of mortality in the usual manner, thus: —
Plague, 2. Parishes infected, 1.
The people showed a great concern at this, and began to be alarmed all over the town, and the more because in the last week in December, 1664, another man died in the same house and of the same distemper. And then we were easy again for about six weeks, when, none having died with any marks of infection, it was said the distemper was gone; but after that, I think it was about the 12th of February, another died in another house, but in the same parish and in the same manner.
This turned the people's eyes pretty much towards that end of the town; and, the weekly bills showing an increase of burials in St. Giles's Parish more than usual, it began to be suspected that the plague was among the people at that end of the town, and that many had died of it, though they had taken care to keep it as much from the knowledge of the public as possible. This possessed the heads of the people very much; and few cared to go through Drury Lane, or the other streets suspected, unless they had extraordinary business that obliged them to it.
This increase of the bills stood thus: the usual number of burials in a week, in the parishes of St. Giles-in-the-Fields and St. Andrew's, Holborn, 11 11 Pronounced Hō´burn.
were 12 12 Was.
from twelve to seventeen or nineteen each, few more or less; but, from the time that the plague first began in St. Giles's Parish, it was observed that the ordinary burials increased in number considerably. For example: —
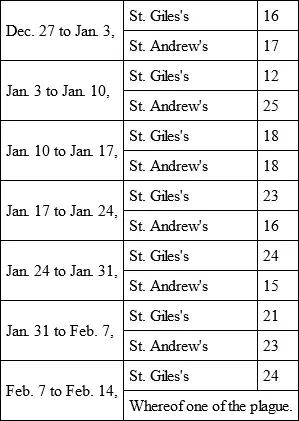
The like increase of the bills was observed in the parishes of St. Bride's, adjoining on one side of Holborn Parish, and in the parish of St. James's, Clerkenwell, adjoining on the other side of Holborn; in both which parishes the usual numbers that died weekly were from four to six or eight, whereas at that time they were increased as follows: —
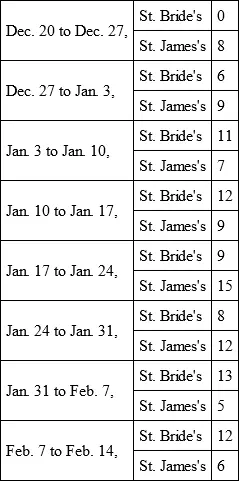
Besides this, it was observed, with great uneasiness by the people, that the weekly bills in general increased very much during these weeks, although it was at a time of the year when usually the bills are very moderate.
The usual number of burials within the bills of mortality for a week was from about two hundred and forty, or thereabouts, to three hundred. The last was esteemed a pretty high bill; but after this we found the bills successively increasing, as follows: —
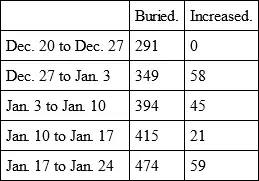
This last bill was really frightful, being a higher number than had been known to have been buried in one week since the preceding visitation of 1656.
However, all this went off again; and the weather proving cold, and the frost, which began in December, still continuing very severe, even till near the end of February, attended with sharp though moderate winds, the bills decreased again, and the city grew healthy; and everybody began to look upon the danger as good as over, only that still the burials in St. Giles's continued high. From the beginning of April, especially, they stood at twenty-five each week, till the week from the 18th to the 25th, when there was 13 13 Were.
buried in St. Giles's Parish thirty, whereof two of the plague, and eight of the spotted fever (which was looked upon as the same thing); likewise the number that died of the spotted fever in the whole increased, being eight the week before, and twelve the week above named.
This alarmed us all again; and terrible apprehensions were among the people, especially the weather being now changed and growing warm, and the summer being at hand. However, the next week there seemed to be some hopes again: the bills were low; the number of the dead in all was but 388; there was none of the plague, and but four of the spotted fever.
But the following week it returned again, and the distemper was spread into two or three other parishes, viz., St. Andrew's, Holborn, St. Clement's-Danes; and, to the great affliction of the city, one died within the walls, in the parish of St. Mary-Wool-Church, that is to say, in Bearbinder Lane, near Stocks Market: in all, there were nine of the plague, and six of the spotted fever. It was, however, upon inquiry, found that this Frenchman who died in Bearbinder Lane was one who, having lived in Longacre, near the infected houses, had removed for fear of the distemper, not knowing that he was already infected.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «History of the Plague in London»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «History of the Plague in London» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «History of the Plague in London» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












