Thomas Bulfinch - The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Thomas Bulfinch - The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_antique, foreign_prose, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911): краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911) — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:

Fig. 70. A Young River-god
"Oh, save me! Oh, guide me!
And bid the deep hide me,
For he grasps me now by the hair!"
The loud Ocean heard,
To its blue depth stirred,
And divided at her prayer;
And under the water
The Earth's white daughter
Fled like a sunny beam;
Behind her descended
Her billows unblended
With the brackish Dorian stream: —
Like a gloomy stain
On the emerald main,
Alpheüs rushed behind, —
As an eagle pursuing
A dove to its ruin
Down the streams of the cloudy wind.
Under the bowers
Where the Ocean Powers
Sit on their pearlèd thrones,
Through the coral woods
Of the weltering floods,
Over heaps of unvalued stones;
Through the dim beams
Which amid the streams
Weave a network of colored light;
And under the caves,
Where the shadowy waves
Are as green as the forest's night:
Outspeeding the shark,
And the swordfish dark,
Under the ocean foam,
And up through the rifts
Of the mountain clifts
They past to their Dorian home.
And now from their fountains
In Enna's mountains,
Down one vale where the morning basks,
Like friends once parted
Grown single-hearted,
They ply their watery tasks.
At sunrise they leap
From their cradles steep
In the cave of the shelving hill;
At noontide they flow
Through the woods below
And the meadows of Asphodel:
And at night they sleep
In the rocking deep
Beneath the Ortygian shore; —
Like spirits that lie
In the azure sky
When they love but live no more.
95. The Fate of Actæon. 117 117 Ovid, Metam. 3, 138-252.
Diana's severity toward young Actæon, grandson of Cadmus whose kindred fell under the curse of Mars, is thus narrated.
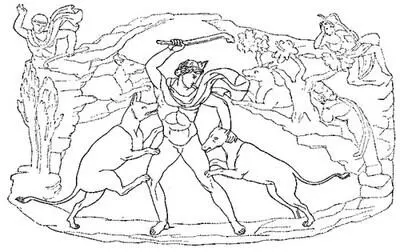
Fig. 71. Actæon
One day, having repaired to a valley inclosed by cypresses and pines, where gushed a fountain of sparkling water, the chaste Diana handed her javelin, her quiver, and her bow to one nymph, her robe to another, while a third unbound the sandals from her feet. Then Crocale, the most skillful of them, arranged her hair, and Nephele, Hyale, and the rest drew water in capacious urns. While the huntress queen was thus employed in the labors of the toilet, Actæon, the son of Autonoë and Aristæus, having quitted his companions of the chase and rambling without any especial object, came to the place, led thither by his destiny. As he presented himself at the entrance of the cave, the nymphs, seeing a man, screamed and rushed towards the goddess to hide her with their bodies. But she was taller than the rest and overtopped them all by a head. Such a color as tinges the clouds at sunset or at dawn came over the countenance of Diana, thus taken by surprise. Surrounded as she was by her nymphs, she yet turned half away and sought with a sudden impulse for her arrows. As they were not at hand, she dashed the water into the face of the intruder, saying, "Now go and tell, if you can, that you have seen Diana unappareled." Immediately a pair of branching stag's horns grew out of the huntsman's head, his neck gained in length, his ears grew sharp-pointed, his hands became feet, his arms, his long legs, and his body were covered with a hairy spotted hide. Fear took the place of his former boldness, and the hero fled. What should he do? – go home to the palace or lie hid in the woods? While he hesitated his dogs saw him. Over rocks and cliffs, through mountain gorges that seemed impracticable, he fled, and they followed. The air resounded with the bark of the dogs. Presently one fastened on his back, another seized his shoulder; the rest of the pack came up and buried their teeth in his flesh. His friends and fellow-huntsmen cheered on the dogs, and, looking everywhere for Actæon, called on him to join the sport. At the sound of his name, he turned his head and heard them regret that he should be away. He earnestly wished he was. But Diana had no pity for him, nor was her anger appeased till the dogs had torn his life out.
96. The Fortunes and Death of Orion.Orion, the son of Neptune, was a giant and a mighty hunter, whose prowess and manly favor gained for him the rare good will of Diana.
It is related that he loved Merope, the daughter of Œnopion, king of Chios, and sought her in marriage. He cleared the island of wild beasts and brought the spoils of the chase as presents to his beloved; but as Œnopion constantly deferred his consent, Orion attempted to gain possession of the maiden by violence. Her father, incensed at his conduct, made Orion drunk, deprived him of his sight, and cast him out on the seashore. The blinded hero, instructed by an oracle to seek the rays of morning, followed the sound of a Cyclops' hammer till he reached Lemnos, where Vulcan, taking pity on him, gave him Cedalion, one of his men, to be his guide to the abode of the sun. Placing Cedalion on his shoulders, Orion proceeded to the east, and there meeting the sun-god, was restored to sight by his beam. 118 118 Apollodorus, 1, 4, § 3.
After this he dwelt as a hunter with the queen of the echoing chase; and it was even hinted that she loved him. Her brother, highly displeased, often chid her, but to no purpose. One day, therefore, observing Orion as he waded through the sea with his head just above the water, Apollo pointed out the black object to his sister, and maintained that she could not hit it. The archer goddess discharged a shaft with fatal aim: the waves rolled the dead body of Orion to the land. Then bewailing her fatal error with many tears, Diana placed him among the stars, where he appears as a giant, with a girdle, sword, lion's skin, and club.
Sirius, his dog, follows him, and the Pleiads fly before him. 119 119 Ovid, Fasti, 5, 537; Iliad, 18, 486, and 22, 29; Odyssey, 5, 121, 274.
In the beginning of winter, all through the night, Orion follows the chase across the heavens; but with dawn he sinks toward the waters of his father Neptune. In the beginning of summer, he may be seen with daybreak in the eastern sky, where, beloved by Aurora, he remains gradually paling before the light of day till, finally, Diana, jealous of his happiness, draws her gentle darts and slays him.

Fig. 72. The Pleiades
From the painting by Vedder
97. The Pleiads, 120 120 The story is told by Hyginus in his Fables, and in his Poetical Astronomy.
who still fly before Orion in the heavens, were daughters of Atlas, and nymphs of Diana's train. One day Orion saw them in Bœotia, became enamored of them, and gave pursuit. In their distress they prayed to the gods to change their form. Jupiter, accordingly, turned them into pigeons, and made them a constellation. Though their number was seven, only six stars are visible; for Electra, it is said, left her place that she might not behold the ruin of Troy, which had been founded by her son Dardanus. The sight had such an effect on her sisters that they blanched, and have been pale ever since. But Electra became a comet; her hair floating wildly behind her, she still inconsolably ranges the expanse of heaven. According to some, the lost Pleiad is Merope, who was vested with mortality in consequence of her marriage with the mortal Sisyphus, king of Corinth.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












