Thomas Bulfinch - The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Thomas Bulfinch - The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_antique, foreign_prose, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911): краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911) — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Another great division of the Greek people, the Pelasgic, resident in the Peloponnesus or southern portion of the peninsula, was said to have sprung from a different stock of heroes, that of Pelasgus, son of Phoroneus of Argos and grandson of the river-god Inachus.
The demigods and heroes were of matchless worth and valor. Their adventures form the subject of many of the succeeding chapters. The Older Heroes, especially, were endowed with godlike qualities, which they devoted to the service of mankind in the destruction of monsters, the founding of cities, or the introduction of civilization. Such were Perseus, the hero of Argos and his descendant Hercules, who came to be worshiped as the national hero of the Greeks. Such, too, Cadmus, the founder of Thebes, and Cecrops of Athens, and one of his successors, Theseus, a "second Hercules." Each city of Greece had its patron hero, to whom it accorded the honors of divinity. The Younger Heroes were chieftains in the Theban and the Trojan wars and in numerous other military or predatory expeditions.

Fig. 5. Poseidon, Dionysus, and Goddess
CHAPTER II
THE GODS OF HEAVEN 16 16 Consult, in general, corresponding sections of the Commentary.

Fig. 6. Two Hours
22. Olympus.The heaven of the Greek gods was the summit of an ideal mountain called Olympus. 17 17 Symbolized on earth by Mount Olympus in Thessaly.
A gate of clouds, kept by goddesses, the Hours or Seasons, opened to permit the passage of the Celestials to earth, and to receive them on their return. The gods had their separate dwellings; but all, when summoned, repaired to the palace of Jupiter, – even the deities whose usual abode was the earth, the waters, or the underworld. In the great hall of the Olympian king the gods feasted each day on ambrosia and nectar. Here they conversed of the affairs of heaven and earth; and as they quaffed the nectar that Hebe poured, Apollo made melody with his lyre and the Muses sang in responsive strain. When the sun was set, the gods withdrew to their respective dwellings for the night.
The following lines from the Odyssey express the conception of Olympus entertained by Homer:
So saying, Minerva, goddess, azure-eyed,
Rose to Olympus, the reputed seat
Eternal of the gods, which never storms
Disturb, rains drench, or snow invades, but calm
The expanse and cloudless shines with purest day.
There the inhabitants divine rejoice
Forever. 18 18 Cowper's translation.
23. The Great Gods.The gods of Heaven were the following: 19 19 See Commentary, § 23, for Gladstone's latest utterance on the number of the Olympians.
• Jupiter (Zeus). 20 20 The names included in parentheses represent the Greek, the others being Roman equivalents, Latin names, or names common to both Greek and Roman usage.
• His daughter, Minerva (Athena), who sprang from his brain, full-grown and full-armed.
• His sister and wife, Juno (Hera).
• His children by Juno, – Mars (Ares), Vulcan (Hephæstus), and Hebe.
• His children by Latona, – Apollo, or Phœbus, and Diana (Artemis).
• His daughter by Dione, – Venus (Aphrodite). 21 21 See Commentary, § 34.
• His son by Maia, – Mercury (Hermes).
• His sister, Vesta (Hestia), the oldest born of Cronus and Rhea.
Of these all were deities of the highest order save Hebe, who must be ranked with the lesser gods. With the remaining ten "Great Gods" are sometimes reckoned the other sister of Jupiter, Ceres (Demeter), properly a divinity of earth, and Neptune (Poseidon), ruler of the sea.
24. Jupiter 22 22 On the Latin name, see Commentary, § 24.
(Zeus).The Greek name signifies the radiant light of heaven. Jupiter was the supreme ruler of the universe, wisest of the divinities and most glorious. In the Iliad he informs the other gods that their united strength would not budge him: that, on the contrary, he could draw them and earth and the seas to himself, and suspend all from Olympus by a golden chain. Throned in the high, clear heavens, Jupiter was the gatherer of clouds and snows, the dispenser of gentle rains and winds, the moderator of light and heat and the seasons, the thunderer, the wielder of the thunderbolt. Bodily strength and valor were dear to him. He was worshiped with various rites in different lands, and to him were sacred everywhere the loftiest trees and the grandest mountain peaks. He required of his worshipers cleanliness of surroundings and person and heart. Justice was his; his to repay violation of duty in the family, in social relations, and in the state. Prophecy was his; and his will was made known at the oracle of Dodona, where answers were given to those who inquired concerning the future. This oracular shrine was the most ancient in Greece. According to one account two black doves had taken wing from Thebes in Egypt. One flew to Dodona in Epirus, and, alighting in a grove of oaks, proclaimed to the inhabitants of the district that they should establish there an oracle of Jupiter. The other dove flew to the temple of Jupiter Ammon in the Libyan oasis, and delivered a similar command. According to another account, these were not doves but priestesses who, carried off from Thebes by the Phœnicians, set up oracles at Oasis and Dodona. The responses of the oracle were given by the rustling of the oak trees in the wind. The sounds were interpreted by priests.
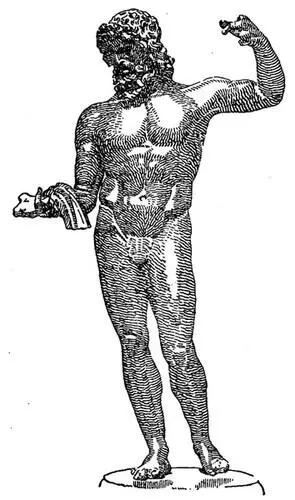
Fig. 7. Zeus
That Jupiter himself, though wedded to the goddess Juno, should be charged with numerous other love affairs, not only in respect of goddesses but of mortals, is, in part, explained by the fact that to the supreme divinity of the Greeks have been ascribed attributes and adventures of numerous local and foreign divinities that were gradually identified with him. It is, therefore, not wise to assume that the love affairs of Jupiter and of other divinities always symbolize combinations of natural or physical forces that have repeated themselves in ever-varying guise. It is important to understand that the more ideal Olympian religion absorbed features of inferior religions, and that Jupiter, when represented as appropriating the characteristics of other gods, was sometimes, also, accredited with their wives.
Beside the children of Jupiter already enumerated, there should here be mentioned, as of peculiar consequence, Bacchus (Dionysus), the god of wine, a deity of earth, – Proserpine, the wife of Pluto and queen of the underworld, – and Hercules, the greatest of the heroes.

Fig. 8. Zeus after Phidias
25. Conceptions of Jupiter.The Greeks usually conceived the Jupiter of war as riding in his thunder-car, hurling the thunderbolt or lashing his enemies with a scourge of lightning. He wore a breastplate or shield of storm-cloud like the skin of a gray goat (the Ægis ), fearful to behold, and made by the god of fire. His special messenger was the eagle. It was, however, only with the passage of generations that the Greeks came to represent their greatest of the gods by the works of men's hands. The statue of Olympian Jove by Phidias was considered the highest achievement of Grecian sculpture. It was of colossal dimensions and, like other statues of the period, "chryselephantine," that is, composed of ivory and gold. For the parts representing flesh were of ivory laid on a framework of wood, while the drapery and ornaments were of gold. The height of the figure was forty feet, of the pedestal twelve. The god was represented as seated on his throne. His brows were crowned with a wreath of olive; he held in his right hand a scepter, and in his left a statue of Victory. The throne was of cedar, adorned with gold and precious stones.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «The Classic Myths in English Literature and in Art (2nd ed.) (1911)» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












