Samuel Drake - The Campaign of Trenton 1776-77
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Samuel Drake - The Campaign of Trenton 1776-77» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_antique, foreign_prose, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:The Campaign of Trenton 1776-77
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
The Campaign of Trenton 1776-77: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «The Campaign of Trenton 1776-77»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
The Campaign of Trenton 1776-77 — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «The Campaign of Trenton 1776-77», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Fort Washington.
Fort Washington [5] Fort Washington stood at the present 183d street. Besides defending the approaches from King's Bridge, it also obstructed the passage of the enemy's ships up the Hudson, at its narrowest point below the Highlands. At the same time Fort Lee, first called Fort Constitution, was built on the brow of the lofty Palisades, opposite, and a number of pontoons filled with stones were sunk in the river between. The enemy's ships ran the blockade, however, with impunity.
was, therefore, built on a commanding height two and a half miles below King's Bridge, with outworks covering the approaches to the bridge, either by the country roads coming in from the north or from Harlem River at the east. These works were never finished, but even if they had been they could not solve the problem of a successful defence, because it lay always in the power of the strongest army to cut off all communication with the country beyond – and that means the passing in of reënforcements or supplies – by merely throwing itself across the roads just referred to. This done, the army in New York must either be shut up in the island, or come out and fight, provided the enemy had not already put it out of their power to do so by promptly seizing King's Bridge. And in that case there was no escape except by water, under fire of the enemy's ships of war.
One watchful eye, therefore, had to be kept constantly to the front, and another to the rear, between positions lying twelve to thirteen miles apart, and separated by a wide and deep river.
It thus appears that the defence of New York was a much more formidable task than had, at first, been supposed, and that an army of 40,000 men was none too large for the purpose, especially as it was wholly impracticable to reënforce King's Bridge from Brooklyn, or vice versa . But from one or another cause the army had fallen below 25,000 effectives by midsummer, counting also the militia, who formed a floating and most uncertain constituent of it. For the present, therefore, King's Bridge was held as an outpost, or until the enemy's plan of attack should be clearly developed; for whether Howe would first assail the works at Brooklyn, Bunker Hill fashion, or land his troops beyond King's Bridge, bringing them around by way of Long Island Sound, were questions most anxiously debated in the American camp.
However, the belief in a successful defence was much encouraged by the recent crushing defeat that the British fleet had met with in attempting to pass the American batteries at Charleston. Thrice welcome after the disasters of the unlucky Canada campaign, this success tended greatly to stiffen the backbone of the army, in the face of the steady and ominous accumulation of the British land and naval forces in the lower bay. Then again, the Declaration of Independence, read to every brigade in the army (July 9), was received with much enthusiasm. Now, for the first time since hostilities began, officers and men knew exactly what they were fighting for. There was at least an end to suspense, a term to all talk of compromise, and that was much.
The British army.
Thus matters stood in the American camps, when the British army that had been driven from Boston, heavily reënforced from Europe, and by calling in detachments from South Carolina, Florida, and the West Indies, so bringing the whole force in round numbers up to 30,000 men, 6 6 The British regiments serving with Howe were the Fourth, Fifth, Sixth, Tenth, Fourteenth, Fifteenth, Sixteenth, Seventeenth, Twenty-second, Twenty-third, Twenty-seventh, Twenty-eighth, Thirty-third, Thirty-fifth, Thirty-seventh, Thirty-eighth, Fortieth, Forty-second, Forty-third, Forty-fourth, Forty-fifth, Forty-sixth, Forty-ninth, Fifty-second, Fifty-fourth, Fifty-fifth, Fifty-seventh, Sixty-third, Sixty-fourth, and Seventy-first, or thirty battalions with an aggregate of 24,513 officers and men. To these should be added 8,000 Hessians hired for the war, bringing the army up to 32,500 soldiers. Twenty-five per cent. would be a liberal deduction for the sick, camp-guards, orderlies, etc. The navy was equally powerful in its way, though it did little service here. Large as it was, this army was virtually destroyed by continued attrition.
cast anchor in the lower bay. Never before had such an armament been seen in American waters. Backed by this imposing display of force, royal commissioners had come to tender the olive branch, as it were, on the point of the bayonet. They were told, in effect, that those who have committed no crime want no pardon. Washington was next approached. As the representative soldier of the new nation, he refused to be addressed except by the title it had conferred upon him. The etiquette of the contest must be asserted in his person. Failing to find any common ground, upon which negotiations could proceed, resort was had to the bayonet again.
III
LONG ISLAND TAKEN
British move to L. Island.
Up to August 22, the British army made no move from its camps at Staten Island. On their part, the Americans could only watch and wait. On this day, however, active operations began with the landing of Howe's troops, in great force, on the Long Island shore, opposite. This force immediately spread itself out through the neighboring villages from Gravesend, to Flatbush and Flatlands, driving the American skirmishers before them into a range of wooded hills, [1] This range of hills includes the present Prospect Park and Greenwood Cemetery.
which formed their outer line of defence. Howe had determined to attack in front, clearing the way as he went.
Plan of attack.
As the enemy would have to force his way across these hills, before he could reach the American intrenched lines around Brooklyn, all the roads leading over them were strongly guarded, except out at the extreme left, beyond Bedford village, where only a patrol was posted. [2] This weak point was the approach from the east where the Jamaica road crossed the hills into Bedford village. By striking this road somewhat higher up, the enemy got to Bedford before the Americans, guarding the hills beyond, had notice of their approach.
This fatal oversight, of which Howe was well informed, suggested the British plan of attack, which was quickly matured and successfully carried out. It included a demonstration on the American left, to draw attention to that point, while another corps was turning the right, at its unguarded point.
A third column was held in readiness to move upon the American centre from Flatbush, just as soon as the other attacks were well in progress. When the flanking corps was in position, these demonstrations were to be turned into real attacks, which, if successful, would throw the Americans back upon the flanking column, which, in its turn, would cut off their retreat to their intrenchments.
This clever combination, showing a perfect knowledge of the ground, worked exactly as planned.
By making a night march, the turning column got quite around the American flank and rear unperceived, and on the morning of the 27th was in position, near Bedford, at an early hour, waiting for the signal-guns to announce the beginning of the battle at the British left.
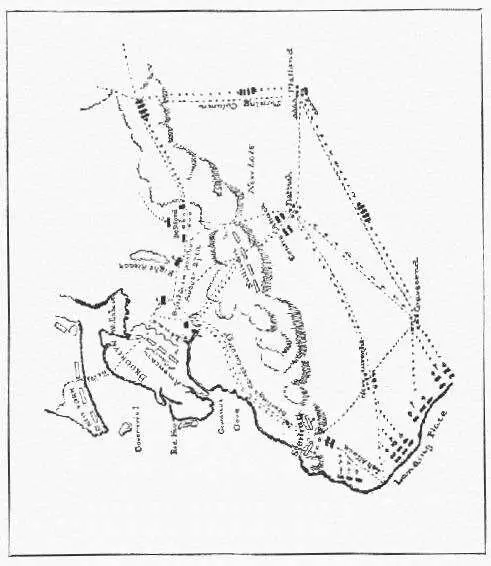
BATTLE OF LONG ISLAND.
Battle of Long Island.
Both columns then advanced to the attack. Being strongly posted, and well commanded, the Americans made an obstinate resistance and did hold the enemy in check for some hours at one end of the line, only to find themselves cut off by the hurried retreat of all the troops posted at the passes on their left; for as soon as the firing there showed that the turning column had come up in their rear, these troops, with great difficulty, fought their way back to the Brooklyn lines, leaving three generals and upwards of 1,000 men in the enemy's hands.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «The Campaign of Trenton 1776-77»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «The Campaign of Trenton 1776-77» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «The Campaign of Trenton 1776-77» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












