John Ruskin - The Stones of Venice, Volume 1 (of 3)
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «John Ruskin - The Stones of Venice, Volume 1 (of 3)» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_antique, foreign_home, architecture_book, literature_19, visual_arts, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:The Stones of Venice, Volume 1 (of 3)
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
The Stones of Venice, Volume 1 (of 3): краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «The Stones of Venice, Volume 1 (of 3)»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
The Stones of Venice, Volume 1 (of 3) — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «The Stones of Venice, Volume 1 (of 3)», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Thus far we have traced the probable conditions of shaft structure in pure theory; I shall now lay before the reader a brief statement of the facts of the thing in time past and present.
§ XXIII. In the earliest and grandest shaft architecture which we know, that of Egypt, we have no grouped arrangements, properly so called, but either single and smooth shafts, or richly reeded and furrowed shafts, which represent the extreme conditions of a complicated group bound together to sustain a single mass; and are indeed, without doubt, nothing else than imitations of bundles of reeds, or of clusters of lotus: 42but in these shafts there is merely the idea of a group, not the actual function or structure of a group; they are just as much solid and simple shafts as those which are smooth, and merely by the method of their decoration present to the eye the image of a richly complex arrangement.
§ XXIV. After these we have the Greek shaft, less in scale, and losing all suggestion or purpose of suggestion of complexity, its so-called flutings being, visibly as actually, an external decoration.
§ XXV. The idea of the shaft remains absolutely single in the Roman and Byzantine mind; but true grouping begins in Christian architecture by the placing of two or more separate shafts side by side, each having its own work to do; then three or four, still with separate work; then, by such steps as those above theoretically pursued, the number of the members increases, while they coagulate into a single mass; and we have finally a shaft apparently composed of thirty, forty, fifty, or more distinct members; a shaft which, in the reality of its service, is as much a single shaft as the old Egyptian one; but which differs from the Egyptian in that all its members, how many soever, have each individual work to do, and a separate rib of arch or roof to carry: and thus the great Christian truth of distinct services of the individual soul is typified in the Christian shaft; and the old Egyptian servitude of the multitudes, the servitude inseparable from the children of Ham, is typified also in that ancient shaft of the Egyptians, which in its gathered strength of the river reeds, seems, as the sands of the desert drift over its ruin, to be intended to remind us for ever of the end of the association of the wicked. “Can the rush grow up without mire, or the flag grow without water?—So are the paths of all that forget God; and the hypocrite’s hope shall perish.”
§ XXVI. Let the reader then keep this distinction of the three systems clearly in his mind: Egyptian system, an apparent cluster supporting a simple capital and single weight; Greek and Roman system, single shaft, single weight; Gothic system, divided shafts, divided weight: at first actually and simply divided, at last apparently and infinitely divided; so that the fully formed Gothic shaft is a return to the Egyptian, but the weight is divided in the one and undivided in the other.
§ XXVII. The transition from the actual to the apparent cluster, in the Gothic, is a question of the most curious interest; I have thrown together the shaft sections in Plate II.to illustrate it, and exemplify what has been generally stated above. 43
II.
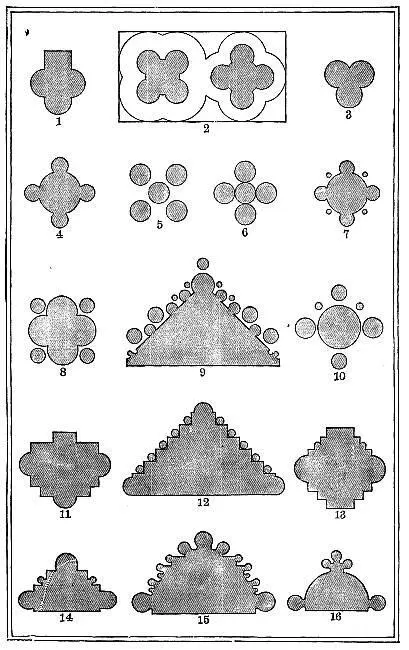
PLANS OF PIERS.
1. The earliest, the most frequent, perhaps the most beautiful of all the groups, is also the simplest; the two shafts arranged as at b or c , ( Fig. XIV.) above, bearing an oblong mass, and substituted for the still earlier structure a , Fig. XIV.In Plate XVII.( Chap. XXVII.) are three examples of the transition: the one on the left, at the top, is the earliest single-shafted arrangement, constant in the rough Romanesque windows; a huge hammer-shaped capital being employed to sustain the thickness of the wall. It was rapidly superseded by the double shaft, as on the right of it; a very early example from the cloisters of the Duomo, Verona. Beneath, is a most elaborate and perfect one from St. Zeno of Verona, where the group is twice complicated, two shafts being used, both with quatrefoil sections. The plain double shaft, however, is by far the most frequent, both in the Northern and Southern Gothic, but for the most part early; it is very frequent in cloisters, and in the singular one of St. Michael’s Mount, Normandy, a small pseudo-arcade runs along between the pairs of shafts, a miniature aisle. The group is employed on a magnificent scale, but ill proportioned, for the main piers of the apse of the cathedral of Coutances, its purpose being to conceal one shaft behind the other, and make it appear to the spectator from the nave as if the apse were sustained by single shafts, of inordinate slenderness. The attempt is ill-judged, and the result unsatisfactory.
Fig. XVII.
§ XXVIII. 2. When these pairs of shafts come near each other, as frequently at the turnings of angles ( Fig. XVII.), the quadruple group results, b 2, Fig. XIV., of which the Lombardic sculptors were excessively fond, usually tying the shafts together in their centre, in a lover’s knot. They thus occur in Plate V., from the Broletto of Como; at the angle of St. Michele of Lucca, Plate XXI.; and in the balustrade of St. Mark’s. This is a group, however, which I have never seen used on a large scale. 44
§ XXIX. 3. Such groups, consolidated by a small square in their centre, form the shafts of St. Zeno, just spoken of, and figured in Plate XVII., which are among the most interesting pieces of work I know in Italy. I give their entire arrangement in Fig. XVIII.: both shafts have the same section, but one receives a half turn as it ascends, giving it an exquisite spiral contour: the plan of their bases, with their plinth, is given at 2, Plate II.; and note it carefully, for it is an epitome of all that we observed above, respecting the oblique and even square. It was asserted that the oblique belonged to the north, the even to the south: we have here the northern Lombardic nation naturalised in Italy, and, behold, the oblique and even quatrefoil linked together; not confused, but actually linked by a bar of stone, as seen in Plate XVII., under the capitals.
Fig. XVIII.
4. Next to these, observe the two groups of five shafts each, 5 and 6, Plate II., one oblique, the other even. Both are from upper stories; the oblique one from the triforium of Salisbury; the even one from the upper range of shafts in the façade of St. Mark’s at Venice. 45
§ XXX. Around these central types are grouped, in Plate II., four simple examples of the satellitic cluster, all of the Northern Gothic: 4, from the Cathedral of Amiens; 7, from that of Lyons (nave pier); 8, the same from Salisbury; 10, from the porch of Notre Dame, Dijon, having satellites of three magnitudes: 9 is one of the piers between the doors of the same church, with shafts of four magnitudes, and is an instance of the confusion of mind of the Northern architects between piers proper and jamb mouldings (noticed farther in the next chapter, § XXXI.): for this fig. 9, which is an angle at the meeting of two jambs, is treated like a rich independent shaft, and the figure below, 12, which is half of a true shaft, is treated like a meeting of jambs.
All these four examples belonging to the oblique or Northern system, the curious trefoil plan, 3, lies between the two, as the double quatrefoil next it unites the two. The trefoil is from the Frari, Venice, and has a richly worked capital in the Byzantine manner,—an imitation, I think, of the Byzantine work by the Gothic builders: 1 is to be compared with it, being one of the earliest conditions of the cross shaft, from the atrium of St. Ambrogio at Milan. 13 is the nave pier of St. Michele at Pavia, showing the same condition more fully developed: and 11 another nave pier from Vienne, on the Rhone, of far more distinct Roman derivation, for the flat pilaster is set to the nave, and is fluted like an antique one. 12 is the grandest development I have ever seen of the cross shaft, with satellite shafts in the nooks of it: it is half of one of the great western piers of the cathedral of Bourges, measuring eight feet each side, thirty-two round. 46Then the one below (15) is half of a nave pier of Rouen Cathedral, showing the mode in which such conditions as that of Dijon (9) and that of Bourges (12) were fused together into forms of inextricable complexity (inextricable I mean in the irregularity of proportion and projection, for all of them are easily resolvable into simple systems in connexion with the roof ribs). This pier of Rouen is a type of the last condition of the good Gothic; from this point the small shafts begin to lose shape, and run into narrow fillets and ridges, projecting at the same time farther and farther in weak tongue-like sections, as described in the “Seven Lamps.” I have only here given one example of this family, an unimportant but sufficiently characteristic one (16) from St. Gervais of Falaise. One side of the nave of that church is Norman, the other Flamboyant, and the two piers 14 and 16 stand opposite each other. It would be useless to endeavor to trace farther the fantasticism of the later Gothic shafts; they become mere aggregations of mouldings very sharply and finely cut, their bases at the same time running together in strange complexity and their capitals diminishing and disappearing. Some of their conditions, which, in their rich striation, resemble crystals of beryl, are very massy and grand; others, meagre, harsh, or effeminate in themselves, are redeemed by richness and boldness of decoration; and I have long had it in my mind to reason out the entire harmony of this French Flamboyant system, and fix its types and possible power. But this inquiry is foreign altogether to our present purpose, and we shall therefore turn back from the Flamboyant to the Norman side of the Falaise aisle, resolute for the future that all shafts of which we may have the ordering, shall be permitted, as with wisdom we may also permit men or cities, to gather themselves into companies, or constellate themselves into clusters, but not to fuse themselves into mere masses of nebulous aggregation.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «The Stones of Venice, Volume 1 (of 3)»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «The Stones of Venice, Volume 1 (of 3)» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «The Stones of Venice, Volume 1 (of 3)» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












