Various - The Atlantic Monthly, Volume 10, No. 58, August, 1862
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Various - The Atlantic Monthly, Volume 10, No. 58, August, 1862» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_antique, periodic, foreign_edu, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:The Atlantic Monthly, Volume 10, No. 58, August, 1862
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
The Atlantic Monthly, Volume 10, No. 58, August, 1862: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «The Atlantic Monthly, Volume 10, No. 58, August, 1862»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
The Atlantic Monthly, Volume 10, No. 58, August, 1862 — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «The Atlantic Monthly, Volume 10, No. 58, August, 1862», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
By way of illustrating the new system of dumb-bell exercises, I subjoin a few cuts. The entire series contains more than fifty exercises.
The pupil, assuming these five positions, in the order presented, twists the arms. In each twisting, the ends of the dumb-bells should, if possible, be exactly reversed. Great precision will sustain the interest through a thousand repetitions of this or any other exercise. The object in these twisting exercises is to break up all rigidity of the muscles and ligaments about the shoulder-joint. To remove this should be the primary object in gymnastic training. No one can have examined the muscles of the upper half of the body without being struck with the fact that nearly all of them diverge from the shoulder like a fan. Exercise of the muscles of the upper part of the back and chest is dependent upon the shoulder. It is the centre from which their motions are derived. As every one not in full training has inflexibility of the parts about the shoulder-joint, this should be the first object of attack. These twistings are well calculated to effect the desired result. While practising them, the position should be a good one,–head, shoulders, and hips drawn far back.
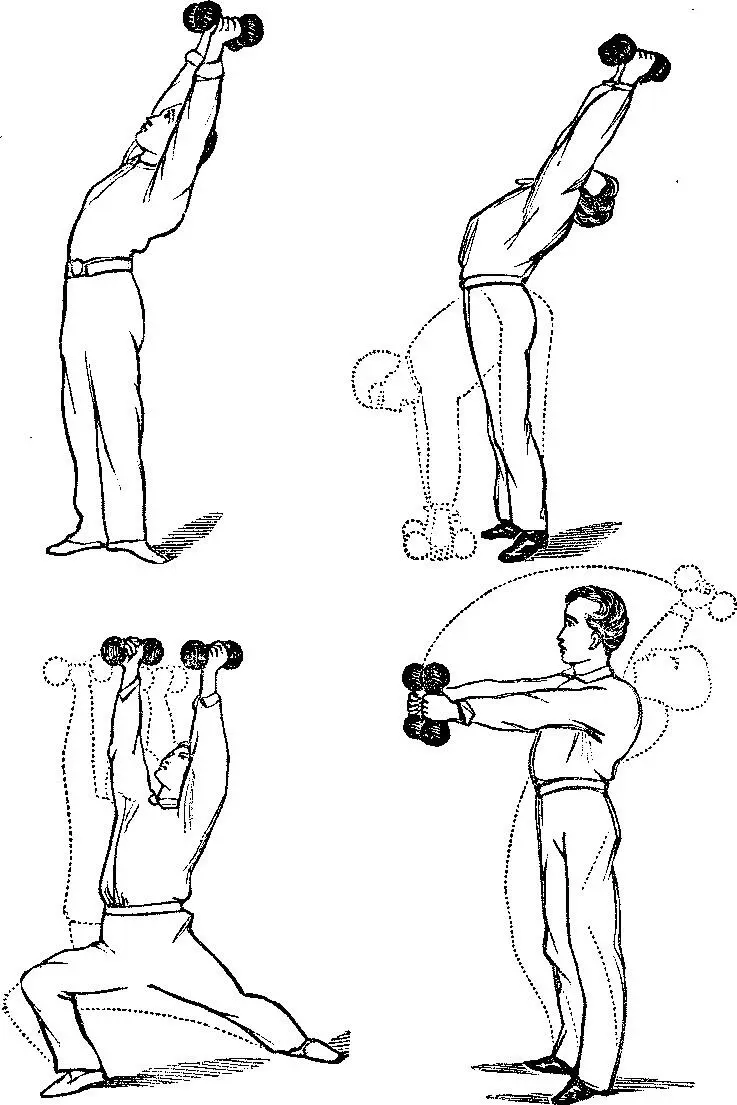
In our attempts to correct stooping shoulders, one good series of exercises is found in thrusting the dumb-bells directly upwards. While performing this the positions must be varied. A few illustrations are offered.
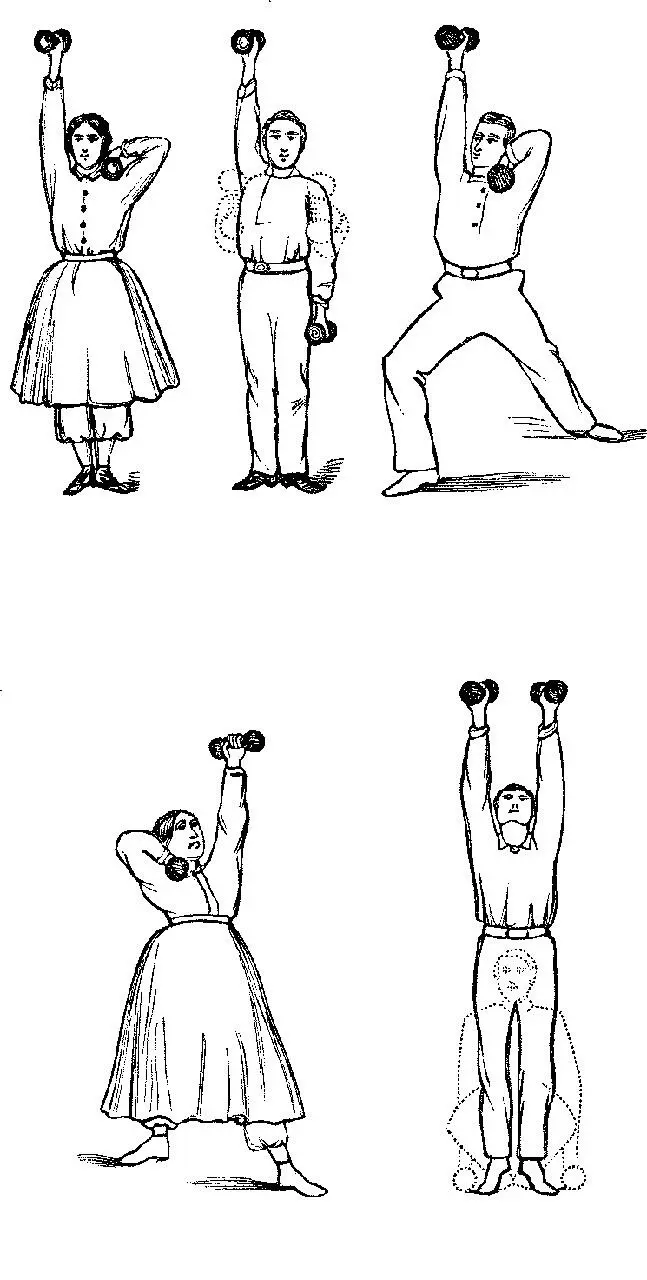
As effective means by which to call into vigorous play neck, shoulders, back, hips, arms, and legs, I submit the following exercises.
Bearing burdens on the head results in an erect spine and well-balanced gait. Observing persons, who have visited Switzerland, Italy, or the Gulf States, have noticed a thousand verifications of this physiological law.
Cognizant of the value of this feature of gymnastic training, I have employed, within the last twelve years, various sorts of weights, but have recently invented an iron crown, which I think completely satisfactory. I have it made to weigh from five to thirty pounds. It is so padded within that it rests pleasantly on the head, and yet so arranged that it requires skill to balance it.
The skull-cap, which is fitted to the top of the head, must have an opening of two inches in diameter at the crown, so that that part of the head shall receive no pressure. If this be neglected, many persons will suffer headache. The skull-cap should be made of strong cotton, and supported with a sliding cord about the centre. With such an arrangement, a feeble girl can easily carry a crown, weighing ten or fifteen pounds, sufficiently long, morning and evening, to secure an erect spine in a few months.
The crown which I employ is so constructed as to admit within itself two others, whereby it may be made to weigh nine, eighteen, or twenty-seven pounds, at the pleasure of the wearer. This is a profitable arrangement, as in the first use nine pounds might be as heavy as could be well borne, while twenty-seven pounds could be as easily borne after a few weeks.
The crown may be used at home. It has been introduced into schools with excellent results.
Instead of this iron crown, a simple board, with an oblong rim on one side so padded with hair that the crown of the head entirely escapes pressure, may prove a very good substitute. The upholsterer should so fill the pad that the wearer will have difficulty in balancing it. It may be loaded with bags of beans.
Wear it five to fifteen minutes morning and evening. Hold the body erect, hips and shoulders thrown far back, and the crown rather on the front of the head.
Walk up and down stairs, keeping the body very erect. While walking through the hall or parlors, first turn the toes inward as far as possible; second, outward; third, walk on the tips of the toes; fourth, on the heels; fifth, on the right heel and left toe; sixth, on the left heel and right toe; seventh, walk without bending the knees; eighth, bend the knees, so that you are nearly sitting on the heels while walking; ninth, walk with the right leg bent at the knee, rising at each step on the straight left leg; tenth, walk with the left leg bent, rising at each step on the straight right leg.
With these ten different modes of walking, the various muscles of the back will receive the most invigorating exercise.
Wearing the crown is the most valuable of all exercises for young people. If perseveringly practised, it would make them quite erect, give them a noble carriage of the head, and save them from those maladies of the chest which so frequently take their rise in drooping shoulders.
After the exercises with the crown, those with the new gymnastic ring are the best ever devised. Physiologists and gymnasts have everywhere bestowed upon them the most unqualified commendation. Indeed, it is difficult to conceive any other series so complete in a physiological point of view, and so happily adapted to family, school, and general use.
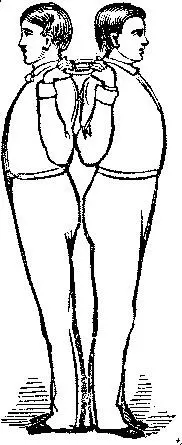
If a man were as strong as Samson, he would find in the use of these rings, with another man of equal muscle, the fullest opportunity to exert his utmost strength; while the frailest child, engaged with one of equal strength, would never be injured.
There is not a muscle in the entire body which may not be brought into direct play through the medium of the rings. And if one particular muscle or set of muscles is especially deficient or weak, the exercise may be concentrated upon that muscle or set of muscles.
Wherever these rings are introduced, they will obtain favor and awaken enthusiasm.
The rings are made of three pieces of wood, glued together with the grain running in opposite directions. They are round, six inches in diameter with body one inch thick, and finished with a hard, smooth polish.
The first series with the rings consists of a number of twisting exercises with the arms. Not only are these valuable in producing freedom about the shoulder-joint, which, as has been explained, is a great desideratum, but twisting motions of the limbs contribute more to a rounded, symmetrical development than any other exercises. If the flexors and extensors are exercised in simple, direct lines, the muscular outlines will be too marked.
In twisting with the rings, the arms may be drawn into twenty positions, thus producing an almost infinite variety of action in the arm and shoulder.
Two of the positions assumed in this series are shown in the cuts.
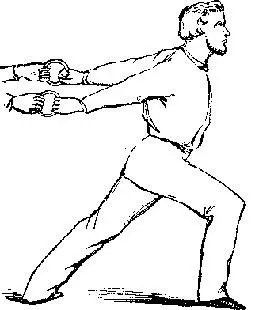
It is our policy in these exercises to pull with a force of from five to fifty pounds, and thus add indefinitely to the effectiveness of the movements.
To illustrate a few of the many hundred exercises possible with rings, the subjoined cuts are introduced.
In this exercise, the rings are made to touch the floor, as shown, in alternation with the highest point they can be made to reach, all without bending the knees or elbows.
The hands are thrust upward, outward, and downward with force.
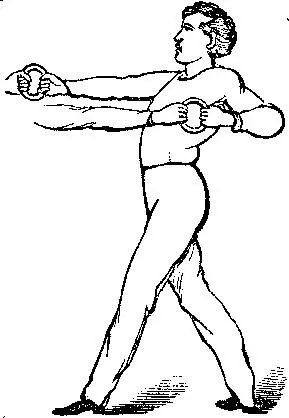
The hands are thrust forward and drawn backward in alternation as far as the performers can reach.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «The Atlantic Monthly, Volume 10, No. 58, August, 1862»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «The Atlantic Monthly, Volume 10, No. 58, August, 1862» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «The Atlantic Monthly, Volume 10, No. 58, August, 1862» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












