Milburg Mansfield - In the Land of Mosques & Minarets
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Milburg Mansfield - In the Land of Mosques & Minarets» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. ISBN: , Жанр: foreign_prose, Путешествия и география, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:In the Land of Mosques & Minarets
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:http://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/46705
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
In the Land of Mosques & Minarets: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «In the Land of Mosques & Minarets»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
In the Land of Mosques & Minarets — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «In the Land of Mosques & Minarets», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
The Barbary pirates had little inlets and outlets which they alone knew, and flitted in and out of on their nefarious projects; but only at Algiers, until in comparatively recent times, were there any ports or harbours, legitimately so called, in either Algeria or Tunisia, though the Spaniards, when in occupation of Oran in the eighteenth century, made some inefficient attempts towards waterside improvements of a permanent character.
In thinking of North Africa it is well to recall that it is not a tropical belt, nor even a subtropical one. It is very like the climate of the latitude of Washington, though perhaps with less rain in winter. It is not for a moment to be compared with California or Bermuda.
The temperature on the Algerian coast is normally as follows: —
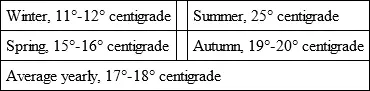
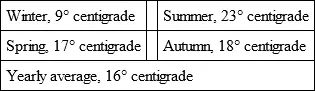
As compared with the temperature of the French Riviera, taking Nice as an example, the balance swings in favour of Algeria in winter, and a trifle against it for summer, as the following figures show: —
One pertinent observation on North Africa is that regarding the influx of outside civilizing influences. The American invasion of manufactured products is here something considerable; but as yet it has achieved nothing like its possibilities, save perhaps in electrical tramway installation, sewing machines and five-gallon tins of kerosene. The French have got North Africa, mostly; the Germans the trade in cutlery; the English (or the Scotch) that in whiskey and marmalade; but the American shipments of “Singers” and “Standards” must in total figures swamp any of the other single “foreign imports” in value. One does not speak of course of imports from France. As the argument of the dealers, who push the sewing-machine into the desert gourbis of the nomads and the mountain dwellings of the Kabyles, has it, the civilizing influences of Algeria have been railways, public schools and “Singers.” What progressive Arab could be expected to resist such an argument for progress, with easy-payment terms of a franc a week as the chief inducement? The only objection seems to be that his delicately fashioned, creamy, woollen burnous of old is fast becoming a ready-made “lock-stitch” affair, which lacks the loving marks of the real hand-made article. Other things from America are agricultural machinery, ice-cream freezers, oil-stoves, corn meal, corned beef, salmon from Seattle, and pickles from Bunker Hill. As yet the trade in these “staples” is infinitesimal when compared with what it might be if “pushed,” which it is not because all these things come mostly through London warehouse men, who “push” something else when they can.
A few things America will not be able to sell in North Africa are boots and shoes, the Arab wears his neatly folded down at the heel, and ours are not that kind; nor socks, nor stockings, the Arab buys a gaudy “near-silk,” made in the Vosges, when he buys any, and the women don’t wear them; nor hats, though a Stetson, No. 7, would please them mightily, all but the price. There is no demand for folding-beds or elastic bookcases. The Arab sleeps on the floor, and the only book he possesses, if he can read, is a copy of the Koran, which he tucks away inside his burnous and carries about with him everywhere. Chairs he has no need for; when the Arab doesn’t lie or huddle on the ground, he sits dangle-legged or cross-legged on a bench, which is a home-made affair. The women mostly squat on their heels, which looks uncomfortable, but which they seem to enjoy.
Besides the American invasion, there is the German occupation to reckon with – in a trade sense.
“Those terrible Germans,” is a newspaper phrase of recent coinage which is applicable to almost any reference to the German trade invasion of every country under the sun, save perhaps the United States and Canada. In South America, in Russia, and in the African Mediterranean States and Provinces, the Teuton has pushed his trading instincts to the utmost. He may be no sort of a colonizer himself, but he knows how to sell goods. In North Africa, in the coast towns, over a thousand German firms have established themselves within the last ten years, all the way from Tangier to Port Saïd. This may mean little or nothing to the offhand thinker; but when one recalls that the blackamoor and the Arab have learned to use matches and folding pocket-knives, and have even been known to invest in talking machines, it is also well to recall that the German can produce these things, “machine-made,” and market them cheaper than any other nation. For this reason he floods the market, where the taste is not too critical, and the cry is here for cheapness above all things. This is the Arab’s point of view, hence the increasing hordes of German traders.
To show the German is indefatigable, and that he knows North Africa to its depths, the case of the late German consul at Cairo, Paul Gerhard, who wrote a monumental work on the butterflies of North Africa, is worth recalling.
CHAPTER III
ALGERIA OF TO-DAY
“Le coq Gaulois est le coq de la gloire.
Il chante bien fort quand il gagne une victoire
Et encore plus fort quand il est battu.”
Algeria is by no means savage Africa, even though its population is mostly indigène . It forms a “ circonscription académique ” of France. It has a national observatory, a branch of that at Paris, founded in 1858; a school of medicine and pharmacy; a school of law; a faculty of letters and sciences, and three endowed chairs of Arabic, at Algiers (founded in 1836); Oran (1850) and Constantine (1858).
Algeria has a great future in store, although it has cost France 8,593,000,000 francs since its occupation seventy years ago, and has only produced a revenue of 2,330,000,000 francs, which represents the loss of a sum greater than the war indemnity of 1870. The Algerian budget balanced for the first time in 1901 without subsidies from home.
The entire population of Algeria is 4,124,732, of which 3,524,000 are Arabs, Kabyles or
Berbers, and the subdivided races hereafter mentioned, leaving in the neighbourhood of 600,000 Europeans, whose numbers are largely increasing each year.
The rate of increase of the European population, from 1836, when the French first occupied the country, has been notable. In 1836 there were 14,561 Europeans in the colony; in 1881, 423,881, of which 233,937 were French, 112,047 Spanish, and 31,865 Italians, and to-day the figure is over 600,000.
The Arab and Berber population, too, are notably increasing; they are not disappearing like the red man. From 2,320,000, in 1851, they have increased, in 1891, to 3,524,000.
In addition to the Arab and Berber population of Algeria, and the “foreigners” and Europeans, there are the following:
Moors – (90,500), the mixed issue of the Berbers and all the races inhabiting Algeria.
Koulouglis – (20,000), born of Turks and Moorish women.
Jews – (47,667), who by the decree of 1870 were made French. (This does not include unnaturalized Jews.)
Negroes – (5,000), the former slaves who were freed in 1848.
The French colonist in Algeria, the man on the spot, understands the Arab question better than the minister and officials of the Colonial Office of the Pavilion Sully, though the French have succeeded in making of Algeria what they have never accomplished with their other colonies – a paying proposition at last. Still France governs Algeria under a sort of “up-the-state,” “Raines-law” rule, and treats the indigène of Laghouat or Touggourt as they would a boatman of Pontoise or a farm labourer of Étampes. The French colonial howls against all the mistakes and indiscretions of a “Boulevard Government” for the Sahara, and even revile the Governor General, whom he calls a civilian dressed up in military garb and no governor at all. Que diable! This savours of partisanship and politics, but it is an echo of what one hears as “café talk” any time he opens his ears in Algiers.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «In the Land of Mosques & Minarets»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «In the Land of Mosques & Minarets» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «In the Land of Mosques & Minarets» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












