Peaty soils , of course, contain large quantities of organic matter. 16 16 These distinctions are not essential to be learned, but are often convenient.
How large a part of the soil may be used as food by plants?
What do we learn from the analyses of barren and fertile soils?
We will now take under consideration that part of the soil on which depends its ability to supply food to the plant. This portion rarely constitutes more than five or ten per cent. of the entire soil, sometimes less—and it has no reference to the sand, clay, and vegetable matters which they contain. From analyses of many fertile soils, and of others which are barren or of poorer quality, it has been ascertained that the presence of certain ingredients is necessary to fertility. This may be better explained by the assistance of the following table:
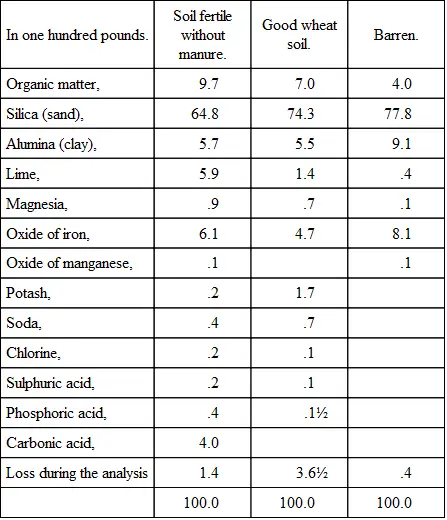
What can you say of the soils represented in the table of analyses?
What proportion of the fertilizing ingredients is required?
If the soil represented in the third column contained all the ingredients required except potash and soda, would it be fertile?
What would be necessary to make it so?
What is the reason for this?
What are the offices performed by the inorganic part of soils?
The soil represented in the first column might still be fertile with less organic matter, or with a larger proportion of clay (alumina), and less sand (silica). These affect its mechanical
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на ЛитРес.
Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.
By saturated , we mean that it contains all that it is capable of holding.
Bromine, iodine, etc., are sometimes detected in particular plants, but need not occupy the attention of the farmer.
This classification is not strictly scientific, but it is one which the learner will find it well to adopt. These bodies are called neutrals because they have no decided alkaline or acid character.
In some soils the fluorides undoubtedly supply plants with soluble silicates, as fluoric acid has the power of dissolving silica. Thus, in Derbyshire (England), where the soil is supplied with fluoric acid, grain is said never to lodge.
Sourness.
There is reason to suppose that alumina is an essential constituent of many plants.
By proximate principle , we mean that combination of vegetable elements which is known as a vegetable product, such as wood , etc.
Muscle is lean meat , it gives to animals their strength and ability to perform labor.
This, of course, supposes that the soil is fertile in other respects.
This pectic acid gelatinizes food in the stomach, and thus renders it more digestible.
See Johnston's Elements, page 41.
Sifted through a fine cloth called a bolting cloth.
The spaces between the particles.
In very many instances the crevices and seams of rocks are permeated by roots, which, by decaying and thus inducing the growth of other roots, cause these crevices to become filled with organic matter. This, by the absorption of moisture, may expand with sufficient power to burst the rock.
Some rocks contain sulphur, phosphorus, etc., and these may, perhaps, be considered as organic matter.
These distinctions are not essential to be learned, but are often convenient.













