Venera 9 not only made it to the surface and operated for 53 minutes in October 1975 but was also the first craft to successfully deploy its camera on the ground and transmit an image back to Earth. In the first-ever picture taken from the surface of another planet, the black and white fractured image revealed a rocky, desolate landscape with measurements confirming it to be a blistering 485 degrees Celsius, with an atmospheric pressure of 90 atm (standard atmosphere) crushing down.
By the time Venera 13 launched, on 30 October 1981, the ambition of the missions and the confidence in delivering data from the surface had been radically transformed. Venera 13 functioned for 127 minutes in recorded temperatures of 457 degrees Celsius and a pressure of 89 Earth atmospheres. The probe’s cameras deployed, taking the first colour image from the surface of Venus, spring-loaded arms measured the compressibility of the soil, while a mechanical drill arm took a sample of the Venusian surface that was analysed by an onboard spectrometer. If that wasn’t enough, onboard microphones were deployed to record the vicious winds that were assumed to be whipping the surface of Venus, the first-ever recording of the sound of another planet.
As the Venera missions came to a close in 1983, not even the smallest doubt remained of Venus’s hostility. Far from the benign water world we had once imagined, the reality was that this was not a sister we recognised – in our search of the heavens for a place like home we’d found a toxic, fiery hellscape.
Venus is an enigmatic world – almost Earth-like in size, position and potential, and yet as far from paradise as it’s possible to imagine. If Mercury’s story is one of catastrophic orbital change and Earth’s of balance and stability, the story of Venus is a tragedy; a tale of subtle, yet relentless decline. So why did it all go wrong for Venus? Why did a world born with such similarities to the Earth take such a different path? To answer that, we need to look beyond the tortured planet we see today and go back to a time when Venus was a young thriving planet.

© SPUTNIK / SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
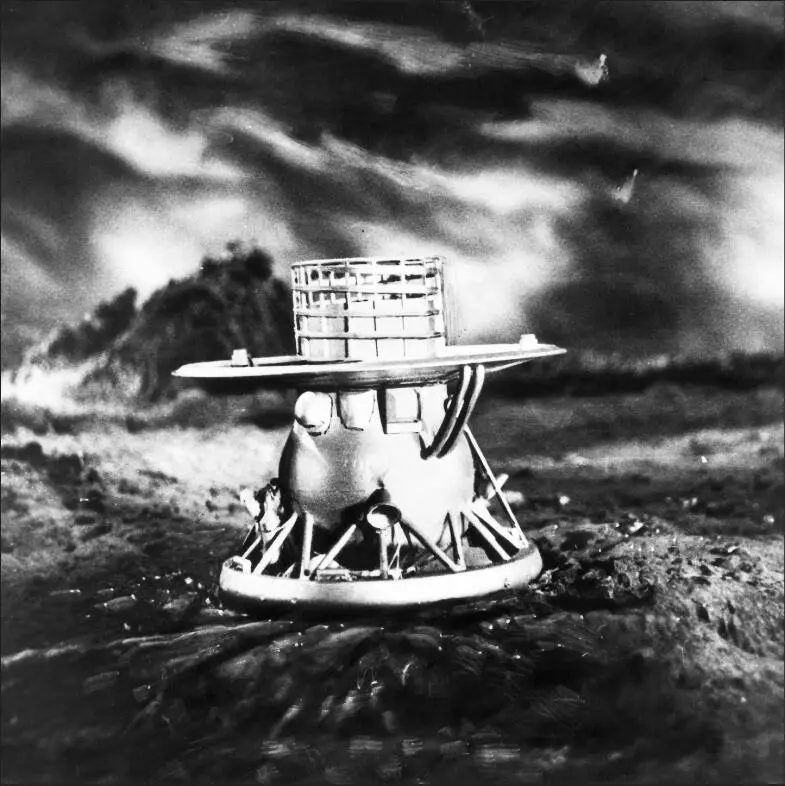
Soviet scientists worked hard on the Venera missions, tweaking the spacecraft at every new incarnation, to get more time to explore Venus’s hostile landscape. This is a model of the Venera 9 spacecraft.
Through the following missions, the Soviet scientists began to overcome each and every challenge Venus put in front of them.
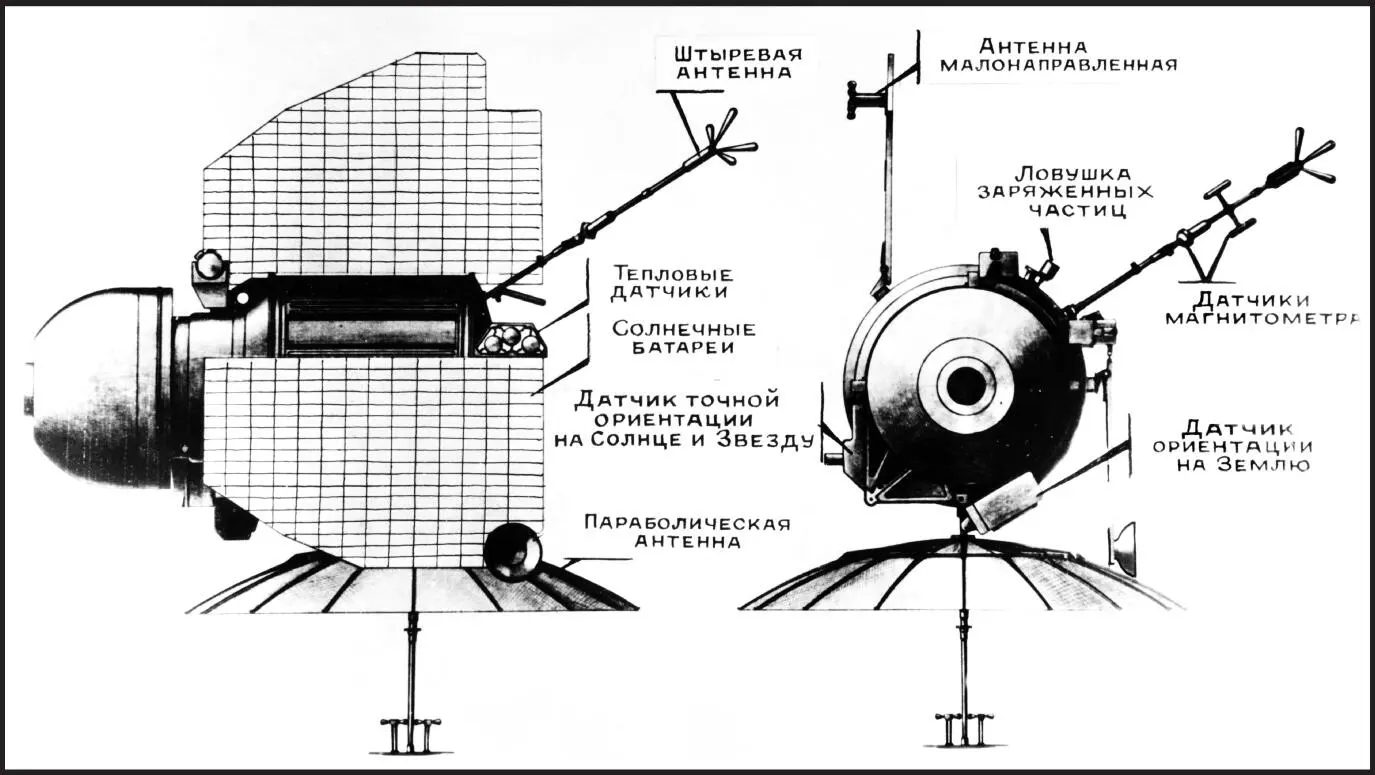
© Sovfoto/UIG via Getty Images
A diagram of Venera 1, the first mission.
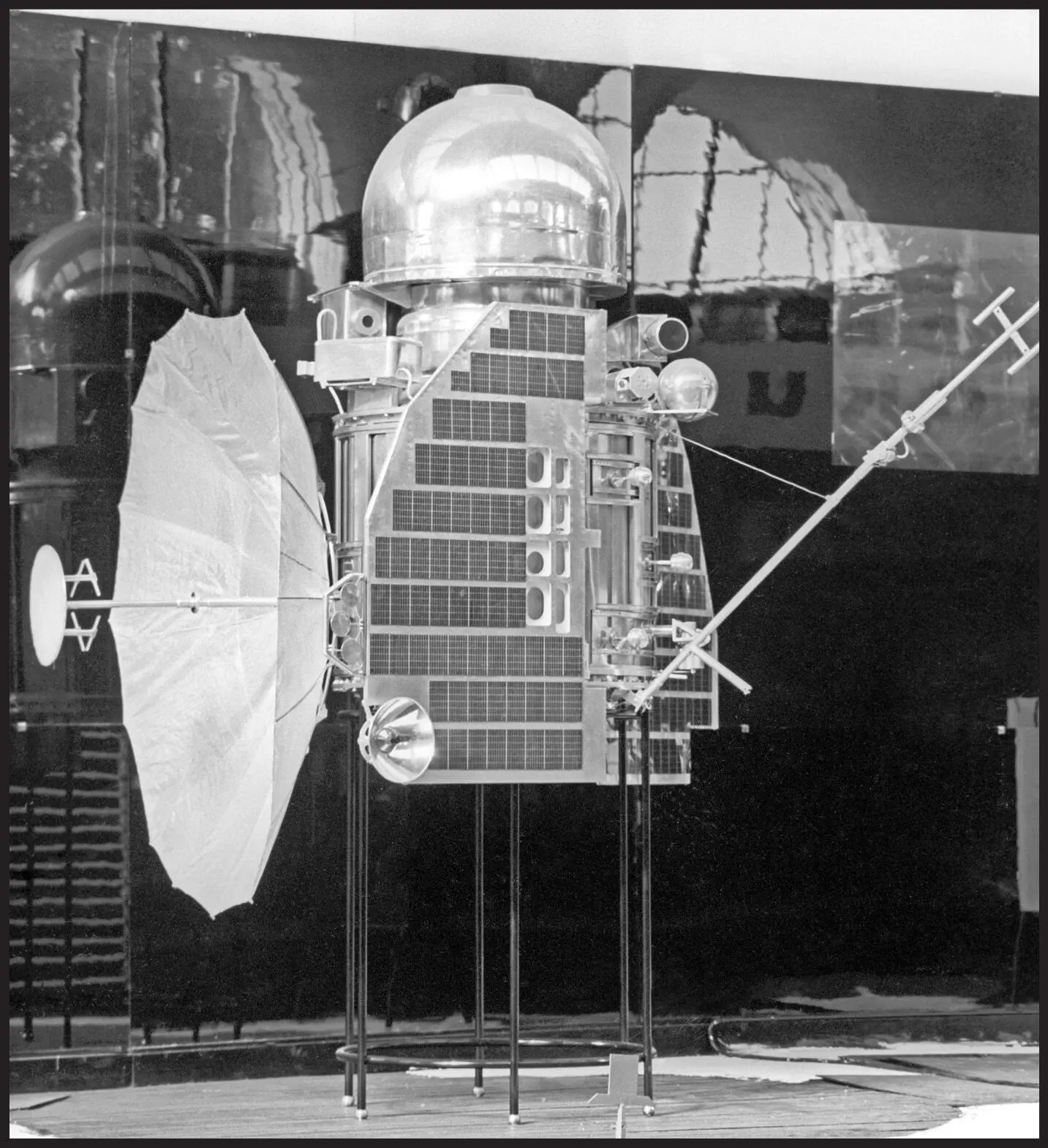
© SPUTNIK / SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
The Venera 1 display in the space (Kosmos) pavilion at the All-Russia Exhibition Centre, in Moscow, Russia.

© SPUTNIK / SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
This radar image taken by Venera 15 and 16, offers a fascinating insight into the terrain of Venus, revealing the Maxwell Montes mountain range in the centre and the 100-km-wide Cleopatra crater.

© SPUTNIK / SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Sediment and rocks visible on the landscape, imaged by Venera 9.
THE BIRTH OF VENUS
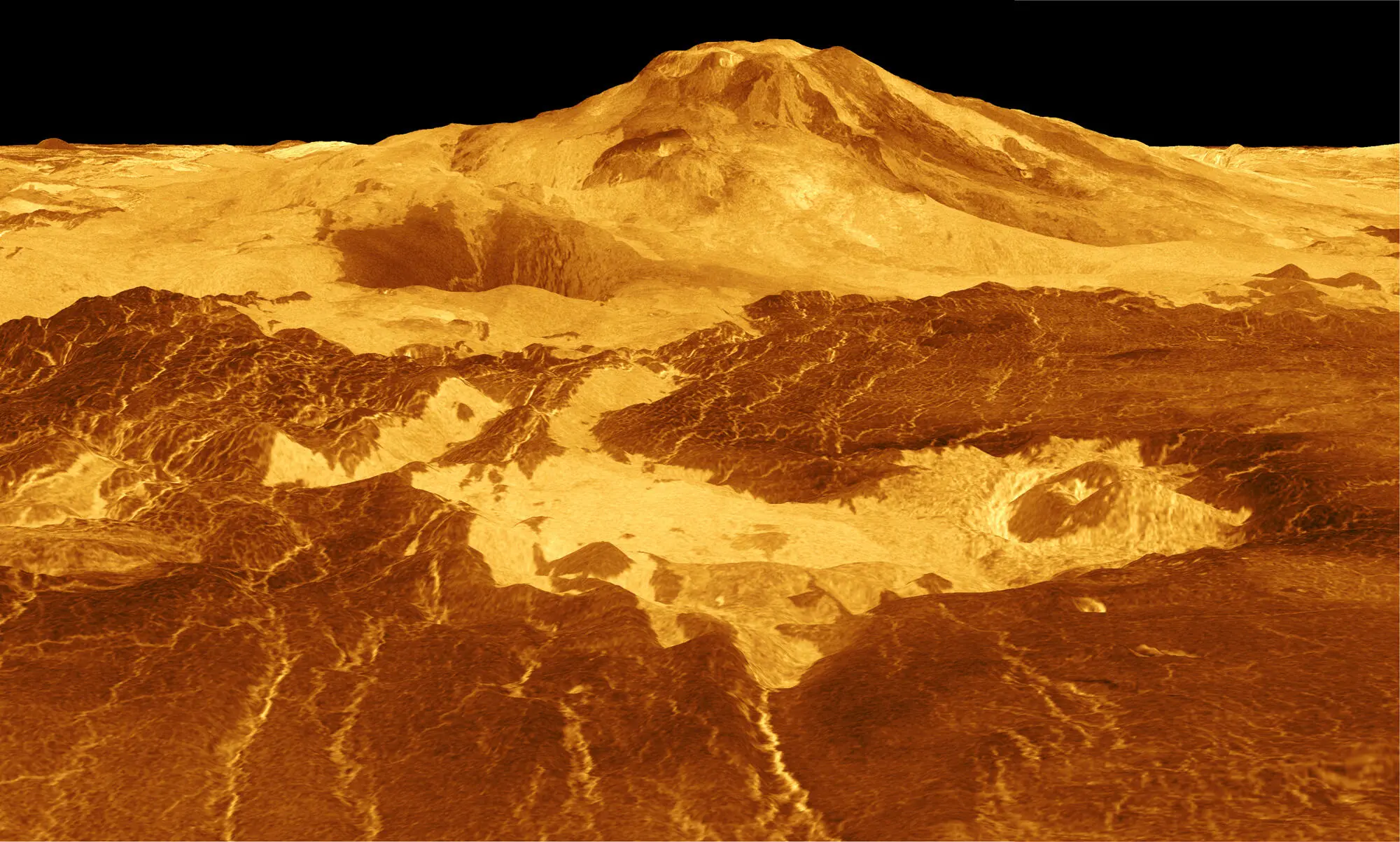
© NASA/JPL
Rising centrally in this computer-generated image is the volcano Maat Mons, surrounded by cascading lava. This three-dimensional image was created using data relayed by Venera 13 and 14.
‘Today Venus is incredibly hostile … so hot, so dry, but what did it start out like, was it ever more Earth-like? We don’t know for sure, so we want to make future spacecraft missions to nail down that early history.’
David Grinspoon, astrobiologist
Four billion years ago, Venus was a familiar world. A world created from the same dust as the Earth, born just about the same size and settled into an orbit that seemed just far enough away from the glare of the Sun to allow a precious process to begin to take hold. In almost every conceivable way, Venus’s early life mirrored that of our own world. As its newly formed crust settled and cooled from the violent heat of its birth, an atmosphere began to grow around the young planet, fed by gases bubbling up from the molten rock below its surface, as well as captured from the clouds of gas and dust it swept through on its orbit around the Sun. Clinging to the young Venus, this thin layer of gas would have certainly contained nitrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide, but most intriguing of all, we are certain it would have also contained large amounts of water vapour.
High in the Venusian atmosphere this water vapour eventually cooled enough to change state from vapour to liquid. And with that transformation, a process began, that perhaps for the first time on any of the planets would have seen the conditions become just right for droplets of liquid water to take shape and begin falling from the Venusian sky. These were the first rains of the Solar System, showering down onto the dry plains of Venus. Gradually these rains would have not just fallen but flooded the surface, rivers would have flowed and shallow oceans taken hold of large swathes of the planet’s surface. Venus, perhaps before even the Earth, became a water world, a planet with skies full of clouds and a surface full of oceans, feeding the cycle of water around this young planet.
How can we be certain this blue version of Venus existed? Unlike Mars, where we can see the evidence of its watery past etched onto its surface, we have no such direct evidence of the presence of liquid water on the surface of Venus. The only physical evidence we have suggests that the planet’s watery past comes from measurements taken by NASA’s Pioneer Venus spacecraft back in 1978. One of its most surprising discoveries revealed an unexpected amount of deuterium (heavy water) in the atmosphere compared with hydrogen. This D/H ratio is far smaller on Venus than it is on Earth, and that’s interesting because when the two planets formed the ratio would have almost certainly been the same. Because hydrogen is far more easily lost from an atmosphere than deuterium, this smaller ratio suggests that Venus has lost a lot more water than the Earth over its lifetime – the signature of a long-lost primordial ocean. As cosmochemist Larry Nittler explains:
‘Scientists believe that Venus once had a lot of water in its oceans, but lost it over time, and perhaps in oceans as recently as a billion years ago. The reason we can tell this is from the isotopic composition of hydrogen measured in its atmosphere by spacecraft. Now, hydrogen has two flavours of isotopes, whereas most hydrogen atoms are just a single proton in the nucleus. Some, a small fraction, are what we call deuterium, that have a proton and a neutron, so they weigh twice as much as the regular hydrogen. What happens when you have evaporation of water from a planet, or the atmosphere, is that the water molecules that contain hydrogen are much lighter than the water molecules that contain deuterium, so they evaporate more easily, and can be lost more easily. So, over time, as you evaporate water, deuterium-bearing molecules stay behind relatively to the regular ones, and you build up a deuterium to hydrogen ratio. And by back-calculating from the measured ratio today, we can figure out how much water has been lost over the billions of years of evolution, and [on Venus] it’s quite a lot.’
Читать дальше

















