Connectivity, Communication, and Data Distribution: IoT devices are connected to the Internet either directly or through another device (gateway) where network connections are used for transporting data and interacting with users. Also, these devices allow users to access information and/or control devices remotely using a variety of communication protocols and technologies.
Automation: Regardless of the application, most IoT devices are about automation, such as in industrial automation, business process automation, or home automation. Thus, such devices can generate, exchange, and produce data with minimal or no human intervention.
Intelligence: Intelligence in IoT lies in the knowledge extraction from the generated data and the smart utilization of this knowledge to solve a challenge, automate a process, or improve a situation. There is no real IoT benefit without artificial intelligence, machine learning, Big Data 2 analytics, and cognitive algorithms.
Figure 1.1depicts the abovementioned IoT characteristics.
1.1.2.3 What Exactly Is a Wearable Device?
The term “wearable devices” generally refers to electronic and computing technologies that are incorporated into accessories or garments which can comfortably be worn on the user's body. These devices are capable of performing several of the tasks and functions as smartphones, laptops, and tablets. However, in some cases, wearable devices can perform tasks more conveniently and more efficiently than portable and hand‐held devices. They also tend to be more sophisticated in terms of sensory feedback and actuating capabilities as compared to hand‐held and portable technologies. The ultimate purpose of wearable technology is to deliver reliable, consistent, convenient, seamless, and hands‐free digital services.
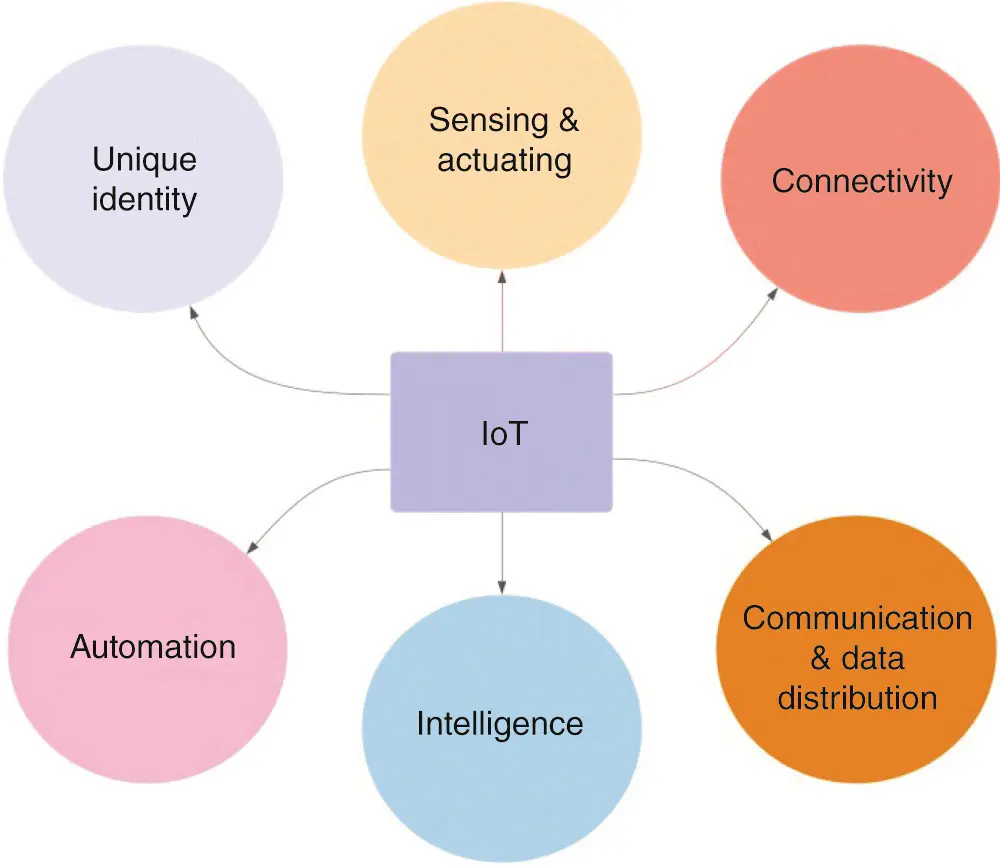
Figure 1.1 Characteristics of the Internet of Things.
Typically, wearable devices provide feedback communications of some sort to allow the user to view/access information in real time. A friendly user interface is also an essential feature of such devices, so is an ergonomic design. Examples of wearable devices include smart watches, bracelets, eyewear (i.e.: glasses, contact lenses), headgears (i.e.: helmets), and smart clothing. Figure 1.2depicts the most important possible forms of wearable devices.
While typical wearable devices tend to refer to items which can be placed external to the body surface or clothing, there are more invasive forms as in the case of implantable electronics and sensors. In the author's opinion, invasive implantables, i.e. ingestible sensors, under the skin microchips, and smart tattoos, which are generally used for medical and tracking purposes, should not be categorized as wearables since they have different mechanisms and operation requirements. The reader should seek other resources which are dedicated to the design and prototyping of such devices.
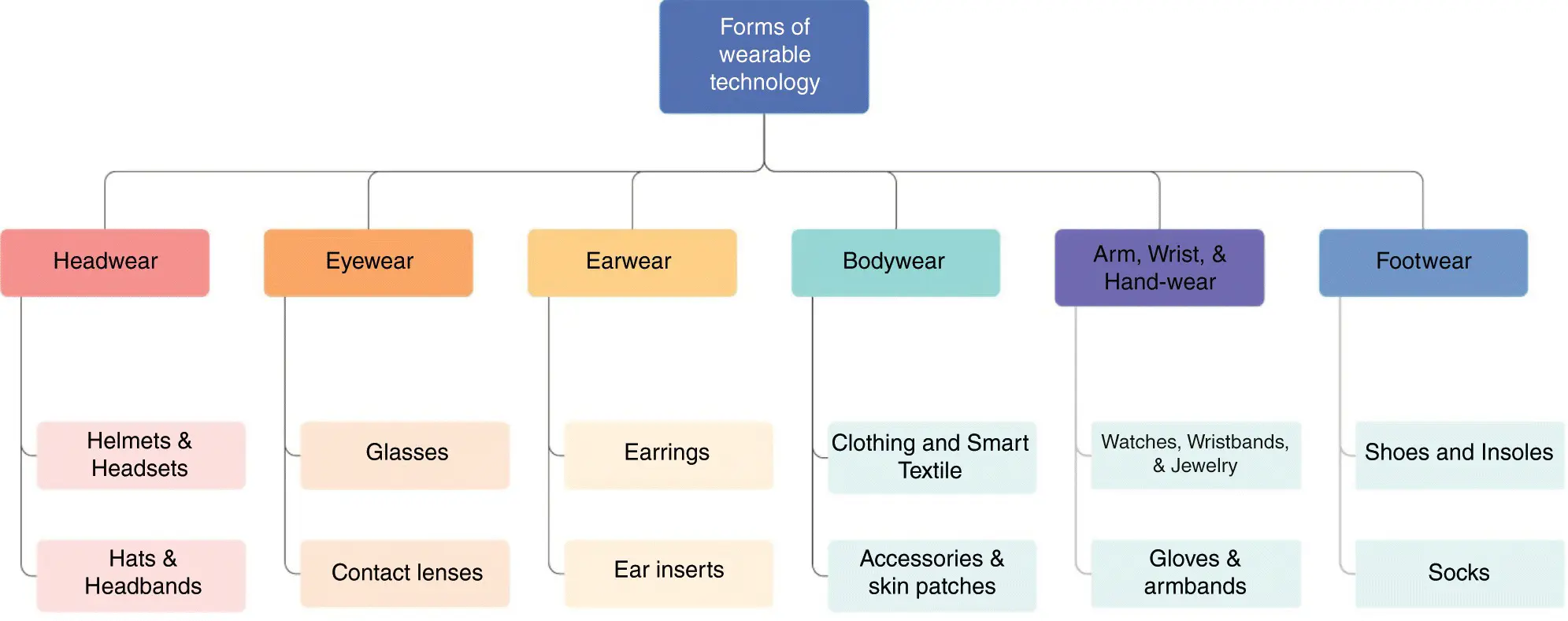
Figure 1.2 Forms of wearable technology.
1.1.2.4 Characteristics of Wearable Devices
The uses of wearables are far reaching and have exciting potentials in the fields of medicine, well‐being, sports, aging, disabilities, education, transportation, enterprise, and entertainment. The main objective of wearable technology in each of these fields is to smoothly incorporate functional and portable electronics into the users' daily routines. Prior to their existence in the consumer market, wearables were primarily employed in the fields of military technology and health sector.
Generally speaking, wearables share many aspects of the sensing, connectivity, automation, and intelligence characteristics with IoT devices. However, there are a few major differences worth highlighting which will be discussed in the following sections.
Form factor is a hardware design aspect in electronics packaging which specifies the physical dimensions, shape, weight, and other components specifications of the printed circuit board (PCB) or the device itself. Although wearable devices have a small form factor in general, it is practically dependent on the type and the way they are worn (rings and wristbands, as opposed to glasses and clothing).
Smaller form factors may offer reduced usage of material, easy handling, and simpler logistics; however, they typically give rise to higher design and manufacturing costs in addition to signal integrity issues and maintenance constraints.
Moreover, durability, comfort, aesthetics, and ergonomic factors are important when it comes to designing a wearable device. Weight, shape, color, and texture must be carefully considered. The general characteristics of wearable technology are presented in Figure 1.3.
M2M describes the technology that enables the communication between two or more machines. With M2M, one could connect machines, devices, and appliances in a wired or wireless fashion via a variety of communications techniques to deliver services with limited human intervention.
The difference between machine to machine (M2M) and IoT can be confusing to many. In fact, the misconception that M2M and IoT are the same has been a continuing subject of debate in the realm of tech industry.
Both M2M and IoT are connectivity solutions that provide remote access to machine data. They both have the capability of exchanging information among machines without human intervention. Thus, the two terms have been mistakenly interchanged often. However, M2M is a predecessor to IoT and had revolutionized enterprise operations by enabling them to monitor and manage their machines and hardware components remotely. M2M set the underlying basis of machine connectivity on which IoT built upon. Nevertheless, IoT is the ultimate manifestation when it comes to connectivity.
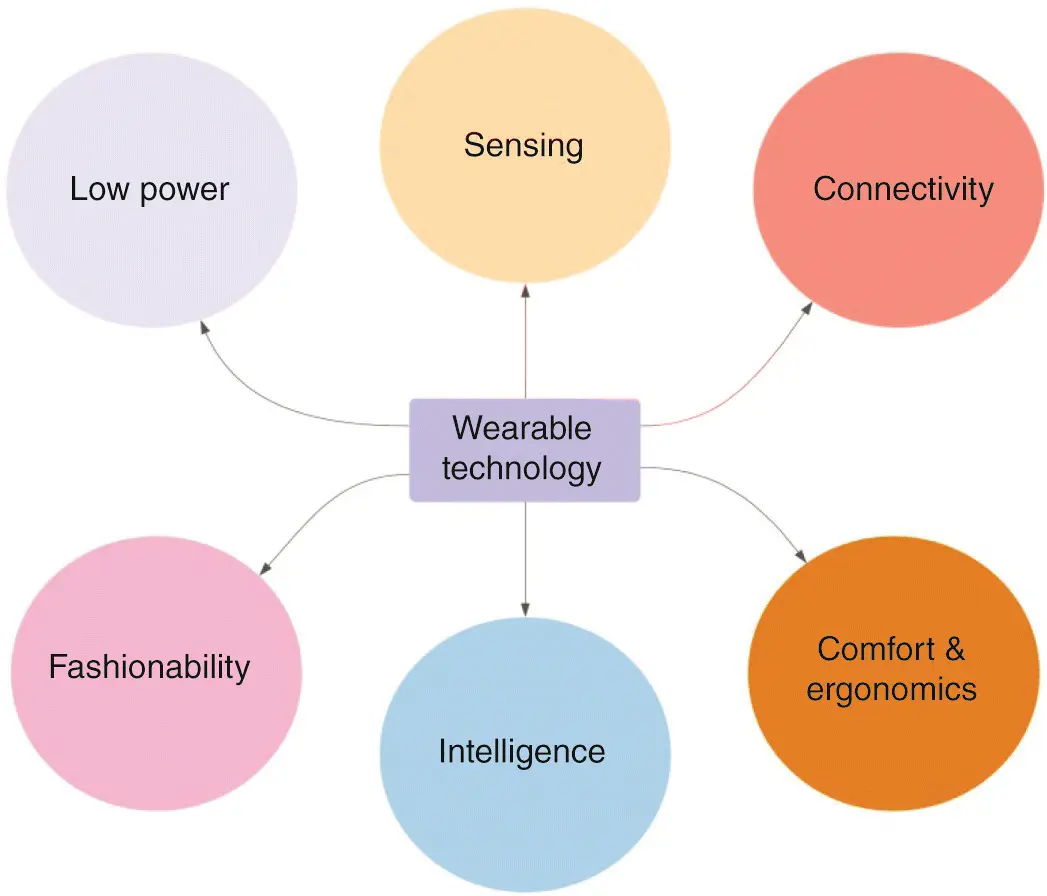
Figure 1.3 Characteristics of wearable technology.
The main objective of M2M is to connect a machine/device to another machine (typically in an industrial setting) via cellular or wired network so that its status can be monitored and its data can be collected, remotely. IoT is more of a universal market technology that aims at serving consumers, industries, and enterprises. Consumer IoT connects users to their devices and enables remote access. On the other hand, enterprise and industrial IoT take it further by allowing tracking, control, and management.
IoT and M2M diverge immensely when it comes to the way they access devices remotely. M2M relies on point‐to‐point communications enabled by dedicated hardware components integrated within the machine. The communication among these connected machines is made possible via wired or conventional cellular network and dedicated software. IoT, on the other hand, typically uses IP networks and integrates web applications to interface device/machine data to a middleware, and in the majority of cases, to cloud.
It is worth noting that IoT is intrinsically more scalable than M2M since cloud‐based architectures do not need additional hard‐wired connections and subscriber identification modules (SIM) which are required in M2M.
1.1.2.6 IoT vs. Wearables
Despite the commonalities, it is clear that there are substantial differences when we speak about wearable technology in the context of fitness trackers as opposed to when IoT is used in the context of manufacturing processes or smart cities. In fact, many experts in the field argue that wearables fall under the umbrella of IoT. One key difference worth highlighting here is that most wearables rely on a gateway device, such as a smartphone, for configuration and connectivity, and in most cases to enable features and process data. It is this M2M aspect that makes wearables a separate class of devices, and that's why we prefer to treat these as two technologies with two sets of characteristics.
Читать дальше















