In section 3.4, we obtain asymptotic expansions for the perturbed semigroups of operators of the respective three-variate Markov process (after the standard extension of the phase space of the perturbed random evolution uε ( t, x ) in the semi-Markov media), provided that the evolution uε ( t, x ) weakly converges to the diffusion process as ε > 0.
In section 3.5, we obtain asymptotic expansions under Kac’s condition in the diffusion approximation for the distribution of a particle position, which performs a random walk in a multidimensional space with Markov switching.
Section 3.6 describes a novel financial formula as an alternative to the well-known Black–Scholes formula for modeling the dynamic behavior of stock markets. This new formula is based on the asymptotic expansion for the singularly perturbed random evolution in Markov media.
Chapter 4of Volume 1 is devoted to the computation of the stationary distributions for random switched processes with reflecting boundaries in Markov and semi-Markov environments. These results are used for the calculation of the efficiency of inventory control systems with feedback, and for some reliability problems of systems that are modeled by Markov and semi-Markov evolution.
In section 4.1, we derive the stationary distribution of transport processes with delaying in the boundaries in Markov media. These results are applicable to the study of multiphase systems with several reservoirs.
Section 4.2deals with the transport process with semi-Markov switching. We find the stationary measure for this process and it is described by the differential equation with phase space on the corresponding interval and constant vector field values that depend on the switching semi-Markov process with a finite set of states.
In section 4.3, we give examples of applications of this method for the calculation of the stationary distributions for random switched processes with reflecting boundaries. In particular, we compute the efficiency coefficient of a single and two-phase inventory control system with feedback.
In section 4.4, we apply random evolutions with delaying barriers to modeling the control of supply systems with feedback, by considering the semi-Markov switching process.
In Chapter 5of Volume 1 we study various models of stochastic evolutions that generalize the Goldstein–Kac telegraph process and investigate their distributions.
Section 5.1is devoted to one-dimensional semi-Markov evolutions in an Erlang environment. In section 5.1.1, we derive a hyperbolic differential equation of the telegraph type for the pdf of the position of a particle moving at finite velocity. The interarrival times between two successive changes of velocity have an Erlang distribution.
In section 5.1.2, a method of solution of this partial differential equation is developed by using monogenic functions associated with a finite-dimensional commutative algebra. Section 5.1.3 extends the results of section 5.1.2 to infinite-dimensional commutative algebras. In section 5.1.4, by using the methods from sections 5.1.2 and 5.1.3, we obtain the distribution of a one-dimensional random evolution in Erlang media.
In section 5.2, we find the distribution of limiting positions of a particle moving according to a fading evolution. We assume that the interarrival times are Erlang or uniform distributed for the switching process.
In section 5.3, differential and integral equations for jump random motions are introduced and some examples have been developed to illustrate the method.
Section 5.4is devoted to the estimation of the number of level crossings by the telegraph process in Kac’s condition.
In Chapter 1of Volume 2 we study random motions in higher dimensions. In section 1.1, we study the random walk of a particle with constant absolute velocity, which changes its direction according to a uniform distribution on the unit sphere at the renewal epochs of a switching process.
Section 1.2deals with random motion with uniformly distributed directions and random velocity for the motion of particles in one, two, three and four dimensions. Similar cases are considered in section 1.3for the distribution of random motion at non-constant velocity in semi-Markov media, and in section 1.4for Goldstein–Kac telegraph equations and random flights in higher dimensions, where the directions of the movement and the velocity change at the renewal epochs. The jump telegraph process in 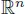 is considered in section 1.5.
is considered in section 1.5.
In Chapter 2of Volume 2 we study a system of interacting particles with Markov and semi-Markov switching. Section 2.1is devoted to an ideal gas model with finite velocity of molecules. In this section, we find the distribution of the first meeting time of two telegraph particles on the line, which started simultaneously from different points.
In section 2.1.2, we estimate the number of particle collisions. In section 2.1.4, we obtain an asymptotic estimate of the number of collisions of the system of telegraph particles when time goes to infinity. Unlike the previous section, the system has no boundaries and particles can move arbitrarily far away in a straight line. Section 2.2is devoted to the generalization of results of section 2.1to the case of semi-Markov switching processes. In section 2.2.1, we obtain a set of renewal-type equations for the Laplace transform of the first collision of two particles. In section 2.2.2, we consider an example regarding a particular case of semi-Markov switching of particle velocity, and we study the limiting properties of the distribution of the particle position. Section 2.2.3is devoted to studying the case where the first time of collision of two particles has finite expectation. We should note that in all previous examples, including the Markov case, expectation of the first time of collision of two particles is infinite.
In Chapter 3of Volume 2 the application of the telegraph process for option prices, as an alternative to the diffusion process in the Black-Scholes formula, is further studied through asymptotic estimation of the corresponding operators. Some numerical results and plots are also presented.
Pricing variance, volatility derivatives, covariance and correlation swaps for financial markets with Markov-modulated volatilities are the main topics of Chapter 4of Volume 2. These results are extended to the case of semi-Markov modulated volatilities in Chapter 5of Volume 2. Numerical results and some plots to illustrate these results are also presented in these last two chapters.
PART 1 Higher-dimensional Random Motions and Interactive Particles
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на ЛитРес.
Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.

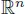 is considered in section 1.5.
is considered in section 1.5.

![О Генри - Русские соболя [Vanity and Some Sables]](/books/405344/o-genri-russkie-sobolya-vanity-and-some-sables-thumb.webp)








