1 ...7 8 9 11 12 13 ...19 Eye micromovements. When you fix the look at the stimulus, you can observe a number of reflex movements, which are called micromovements of the eyes ( tremor ). As a result of micromovements, the axis of the eye describes a closed figure in the form of an ellipse. This is the natural motor background of the activity of oculomotor muscles, which is not consciously controlled. With the help of special devices you can register these micromovements of the eyes. In the process of fixing the eyes are in constant motion, if you completely exclude involuntary, small movements of the eyes, the image of the stimulus on the retina begins to blur and disappear.
Mixed movements. The visual perception of the environment usually occurs through a combination of different types of eye movements; they are mixed movements. For example, observation of a moving object requires both smooth tracking movements and saccadic and vergent movements.
Effective eye movements are achieved at a certain level of development of oculomotor muscles. In children of 4–5 years of age, eye movements are different from those of adults, so their vision is less effective; it is difficult for them to fix their gaze on a particular object. When they were asked to fix their gaze on a small, bright, stationary object in a dark room, their line of sight scanned the area 100 times larger than in adults. Children do not predict changes in the direction of movement of the object; these movements are formed gradually on the basis of practice.
It should be noted that the concept of tracking is used to control attention when designing advertising, when the eye of the observer is directed to a certain part of the visual field. In web design, F-pattern-based navigation is highlighted ( Figure 1.2.11). As you read consecutive lines, the number of commits decreases, and their duration also decreases for any length of line and any line spacing. The movement of our gaze usually covers the right side of the visual field, narrowing as the gaze moves down the text. Our attention avoids non-informative images consisting of small homogeneous elements; they can cause unpleasant sensations and illusions.
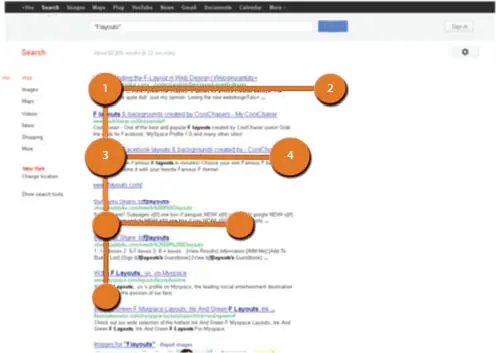
Figure 1.2.11 F-Pattern navigation.
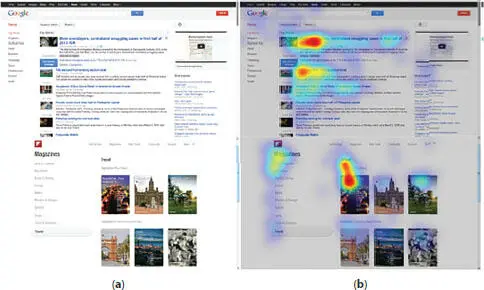
Figure 1.2.12 Comparison of certainty value of web page and saccadic estimation, (a) web pages, (b) thermal map of eye fixation [Xia, Quan, 2020].
The work of [Xia, Quan, 2020] reports the studies on the modeling of users’ attention looking through web pages. The saccadic search model of dynamic visual behavior of people is offered in the work. The multilevel analysis of signs of visual information and definition of probability of user eye fixation are used. The experimental results concerning the eye tracking in the course of free web pages viewing showed the efficiency of the offered method ( Figure 1.2.12).
1.2.4 Effects of Masking and Aftereffects
If visual stimuli occur in close sequence from each other (in time or in space), they can overlap each other and mask the perception of each other. The cause of the masking effect is the inertia of vision due to the slowness of the neural response to the stimulation, as a result of which the response to the stimulus can be maintained even after its disappearance.
During saccades, the flow of visual information stops for a short time, but we do not notice this saccadic overshoot. If we look at ourselves in the mirror to detect these movements, we will not see any movements, overshoots, misting. But looking at other people performing the same actions, we will see how their eyes move. The cause of the saccadic “breakthrough” (empty field) are masking effects.
With long-term observation of the stimulus, not only the inertia of vision can manifest itself, but also adaptation or temporary “fatigue” of the stimulated portion of the retina will occur. These effects can be demonstrated by a slope aftereffect based on the experience of J. Gibson ( Figure 1.2.13) [Shiffman, 2008], [Abbasov, 2019]. To do this, close the vertical grating ( Figure 1.2.13, right), for 40-60 seconds, fix the view on the point between the inclined gratings ( Figure 1.2.13, left). Then open the right side and quickly translate the view on the point between the two vertical bars ( Figure 1.2.13, right). For some time you will find that the vertical lines are inclined in the direction opposite to the direction of inclination of the grating lines in Figure 1.2.13, on the left. The post-slope effect is manifested in the short-term distortion of the perception of the apparent orientation of the visual stimuli that arise due to adaptation to the previous stimulus, oriented differently.
You can also demonstrate the effect of curvature aftereffect. It manifests itself in a violation of the perception of the obvious form of the stimulus due to the prolonged effect of the previous stimulus of a different shape or curvature. This phenomenon is illustrated by the experience presented in Figure 1.2.14. Similarly, for 40-60 seconds, fix your gaze on the point between the two curves ( Figure 1.2.14, on the left), then transfer the glance to the fixation point between the straight lines ( Figure 1.2.14, on the right). Vertical lines will seem curved in the opposite direction to the curve of the curves.
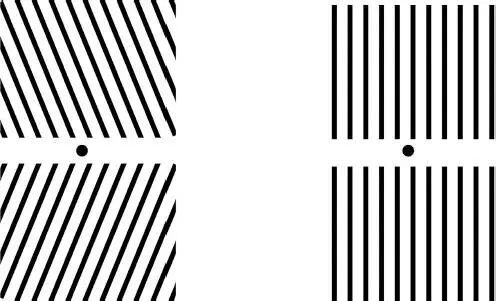
Figure 1.2.13 Tilt action.
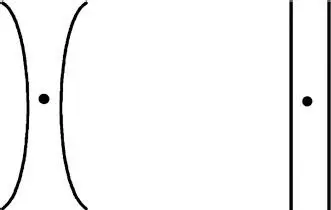
Figure 1.2.14 Curvature after-effect.
1.2.5 Perception of Contour and Contrast
In a consideration of the current works in the field of contrast perception it is necessary to acknowledge the sufficiently detailed survey of [Ghosh, Bhaumik, 2010] in which the historical and philosophical aspects of brightness perception are analyzed. Although these questions have been studied for 200 years the mechanism of influence of some optical illusions has not been determined to a full degree. The neuronal mechanism of perception formation from the visual receptors to brain cortex is described on the basis of bottom-up processes ( Figure 1.2.15). The internal test squares with the same brightness form a contrast to the gradient ground ( Figure 1.2.15, from the left). Moreover, the contrast effect is remained on the ground of sole-colored vertical stripes ( Figure 1.2.15, from the right).
The perception of brightness is offered to be analyzed according to two philosophical tendencies: idealistic and materialistic approaches. The theory of contrast is based on the lateral inhibition similar to the principal dialectic laws: contradictions unity, interrelation, transition from quantity to quality, negation of the negation. Some recent researches of the experimental psychophysics and application of mathematical methods of modeling are based on that. To ensure the adequacy of such models it’s necessary to apply the quantitative representation of complex psychical processes on the basis of dialectic law of interaction between the part and the whole.
In the process of perception of visual information contours play a significant role. Using contours, we recognize the shapes, edges, and borders of surrounding objects. To study the neural mechanisms of perception of the contours, you can use the visual system of the horseshoe crab. The eye of the horseshoe crab is structurally complex and consists of about 1,000 receptors (ommatidia). Each receptor has its own neuron and optic nerve, which responds to the light signal independently of the adjacent receptors. They are not related to each other; stimulation of one receptor is not transmitted to the next. However, at a higher neuronal level, adjacent receptors are connected by lateral nerve fibers, while simultaneous stimulation of neighboring receptors results in the summation of their activity.
Читать дальше
















