
From an old print
A New England Farmhouse
Social Effects of Land Tenure.—Land tenure and the process of western settlement thus developed two distinct types of people engaged in the same pursuit—agriculture. They had a common tie in that they both cultivated the soil and possessed the local interest and independence which arise from that occupation. Their methods and their culture, however, differed widely.
The Southern planter, on his broad acres tilled by slaves, resembled the English landlord on his estates more than he did the colonial farmer who labored with his own hands in the fields and forests. He sold his rice and tobacco in large amounts directly to English factors, who took his entire crop in exchange for goods and cash. His fine clothes, silverware, china, and cutlery he bought in English markets. Loving the ripe old culture of the mother country, he often sent his sons to Oxford or Cambridge for their education. In short, he depended very largely for his prosperity and his enjoyment of life upon close relations with the Old World. He did not even need market towns in which to buy native goods, for they were made on his own plantation by his own artisans who were usually gifted slaves.
The economic condition of the small farmer was totally different. His crops were not big enough to warrant direct connection with English factors or the personal maintenance of a corps of artisans. He needed local markets, and they sprang up to meet the need. Smiths, hatters, weavers, wagon-makers, and potters at neighboring towns supplied him with the rough products of their native skill. The finer goods, bought by the rich planter in England, the small farmer ordinarily could not buy. His wants were restricted to staples like tea and sugar, and between him and the European market stood the merchant. His community was therefore more self-sufficient than the seaboard line of great plantations. It was more isolated, more provincial, more independent, more American. The planter faced the Old East. The farmer faced the New West.
The Westward Movement.—Yeoman and planter nevertheless were alike in one respect. Their land hunger was never appeased. Each had the eye of an expert for new and fertile soil; and so, north and south, as soon as a foothold was secured on the Atlantic coast, the current of migration set in westward, creeping through forests, across rivers, and over mountains. Many of the later immigrants, in their search for cheap lands, were compelled to go to the border; but in a large part the path breakers to the West were native Americans of the second and third generations. Explorers, fired by curiosity and the lure of the mysterious unknown, and hunters, fur traders, and squatters, following their own sweet wills, blazed the trail, opening paths and sending back stories of the new regions they traversed. Then came the regular settlers with lawful titles to the lands they had purchased, sometimes singly and sometimes in companies.
In Massachusetts, the westward movement is recorded in the founding of Springfield in 1636 and Great Barrington in 1725. By the opening of the eighteenth century the pioneers of Connecticut had pushed north and west until their outpost towns adjoined the Hudson Valley settlements. In New York, the inland movement was directed by the Hudson River to Albany, and from that old Dutch center it radiated in every direction, particularly westward through the Mohawk Valley. New Jersey was early filled to its borders, the beginnings of the present city of New Brunswick being made in 1681 and those of Trenton in 1685. In Pennsylvania, as in New York, the waterways determined the main lines of advance. Pioneers, pushing up through the valley of the Schuylkill, spread over the fertile lands of Berks and Lancaster counties, laying out Reading in 1748. Another current of migration was directed by the Susquehanna, and, in 1726, the first farmhouse was built on the bank where Harrisburg was later founded. Along the southern tier of counties a thin line of settlements stretched westward to Pittsburgh, reaching the upper waters of the Ohio while the colony was still under the Penn family.
In the South the westward march was equally swift. The seaboard was quickly occupied by large planters and their slaves engaged in the cultivation of tobacco and rice. The Piedmont Plateau, lying back from the coast all the way from Maryland to Georgia, was fed by two streams of migration, one westward from the sea and the other southward from the other colonies—Germans from Pennsylvania and Scotch-Irish furnishing the main supply. "By 1770, tide-water Virginia was full to overflowing and the 'back country' of the Blue Ridge and the Shenandoah was fully occupied. Even the mountain valleys ... were claimed by sturdy pioneers. Before the Declaration of Independence, the oncoming tide of home-seekers had reached the crest of the Alleghanies."
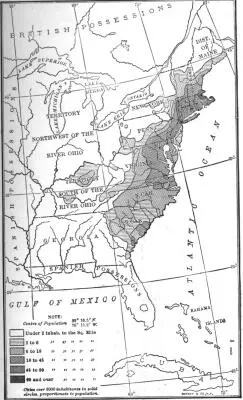
Distribution of Population, 1790
Beyond the mountains pioneers had already ventured, harbingers of an invasion that was about to break in upon Kentucky and Tennessee. As early as 1769 that mighty Nimrod, Daniel Boone, curious to hunt buffaloes, of which he had heard weird reports, passed through the Cumberland Gap and brought back news of a wonderful country awaiting the plow. A hint was sufficient. Singly, in pairs, and in groups, settlers followed the trail he had blazed. A great land corporation, the Transylvania Company, emulating the merchant adventurers of earlier times, secured a huge grant of territory and sought profits in quit rents from lands sold to farmers. By the outbreak of the Revolution there were several hundred people in the Kentucky region. Like the older colonists, they did not relish quit rents, and their opposition wrecked the Transylvania Company. They even carried their protests into the Continental Congress in 1776, for by that time they were our "embryo fourteenth colony."
Industrial and Commercial Development
Though the labor of the colonists was mainly spent in farming, there was a steady growth in industrial and commercial pursuits. Most of the staple industries of to-day, not omitting iron and textiles, have their beginnings in colonial times. Manufacturing and trade soon gave rise to towns which enjoyed an importance all out of proportion to their numbers. The great centers of commerce and finance on the seaboard originated in the days when the king of England was "lord of these dominions."

Domestic Industry: Dipping Tallow Candles
Textile Manufacture as a Domestic Industry.—Colonial women, in addition to sharing every hardship of pioneering, often the heavy labor of the open field, developed in the course of time a national industry which was almost exclusively their own. Wool and flax were raised in abundance in the North and South. "Every farm house," says Coman, the economic historian, "was a workshop where the women spun and wove the serges, kerseys, and linsey-woolseys which served for the common wear." By the close of the seventeenth century, New England manufactured cloth in sufficient quantities to export it to the Southern colonies and to the West Indies. As the industry developed, mills were erected for the more difficult process of dyeing, weaving, and fulling, but carding and spinning continued to be done in the home. The Dutch of New Netherland, the Swedes of Delaware, and the Scotch-Irish of the interior "were not one whit behind their Yankee neighbors."
Читать дальше















