In DBTF‐based product development and validation process, reliability growth continued well into production and the field and was a highly reactive process. Using this approach, design engineers worked independently, then transferred designs either “over the wall” to the next department or external to the company. Eventually, manufacturing had to assemble a product not designed for its processes. Since it was too late to make changes, manufacturing struggled to meet yield, quality, cost, and delivery targets. This required trial‐and‐error crisis management, followed by launch delays, and then quality and reliability issues. This approach has fallen out of favor and been replaced by a combination of concurrent engineering and reliability physics modeling approaches. The newer approaches have the goal of simultaneously optimizing the design across all the DfX disciplines.
Block diagrams are useful for performing system‐reliability models and calculations and may be simple, parallel, or redundant. A series reliability system model is used when one failure of one component results in the failure of the system. Let's calculate the reliability of a simple fuel system, Rfs, as shown in Figure 2.2.
Rfs(t) = Rfp(t) Rfl(t) Rfi(t) Recu(t) Rfw(t)
Rfs(t) = 0.980 0.998 0.985 0.975 0.964 = 0.905 90.5% reliability
F(t) = 1 Rfs(t) = 1 .905 = .0945 9.45% failure
For every 100,000 vehicles built, be prepared for 100,000  0.0945 = 9453 fuel system repairs by time (t).
0.0945 = 9453 fuel system repairs by time (t).
Parallel or redundant reliability system models are used where all the items in a parallel branch must fail in order for the system to fail. They can model backup systems used to maintain system availability of critical functions in case the primary system fails. A repair of the failed unit is still required, but critical functionality is maintained: for example, separate brake channels where the loss of one brake circuit degrades brake performance, but reduced braking capability remains. Let's calculate the reliability of a parallel brake system, as shown in Figure 2.3.
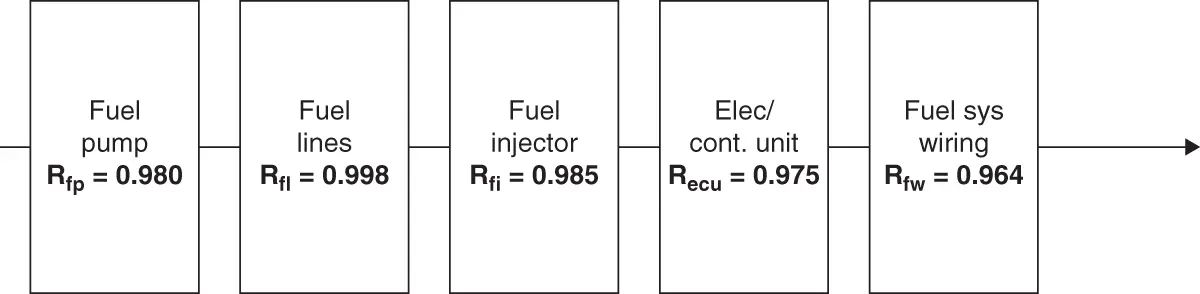
Figure 2.2 Block diagram for a simple fuel system.
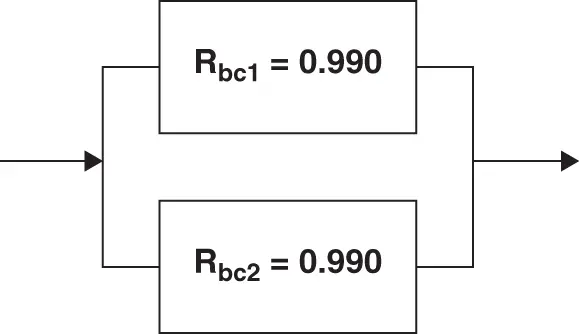
Figure 2.3 Parallel brake system.
Rbt = 1 [1 Rbc1(t)] [1 Rbc2(t)]
= 1 [ 1 0.990] [ 1 0.990]
= 1 [ 0.010] [ 0.010]
= 1 0.0001 = 0.9999 or 99.99%,
then Fbc = 1 [1 0.990] = 0.02 and Fbt =.0001
For one failure out of two, the calculation is 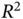 . For two failures out of two, the calculation is
. For two failures out of two, the calculation is 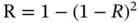 . So, the probability of a single brake circuit failure is
. So, the probability of a single brake circuit failure is 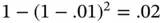 , or 2000 incidents for every 100,000 vehicles built. The probability of both brake circuits failing is 0.0001, or 10 incidents for every 100,000 vehicles built: i.e. 200 times less likely to fail due to the dual design.
, or 2000 incidents for every 100,000 vehicles built. The probability of both brake circuits failing is 0.0001, or 10 incidents for every 100,000 vehicles built: i.e. 200 times less likely to fail due to the dual design.
Automated Design Analysis
Automated design analysis tools represent the latest frontier in reliability analysis and modeling. One example is the ANSYS‐DfR Sherlock automated design analysis software. It is a reliability physics‐based electronics design software that provides fast and accurate life predictions for electronic hardware at the component, board, and system levels in early design stages. Sherlock allows designers to simulate real‐world conditions and accurately model PCBs and assemblies to predict solder fatigue due to thermal, mechanical, and shock and vibration conditions. Approximately 73% of product development costs are spent on the test‐fail‐fix‐repeat cycle. Sherlock design software provides fast and accurate reliability predictions in the earliest design stages tailored to specific materials, components, dies, printed circuit board (PCB)/ball grid array (BGA) stackups, and use conditions. With libraries containing over one million parts, Sherlock reduces FEA modeling time and provides insights before prototyping, eliminating test failures and design flaws, while accelerating product qualification and the introduction of groundbreaking technologies. During preprocessing, Sherlock automatically translates ECAD and MCAE data into 3D finite element models in minutes. In post‐processing, Sherlock automates thermal derating and democratizes the thermal and mechanical analysis of electronics.
Sherlock seamlessly integrates with already existing simulation workflows in the hardware design process. It is most valuable when implemented in the early design stages, such as:
Initial parts selection
Initial parts placement
Selecting the final bill of material
Final layout
Design for manufacturing
Sherlock makes ANSYS SIwave, ANSYS Icepak, and ANSYS Mechanical users more efficient. It directly connects simulation to material and manufacturing costs.
Additionally, Sherlock's locked IP model protects intellectual property in the supply chain. With the locked IP model, designs are transferred back and forth between design suppliers and design users while preserving PCB design details; the intended use of the PCB design will not be disclosed via environmental conditions or reliability requirements. This communication tool enables two entities to work together on a system with a layer of trust built into the reliability calculations. Sherlock simplifies and improves reliability prediction using a unique, three‐phase process consisting of data input, analysis, and reporting and recommendations.
Assessment options include:
Thermal cycling
Solder joint fatigue
PTH fatigue
Mechanical shock
Natural frequency
Harmonic vibration
Random vibration
Bending
Integrated circuit/semiconductor wear‐out
Thermal derating
Failure rate analysis
Conductive anodic filament (CAF) qualification
High‐fidelity PCB modeling
Sherlock provides actionable recommendations and presents results in comprehensive, professional reports suitable for internal and external distribution.
Establishing a comprehensive reliability program requires extensive planning, training, and expertise. Once established, however, an effective program reduces risk, costs, and failures and results in products that function reliably and satisfy customers. The simple truth is that designing in reliability up front pays off immensely over the life of the product. A reliability program ensures that this happens.
As can be seen, each type of test plan has unique properties and approaches.
1 Abernethy, R.B. (2000). The New Weibull Handbook 5e. North Palm Beach, FL: R.B. Abernethy.
2 Allen, G. and Jarman, R. (1999). Collaborative R and D. New York: Wiley and Sons.
3 Ireson, W. and Coombs, C. (1989). Handbook of Reliability Engineering and Management. New York: McGraw Hill.
Читать дальше

 0.0945 = 9453 fuel system repairs by time (t).
0.0945 = 9453 fuel system repairs by time (t).

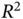 . For two failures out of two, the calculation is
. For two failures out of two, the calculation is 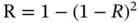 . So, the probability of a single brake circuit failure is
. So, the probability of a single brake circuit failure is 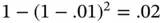 , or 2000 incidents for every 100,000 vehicles built. The probability of both brake circuits failing is 0.0001, or 10 incidents for every 100,000 vehicles built: i.e. 200 times less likely to fail due to the dual design.
, or 2000 incidents for every 100,000 vehicles built. The probability of both brake circuits failing is 0.0001, or 10 incidents for every 100,000 vehicles built: i.e. 200 times less likely to fail due to the dual design.










