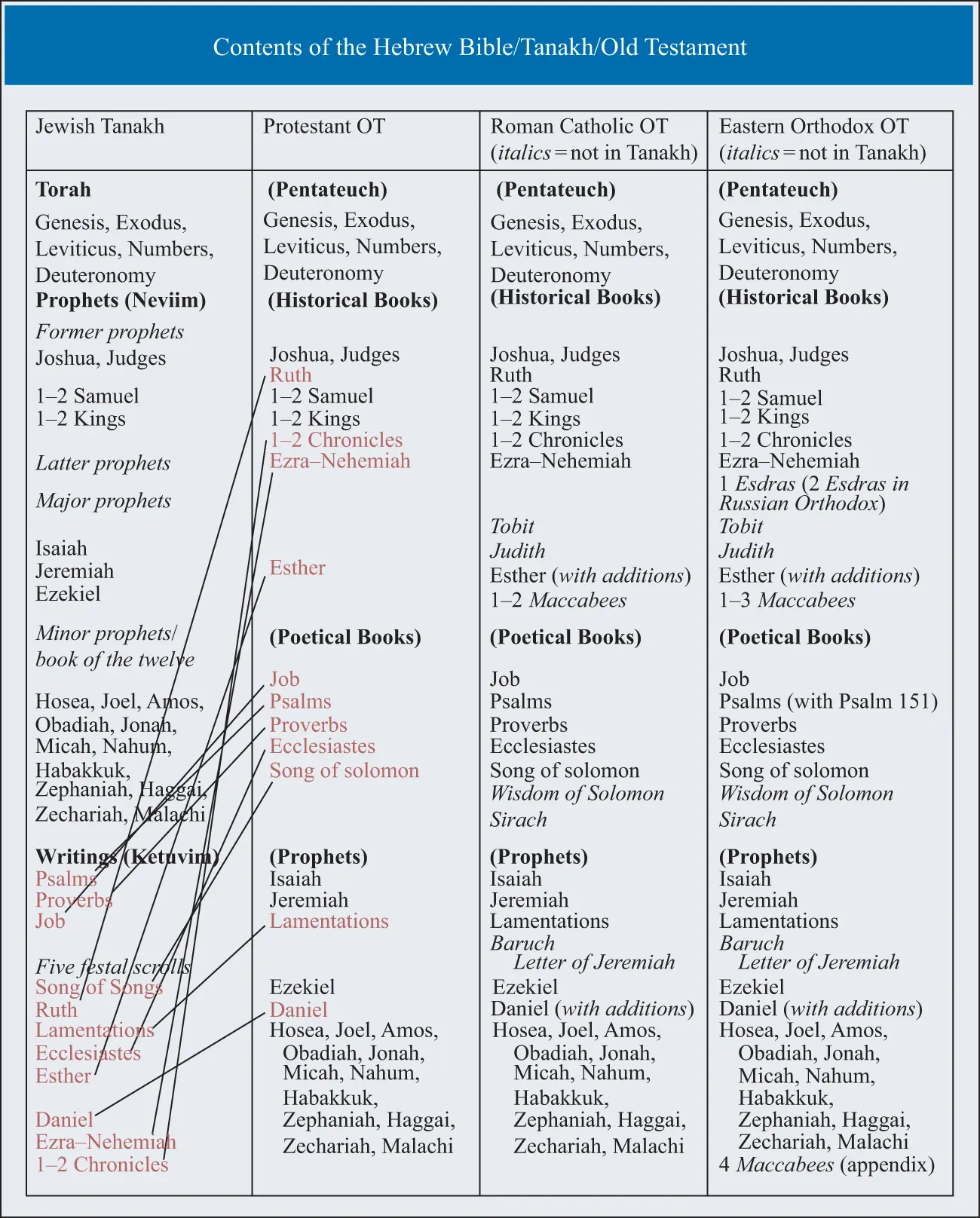
You should also know that there are differences between the books included in different Christian Old Testament collections. The Protestant Old Testament contains the same books as the Jewish Tanakh, though in the above-noted different order leading up to the New Testament. The Roman Catholic Old Testament includes some additional books such as 1 and 2 Maccabees, Sirach, and the Wisdom of Solomon. The Ethiopic church recognizes the book of Enoch as part of its Old Testament, and various forms of Orthodox Christianity likewise recognize slightly different groups of additional books. For Roman Catholics, such additional books (not in the Jewish Tanakh) are “deuterocanonical,” which means that they belong to a “second canon.” For Protestants, such books not in the Jewish Tanakh are not considered true scripture, but “apocrypha,” which means “books hidden away.” We will not hide such books away in this textbook, but neither will we be able to discuss them at length. Instead, in Chapter 8of this Introduction , we will briefly discuss a sampling of them: Ben Sira/Sirach, Enoch, and Judith. In addition, we will discuss how Jewish and Christian communities ended up with these slightly different collections of scriptural books.
“ Hebrew Bible” is yet another term that is often used to designate the scriptures shared by Jews and Christians. Many people prefer the expression “Hebrew Bible” because it avoids the pejorative connotations that the term “Old Testament” has assumed in many Christian circles. The terms “Old” and “New Testament” derive from Greek and Latin terms that have been used by Christians to contrast an old covenant (with Israel) and new covenant through Jesus Christ. Often this has been part of a Christian supersessionistassumption that God’s covenant with the world through Christ superseded any prior covenant that God made with Israel. For Christians who subscribe to this idea, the Old Testament is often treated as the Old and superseded Testament. It is seen as the outdated book of the “law,” as opposed to the New Testament, which is understood to be the truly scriptural word about Jesus, love, and grace. Such views reflect a lack of close reading of both the Old and the New Testament, but they are widespread and influential. This is why many people avoid the term “Old Testament,” with its possible implications of supersessionism, and use terms such as “Hebrew Bible” or “First Testament” instead. Others, however, find these terms odd and/or inaccurate (for example, several chapters in the Tanakh/Old Testament are not in Hebrew, but Aramaic). They prefer sticking with the Christian term “Old Testament,” at least within specifically Christian contexts, but emphasize the more ancient understanding of “Old” as implying something good, rather than the more contemporary idea of “Old” being something that is outdated.
The important thing for academic study of the Bible is to understand the meanings of these different terms for the Tanakh/Old Testament/Hebrew scriptures and the slight differences in contents and order of these otherwise similar collections. These differences reflect the fact that these scriptures have come to belong to multiple faith communities. In addition, the Islamic tradition sees the scriptures of Judaism and Christianity as possessing a secondary authority to that of its central text, the Qur’an. From the Islamic perspective, the Qur’an represents the final part of a long line of divine revelations to human communities, including the Jewish Tanakh and Christian Old and New Testaments.. This Qur’an is quite different in contents from the Tanakh/Old Testament, containing 114 chapters (surahs) of primarily ethical and theological exhortations that were communicated by the prophet Muhammad. It is not a parallel “Old Testament” or “Tanakh.” Nevertheless, parts of the Qur’an reflect post-biblical Jewish traditions about history up to Moses (e.g. about Abraham, Ishmael, Mary) and other Muslim traditions (e.g. the biography and example of the prophet Muhammad).
From this discussion, we can see that there is no one “Bible,” not even one “Hebrew Bible,” shared by Judaism and Christianity, let alone Islam. Even if we focus on the overlapping contents of the Jewish Tanakh and Christian Old Testament, there are significant differences in order and (occasionally) content as well. This is an initial indicator of the quite different readings that Christians and Jews give to the texts they hold in common. We will see others along the way. Moreover, this diversity of Jewish and Christian Bibles is preceded by a diversity of perspectives and voices found within the Hebrew scriptures themselves. In the following chapters, we will see this diversity in texts written at different times and even in texts offering different perspectives on the same time.
Basics on Bible Translations
Since most students do not know Hebrew, Aramaic, or Greek, they can only read a Bible in translation. There are several things that every user of such Bible translations should know about them in order to be an informed user.
First, every translation involves many decisions by the translator about the Hebrew, Greek, or (in a few cases) Aramaic text. Scholars are still not sure about the meanings of some words, and the biblical languages do not translate precisely into English (or other modern languages). In addition, we have no original manuscript of any biblical book, and the existing biblical manuscripts disagree with each other at many points. This means that scholars must use textual criticism to decide the best Hebrew, Aramaic, or Greek text in each case where the manuscripts disagree with each other. Luckily, over the last several centuries much progress has been made in uncovering ancient manuscripts and learning to identify copying errors and other changes in such manuscripts. In addition, there has been a huge growth in knowledge about the biblical languages.
MORE ON METHOD: TEXTUAL CRITICISM
As indicated in the text, “textual criticism” is not a general study of a text. Instead, textual criticism studies the diverse ancient manuscript copies of biblical texts, analyzing their development and providing data that can be used to choose which reading of a biblical text to follow. Over the centuries scribes have introduced tens of thousands of minor changes into biblical texts as they have copied them by hand. Some changes were introduced by accident, as when a scribe might accidentally copy a given line twice or confuse letters. Other changes seem more intentional, where a scribe seems to have added a clarification of a place name or a theological correction or expansion. The ancient copies are often termed manuscript witnessesbecause they “witness” to diverse forms of these hand-copied texts.
Deciding which reading to followA translator or translation committee often needs to decide word by word whether to follow a reading in one manuscript tradition or another. To do this, most scholars use “critical editions” prepared by textual critics that gather and compare the readings found in ancient biblical manuscripts (see Figure 0.1 on p. 8). For the Hebrew Bible, the usual comparison point is the Masoretic text (MT), the authoritative version of the Hebrew/Aramaic text that was produced by Jewish scribes in the medieval period. Most critical editions feature a high-quality version of the Masoretic text as the main section of each page. Notes in the critical edition then provide an overview of variant readings from other important manuscript witnesses for the Hebrew Bible, such as the biblical manuscripts found at the Dead Sea (Qumran), the Pentateuch preserved by the Samaritan community (around Samaria in the north), and very early translations of early Hebrew manuscripts, especially the Septuagint (LXX), an ancient set of translations of various biblical books into Greek.
Читать дальше













