The benefits of such study are substantial. Familiar texts offer new meanings. Difficult biblical texts start to make better sense when placed in their original historical contexts. Where once the Bible might have seemed a monolithic, ancient set of rules, it becomes a rich variety of different perspectives that have stood the test of time. We encourage you to be open to this approach. Frequently consult the historical timeline and overview charts at the outset of the Introduction to orient yourself (see pp. xxvii–xxx), and learn for yourself what this way of studying the Bible has to offer.
The Geography and Major Characters of the Biblical Drama
We start by setting the scene for the drama of biblical history, looking at the geography of the biblical world, major nations, and major historical periods. This information is important, because it will orient you to the quite different world in which the Bible was created.
Asked to picture the land of Israel, many would conjure up images from TV specials or popular movies where biblical events occur amidst sand dunes, palm trees, and small villages. The reality is that the area of Israel encompasses sharp contrasts in topography, rainfall, and vegetation. Imagine Map 1.1 as divided into four narrow strips running up and down. The strip to the left is the coastal plain along the Mediterranean Sea. It is low, flat, and fertile and receives relatively regular rainfall. Non-Israelites lived here through most of Israelite history, and it was ruled from Jerusalem only for short periods. The next strip is the central hill country and runs down the middle of the map, encompassing the hill country of Judah, hill country of Ephraim (Israel), and Galilee. This is an area of rocky hills that eventually rise up to 3000 feet. This hill country is where most of Israelite history took place. It is drier and less accessible than the coastal plain to the west. The third strip is the Jordan Valley , encompassing the Dead Sea, Jordan River, and Sea of Galilee (from south to north). This is one of the lowest places on earth, about 1000 feet below sea level, and – aside from some oases – it is very dry and barren. The fourth strip is the Transjordanian Plateau , including Edom, Moab, Ammon, and the Gilead region (where Israelites settled). This plateau, now in the contemporary nation of Jordan, has similar characteristics to the central highlands of Israel. To the east of it (and off the map) lies the desert.
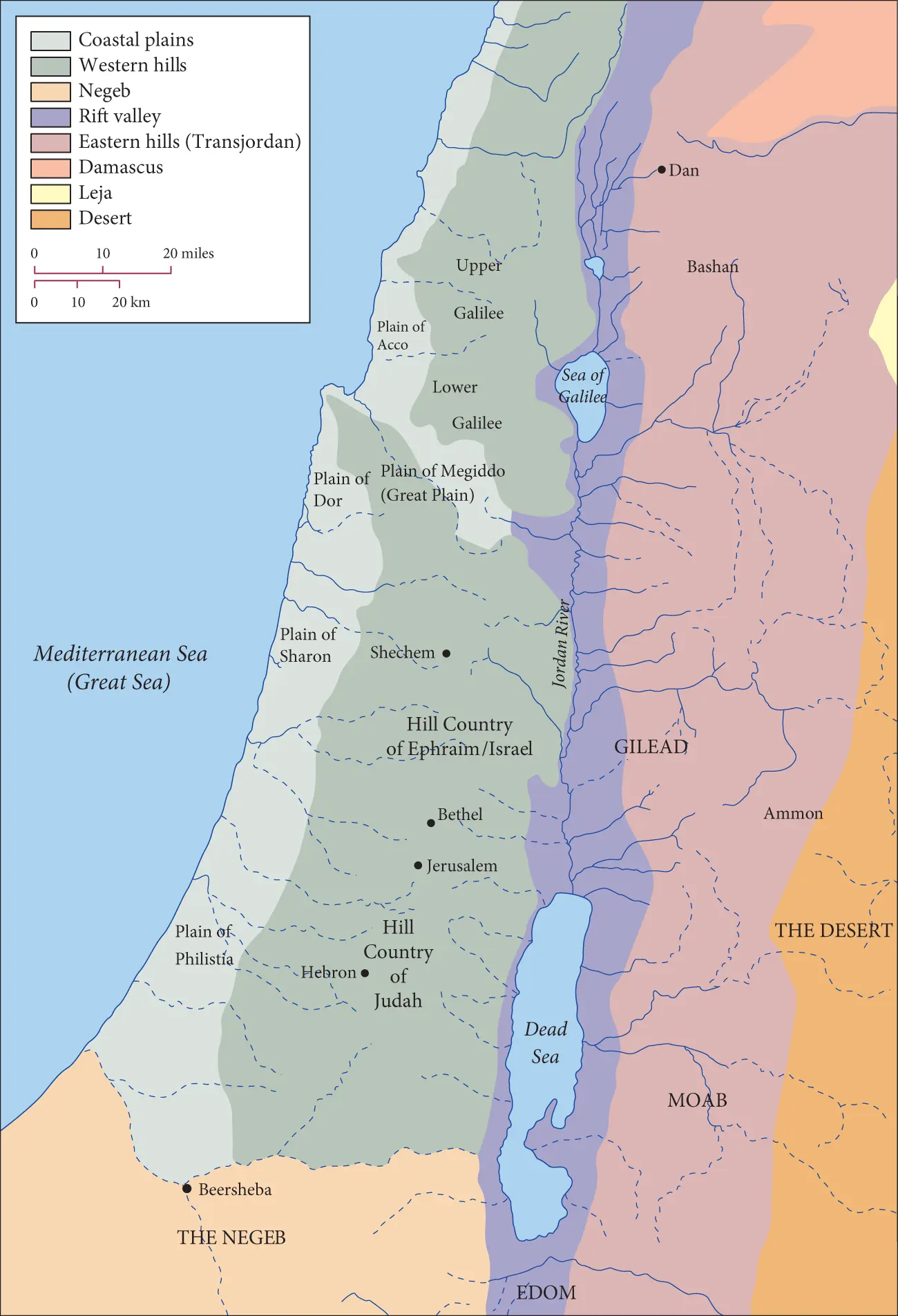
MAP 1.1 The land of Israel and its surroundings. Redrawn from Adrian Curtis (ed.), Oxford Bible Atlas (4th edition). Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press, 2007.
As you start your study of the Bible, it is particularly important to get an understanding of the different parts of the land of Israel and the peoples who lived there. Though people often apply the term “Israel” to this entire area, this term often refers more narrowly to the peoples who settled in the northern highlands described above (“Hill Country of Ephraim/Israel” on Map 1.1, with Shechem at its center) along with parts of the Gilead of the Transjordan. For much of biblical history, this area and this people are to be distinguished from “Judah,” which is located in the southern highlands of the map (“Hill Country of Judah”; Hebron is a Judean city). Note that Jerusalem lay between Israel and Judah and was not “Israelite”/“Judean” until David conquered it by stealth at the outset of his monarchy. This distinction between “Judah” in the south and “Israel” in the north is important for much of Israel’s early history. Later on, the term “Israel” came to encompass Judah as well, and the narratives of the Hebrew Bible – many of them written later – project that picture onto the earliest history of the people. Therefore, the word “ Israel” has at least two major meanings in the Bible: a narrow sense referring to the ancient tribal groups settled in the northern highlands and a broader sense referring to Judah along with those other tribal groups. When people refer to the “land of Israel” or the “people of Israel,” they are usually using the word “Israel” in the broader sense, but there will be numerous times in this Introduction when it will be important to remember the narrower sense of “Israel” (in the north) as opposed to “Judah” (in the south).
Those are the scholarly terms for the region and its inhabitants. As we move forward, it is important to distinguish such terms from contemporary designations for the land. In particular, it is important not to confuse the word “Israelite,” which refers to ancient inhabitants of the land of Israel, and the word “Israeli,” which is a modern term referring to citizens of the contemporary state of Israel. Note also the use of the term “Palestine” to refer to the same area from the Roman period onward. This term is now used by Palestinians and many others to refer to the same land area that Jews and others refer to as “Israel.”
Visualizing (the Possible Ancestors of) Ancient Israelites
These ancient Israelites were different in important ways from all contemporary peoples, including Israelis. Unfortunately we do not have contemporary representations of ancient Israelites. The best we can do are images like Figure 1.1 (a relief painting from an official’s tomb at Beni Hasan), which is an Egyptian depiction of visitors to Egypt from the east, perhaps from the region of Canaan. As we will see in the next chapter, the Israelites likely descended from Canaanite peoples, and so this representation gives us an image of what the ancestors of ancient Israelites (or their near-neighbors) looked like.
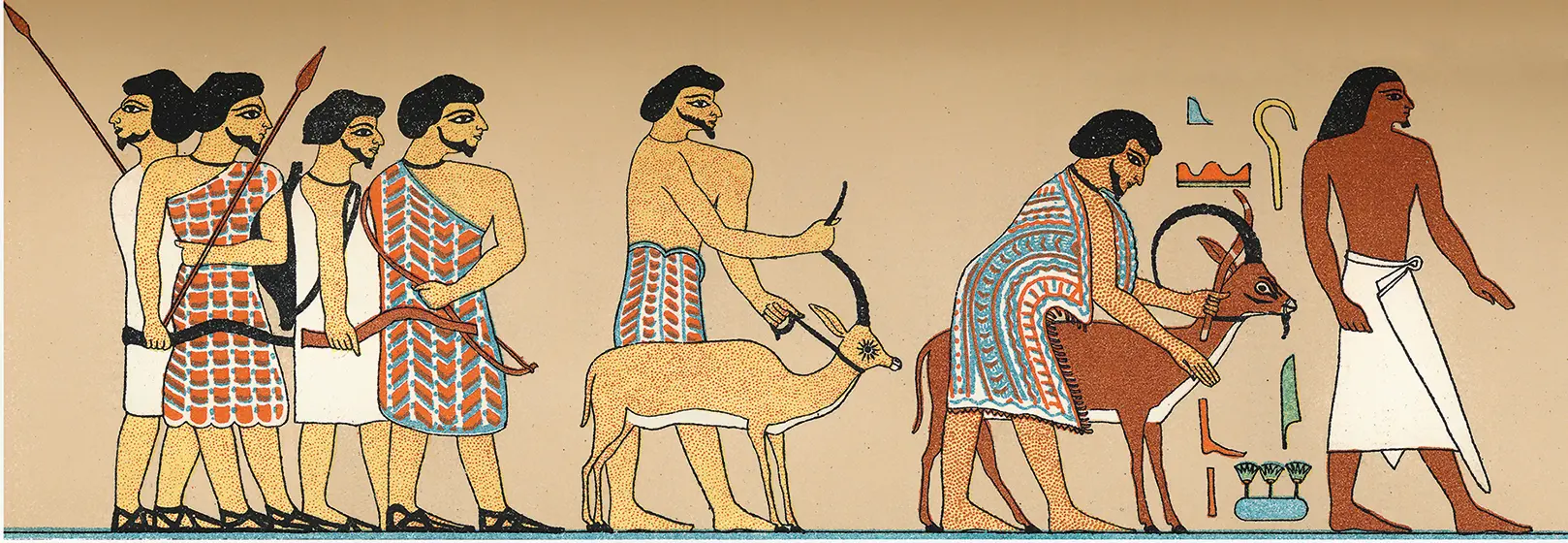

FIGURE 1.1 Ancient visitors to Egypt from the East (Canaanites?).
On the far right of the picture there is a clean-shaven Egyptian with darker brown skin. The visitors from the east (Canaan?) are the six figures to the left of him. They have lighter brown skin, beards, and some colorful tunics. One thing such images make clear is that the people who dwelled east of Egypt looked more like the contemporary inhabitants of the Middle East and Africa than the light-skinned inhabitants of North America and Europe. Indeed, not only were ancient Israelites non-white, but the ancient world lacked an exact correlate to modern concepts of race.
The “land of Israel,” where most biblical events took place, is actually relatively small. As you can see on Map 1.1, the Sea of Galilee is only 30 miles from the Mediterranean Sea, and the Dead Sea is only 60 miles away. The distance from the area around Shechem in the north to Beersheba in the south is about 90 miles. This means that the main setting of biblical history, the area of the central highlands (thus excluding the non-Israelite coastal plains), is about 40 miles by 90 miles – not much bigger than many large metropolitan areas. This tiny area is the site where texts and religious ideas were formed that would change world history. Notably, this highland area also encompasses many areas most in dispute in the contemporary Middle East, areas that are variously designated as “the West Bank,” “occupied territories,” and “Judea and Samaria.” Before 1967 these regions were not part of the modern nation of Israel, but they were seized by Israel from Jordan during the 1967 war, and their status is one major issue in the ongoing Middle East conflict.
Читать дальше














